NASA is closely monitoring 3I/ATLAS, the first interstellar comet to be observed with certainty. Passing through our solar system, it’s raising new questions about the nature of cosmic bodies from outside our solar system. This rare comet is offering scientists a unique opportunity to study material from beyond our star system.

NASA’s latest discovery, 3I/ATLAS, is an interstellar comet passing through the solar system on a hyperbolic trajectory. Its unprecedented origin and characteristics have drawn significant attention from astronomers and scientists. Unlike any comet seen before, 3I/ATLAS presents a rare opportunity for researchers to study material from outside our solar system.
Table of Contents
The Interstellar Comet That Has NASA on Alert
| Key Fact | Detail/Statistic |
|---|---|
| Type of Object | Interstellar comet (3rd ever confirmed) |
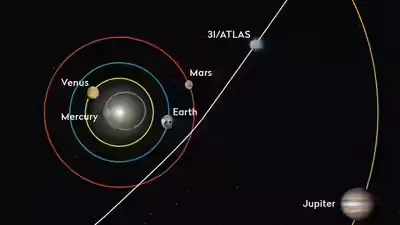
| Discovery Date | July 1, 2025, by the ATLAS survey |
| Closest Approach to Sun (Perihelion) | Expected on October 30, 2025, at about 1.4 AU |
| Expected Closest Approach to Earth | December 2025, 1.8 AU |
The discovery of 3I/ATLAS has provided scientists with a rare and unique opportunity to observe a comet from beyond our solar system. With its unusual composition and behavior, this interstellar visitor is helping to rewrite the rulebook on what we know about comets and interstellar objects.
The data gathered from its journey through the solar system will offer profound insights into the materials that make up distant star systems and could have implications for our understanding of planetary formation and the potential for life beyond Earth.
3I/ATLAS: What Makes This Comet Special?
Interstellar Origin
The comet 3I/ATLAS is unlike any other cosmic object in our solar system. With its hyperbolic trajectory, it is not bound by the Sun’s gravity, meaning it is passing through from a different star system and will eventually continue its journey into deep space.
This is only the third time in history an interstellar object has been definitively identified, following the discovery of ʻOumuamua in 2017 and 2I/Borisov in 2019 .
What sets 3I/ATLAS apart is its status as an interstellar comet, rather than just an asteroid. This means it is made of volatile compounds like ice, which are prone to sublimation when heated by the Sun, releasing gas and dust. Observing such activity so far from the Sun has scientists eager to learn more about its composition and the conditions of its home star system .
Why NASA Is Paying Close Attention
NASA’s Astrobiology Institute and other space agencies are keeping a close eye on 3I/ATLAS due to its rare nature. The object is traveling at speeds of up to 50 kilometers per second, making its journey through the solar system a fleeting event.
This unique position means scientists have only a short time to gather data before the comet exits the system. The upcoming close approach to the Sun in October 2025 will provide scientists with their first opportunity to closely observe its nucleus and tail, critical for understanding its composition .
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and the Hubble Space Telescope are already tracking the comet, and the Near Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec) on JWST will likely provide valuable data about its chemical makeup. These observations could offer insights into the interstellar medium, which is crucial for understanding how stars and planetary systems form .
Scientific Significance: A Rare Glimpse into the Unknown
A Window into Galactic Composition
Comets like 3I/ATLAS contain some of the most primitive material in the universe, having preserved chemical signatures from their formation billions of years ago. By studying this comet, scientists hope to gain insights into the chemical processes that occur in other star systems, particularly those similar to ours. Understanding how elements like carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen are distributed in space will inform theories about the formation of planets and life .
Dr. Anya Sharma, a planetary scientist at NASA, explained, “3I/ATLAS is not just a comet; it is a cosmic messenger that can tell us about star systems beyond our own. We’re studying a time capsule from another part of the galaxy.”
Key Observations to Make
Scientists are particularly interested in the composition of the coma and tail of 3I/ATLAS. The comet’s tail will likely reveal volatile gases and dust that were once present in its home system. Furthermore, its outgassing activity so far from the Sun suggests that it could be releasing materials typically found only in cold interstellar space. As it gets closer to the Sun, astronomers will closely monitor for any changes in its activity .
How Does 3I/ATLAS Compare to Other Interstellar Objects?
The discovery of ʻOumuamua in 2017 shocked the scientific community with its unexpected shape and speed. Initially thought to be an asteroid, it later showed signs of being a long, cigar-shaped object that was tumbling through the solar system at unusual speeds. The true nature of ʻOumuamua remains a subject of debate .
In contrast, 2I/Borisov, observed in 2019, was a typical comet, exhibiting the expected cometary activity, including the release of gas and dust as it passed through our solar system. This behavior provided valuable insights into how interstellar objects might interact with the solar system .
