Research
Army and Researchers Create Super-Copper — Stronger, Lighter, Built for Military Power
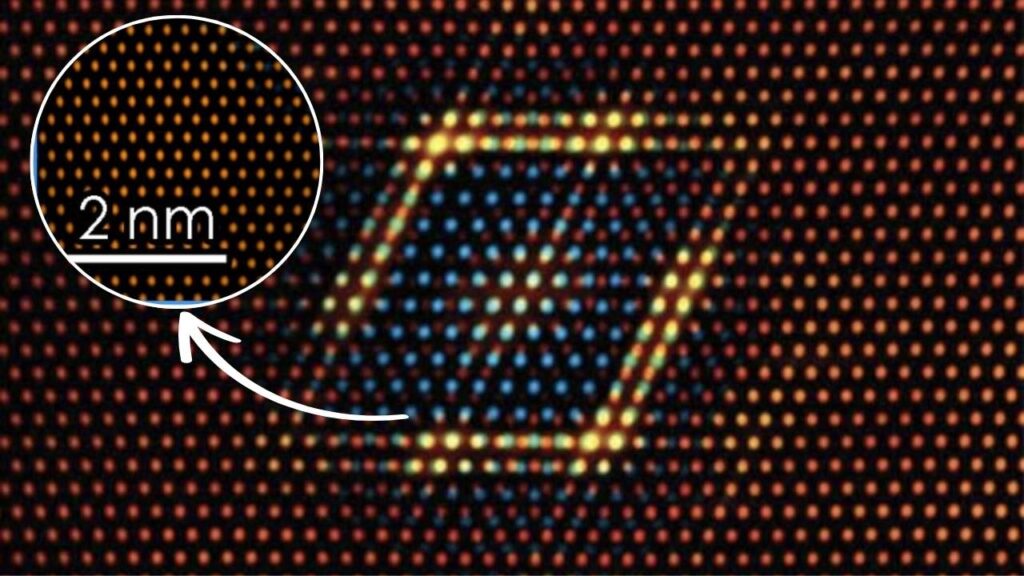
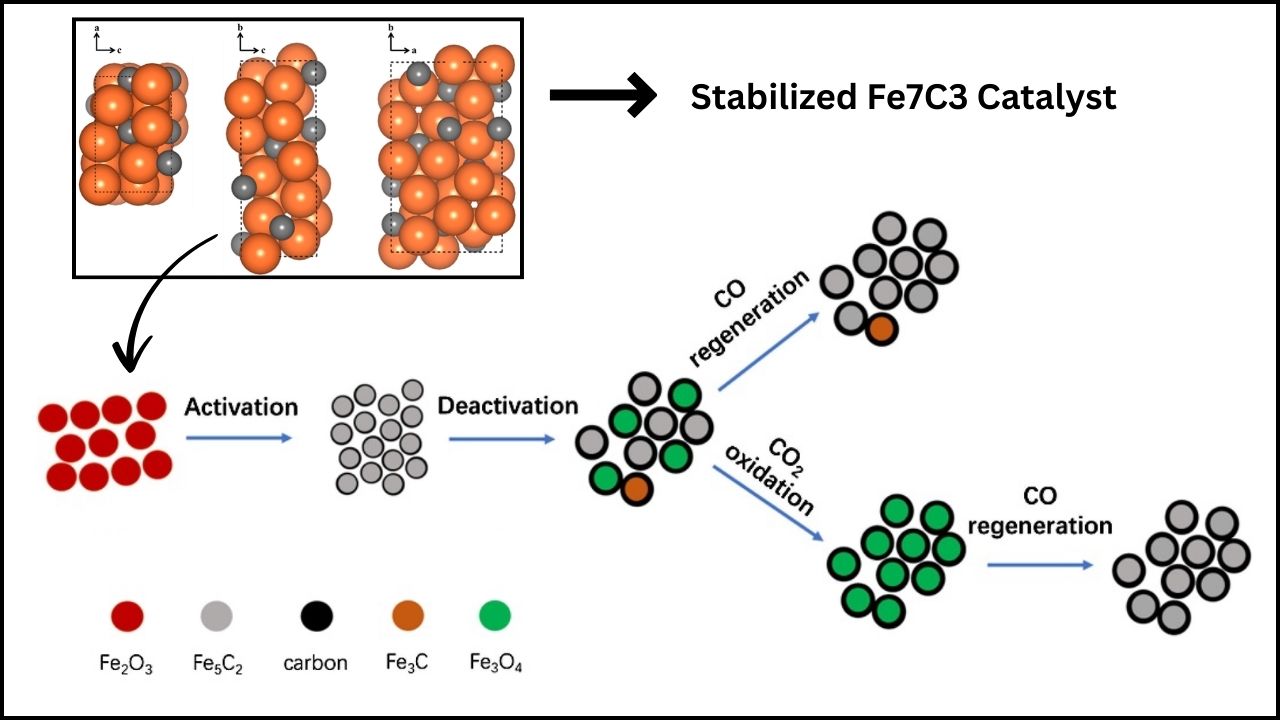
The U.S. Army, collaborating with top universities, has developed an advanced super-copper alloy (Cu-Ta-Li) combining copper’s exceptional conductivity with strength and thermal stability rivaling nickel-based superalloys. This nanostructured alloy withstands sustained temperatures up to 800°C (1500°F), providing lighter, tougher materials for defense, aerospace, and energy sectors. Such breakthrough will transform components exposed to extreme conditions, enhancing military readiness and engineering innovation.
Read More