In a significant shift, the full retirement age (FRA) for Social Security benefits in the United States has officially increased to 67 for individuals born in 1960 or later. This change marks the culmination of a gradual adjustment that began in 1983 when Congress passed legislation to raise the FRA from 65 to 67. The final phase of this transition took effect in November 2025, impacting those born in 1960.

The increase in the full retirement age to 67 signifies a pivotal change in the landscape of Social Security benefits. This adjustment underscores the importance of strategic retirement planning and staying informed about policy developments that impact long-term financial security.
For those planning their retirement, it is crucial to consider how these changes may affect future benefit amounts and to explore other savings options to ensure financial stability during retirement.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Full Retirement Age
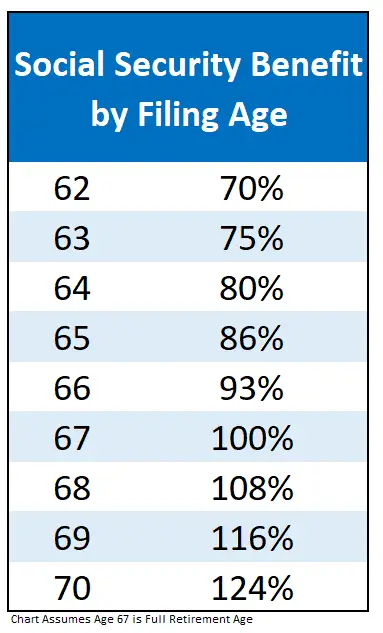
The full retirement age is the age at which individuals can begin receiving full Social Security retirement benefits without any reduction. Claiming benefits before reaching the FRA results in a permanent reduction in monthly payments. Conversely, delaying benefits beyond the FRA up to age 70 increases monthly payments by approximately 8% per year.
Historical Context of Social Security and Retirement Age Changes
The Social Security Act of 1935 initially set the retirement age at 65, the age at which workers could start receiving full benefits. In the early 1980s, due to concerns about the sustainability of the Social Security system and increasing life expectancies, Congress passed reforms gradually raising the retirement age to 67.
This change was first implemented for people born in 1938, and now, with 1960 as the cutoff, the final phase is being realized. These adjustments were made to keep the system solvent as the population ages and more people rely on Social Security.
Implications of the FRA Increase
1. Delayed Access to Full Benefits
Individuals born in 1960 or later must wait until age 67 to claim full Social Security benefits. This delay means that many workers will need to remain employed longer to achieve the same level of retirement income they might have anticipated at age 65.
2. Increased Monthly Payments for Delayed Claims
Delaying benefits beyond the FRA can lead to higher monthly payments. For each year an individual postpones claiming benefits after reaching the FRA, their monthly payment increases by about 8%, up to age 70.
3. Impact on Early Retirees
For those considering early retirement, claiming benefits at age 62 results in a permanent reduction of up to 30% of the monthly benefit amount. The increase in the FRA to 67 means individuals now face a longer wait to receive full benefits, potentially affecting their retirement planning strategies.
Strategic Considerations for Future Retirees
1. Evaluate Health and Employment Status
Assessing personal health and job satisfaction can help determine the optimal time to begin receiving Social Security benefits.
2. Consult Financial Advisors
Engaging with financial professionals can provide personalized strategies to maximize retirement income, considering the changes in the FRA.
3. Stay Informed on Policy Changes
Remaining updated on potential future adjustments to Social Security policies can aid in proactive retirement planning.
Impact on Different Age Groups
The increase in FRA affects those born in 1960 and beyond, but it also indirectly impacts earlier generations, especially those who might have planned their retirement around the earlier 65-year threshold. People between the ages of 50 and 60 today, who were anticipating retirement at 65, may feel pressure to adjust their plans due to this change.
For younger workers (those under 50), this shift may not be as disruptive but does require longer career planning and the consideration of alternative retirement savings methods.
Alternative Strategies for Supplementing Social Security
Given that Social Security benefits are often not enough for a comfortable retirement, many individuals look for ways to supplement their income. These strategies may include:
- Employer-Sponsored Retirement Plans: Contributing to 401(k) or pension plans.
- Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs): Both traditional and Roth IRAs offer tax advantages to help save for retirement.
- Part-Time Work: Some retirees may continue to work part-time to supplement Social Security.
- Investment in Stocks or Real Estate: Building assets through investments or rental income can significantly boost retirement funds.

Public Opinion and Political Debate Around the Change
Raising the retirement age has been a topic of political debate for years. Many argue that the increase in the FRA is a necessary adjustment due to longer life expectancies and the aging Baby Boomer generation.
However, critics claim that this change disproportionately affects low-income workers and those in physically demanding jobs, where extending the working life can be detrimental to health and well-being. Political discussions around this issue continue, with some proposing alternative solutions such as universal basic income or strengthening the pension system.
Related Links
$1,390 IRS Relief Payment 2025 – Are You on the List for the Direct Deposit?
90% VA Disability Benefits Just Changed for November 2025 – See What You’re Owed Now
Global Comparisons: How the U.S. Retirement Age Compares to Other Countries
Many other countries have also adjusted their retirement ages in response to demographic shifts. For instance, in Germany, the retirement age will gradually rise to 67 by 2031, while in France, it is set to rise to 64 by 2030. Meanwhile, countries like Japan have introduced policies to encourage people to stay in the workforce longer due to a declining working-age population.
By raising the FRA, the U.S. is aligning more closely with global trends. However, compared to some nations, the U.S. system remains relatively generous, as many countries are raising the age even higher or implementing more drastic pension reforms.



