3I/ATLAS, however, is exhibiting both common and uncommon behaviors. Its early outgassing and higher-than-expected activity suggest that it may be composed of less typical material or be more volatile than previously observed interstellar comets.
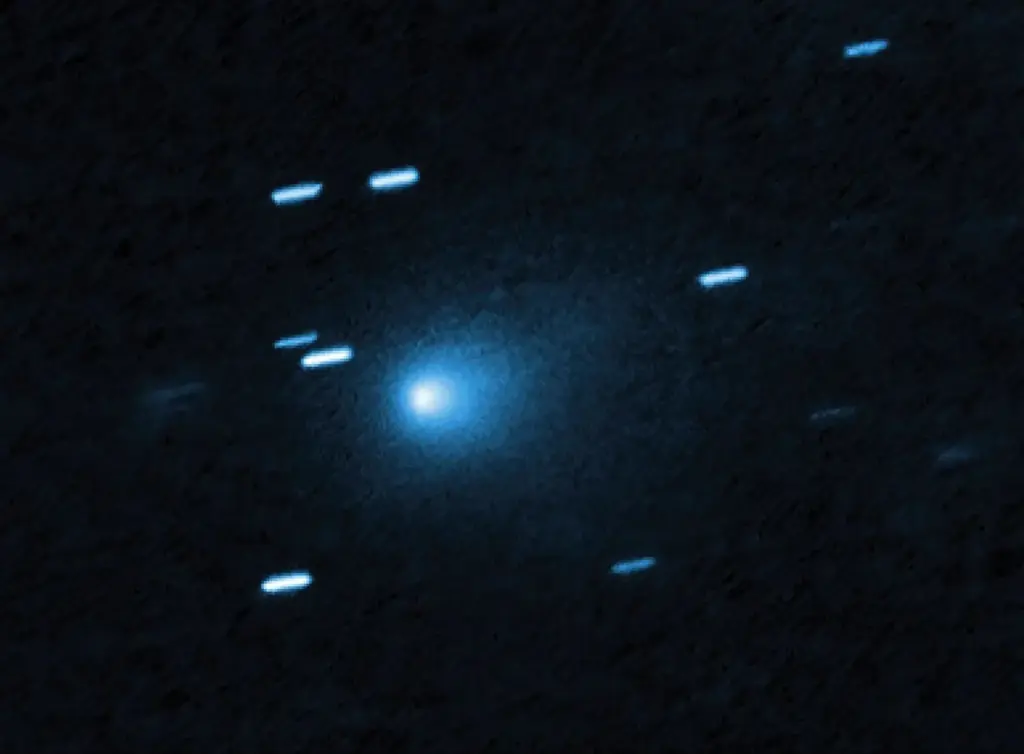

The Race Against Time
Given its swift passage through the solar system, researchers are under a time crunch to gather data. As of now, 3I/ATLAS is already moving quickly away from the Sun and will soon be beyond easy reach for detailed study.
Its closest approach to Earth will occur in December 2025, and this will mark the peak of its brightness as it reaches its farthest point from the Sun . After that, it will exit the solar system, leaving scientists with limited opportunities to observe it.
Related Links
Harvard Scientist Shocked as Interstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS Found Carrying ‘Man-Made’ Metal Alloy
Engineer Claims Breakthrough Method to Overcome Earth’s Gravity: A New Era in Space Propulsion
What Comes Next: Future Observations
NASA is preparing for future interstellar visitors with better equipment and data-gathering techniques. The discovery of 3I/ATLAS is a preview of the many such objects expected to pass through the solar system in the coming decades. NASA’s Verra Rubin Observatory, set to launch soon, will increase the chances of spotting similar objects well before they reach our system, giving scientists more time to prepare for observation .
For now, 3I/ATLAS will continue to be a focal point of astronomical studies, helping scientists understand the dynamics of interstellar objects and expand our knowledge of the universe.
FAQ
Q1: What makes 3I/ATLAS so significant?
A1: 3I/ATLAS is the third interstellar object confirmed to pass through our solar system. Its composition and behavior are offering rare insights into the building blocks of distant star systems and the formation of planetary systems.
Q2: How far is 3I/ATLAS from Earth?
A2: As of its current position, 3I/ATLAS is about 1.8 AU away from Earth, which is approximately 270 million kilometers. It will come closest to Earth in December 2025.
Q3: What instruments are being used to study 3I/ATLAS?
A3: The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and the Hubble Space Telescope, among other observatories, are tracking 3I/ATLAS. These instruments are studying its composition and outgassing activity.
Q4: When will 3I/ATLAS leave the solar system?
A4: 3I/ATLAS is on a hyperbolic trajectory and will leave the solar system soon after its closest approach to Earth in December 2025.