Wearable Technology: Smart clothing isn’t science fiction anymore. The rise of wearable technology has transformed what we wear into something functional, interactive, and intelligent. Thanks to breakthroughs in materials science, clothes are now capable of sensing, reacting, and even powering themselves. This transformation is opening up groundbreaking opportunities in healthcare, sports, fashion, military, and beyond.
From shirts that monitor your heartbeat to jackets that charge your smartphone, wearable technology is redefining the very fabric of modern living. But what powers this innovation? The answer lies in the convergence of cutting-edge materials and smart design. In this article, we’ll break down how specific materials make smart textiles possible—and where the technology is headed next.
Table of Contents
Wearable Technology
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Topic | The rise of wearable technology: Materials behind smart clothing |
| Core Materials | Conductive textiles, nanomaterials, flexible polymers, responsive fabrics, energy-harvesting textiles |
| Industries Impacted | Healthcare, sports, military, fashion, lifestyle |
| Key Benefits | Health tracking, real-time diagnostics, improved athletic performance, energy efficiency, user convenience |
| Challenges | Power supply, washing durability, cost, standardization |
| Notable Resource | Wikipedia: Smart Textiles |
The rise of wearable technology is changing the way we think about clothes. With the help of innovative materials—like conductive fabrics, energy-harvesting textiles, and responsive nanomaterials—smart clothing is improving lives across healthcare, fitness, fashion, and beyond.
What once seemed like science fiction is now sewn into everyday apparel. As this tech continues to evolve, expect more garments that support your health, enhance performance, and even express your personality. The future of clothing is not just about style—it’s about intelligence, utility, and connection.
What Is Smart Clothing?
Smart clothing refers to garments embedded with digital components like sensors, actuators, batteries, and microcontrollers. These turn ordinary clothing into intelligent tools capable of interacting with the human body and external environment.
For example, a smart jacket might adjust temperature based on your body heat, while a fitness shirt could detect heart rate and hydration levels. What makes this possible? Smart materials that are engineered to conduct electricity, respond to stimuli, and maintain comfort.
These garments are designed to do more than look good—they offer functionality, convenience, and even life-saving capabilities. As innovation in e-textiles grows, so does the range of features built into our clothes.
The Key Materials Behind Wearable Technology
1. Conductive Textiles
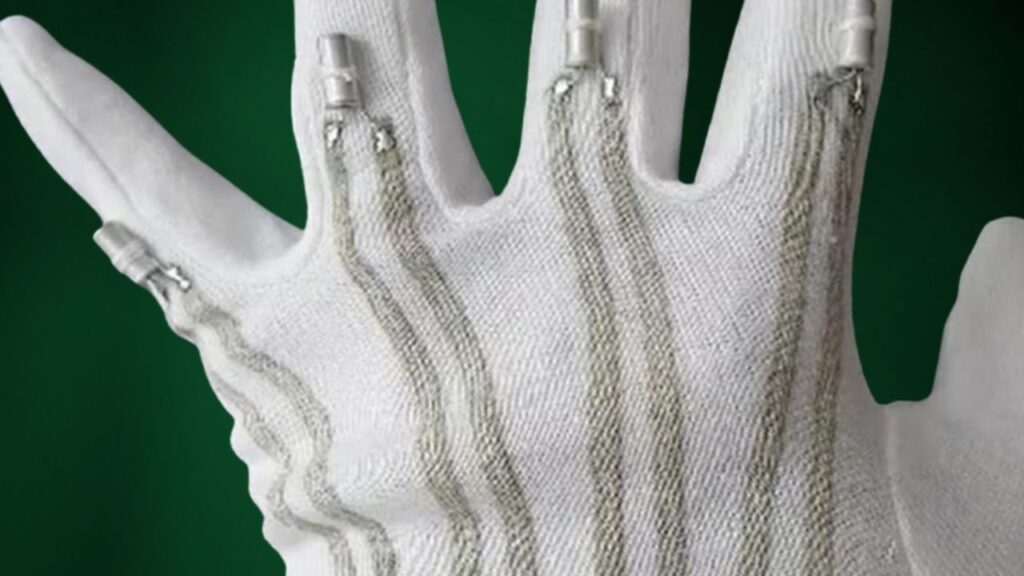

Conductive fabrics are essential to wearable technology. These materials incorporate conductive fibers—usually made from silver, copper, stainless steel, or carbon—into threads and fabrics. They allow electric current to pass through, making the fabric interactive.
- Example: Smart gloves using silver-coated threads can detect hand gestures and transmit that data to control devices.
- Bonus Use: They also serve well in medical environments for sterile monitoring.
2. Flexible Polymers
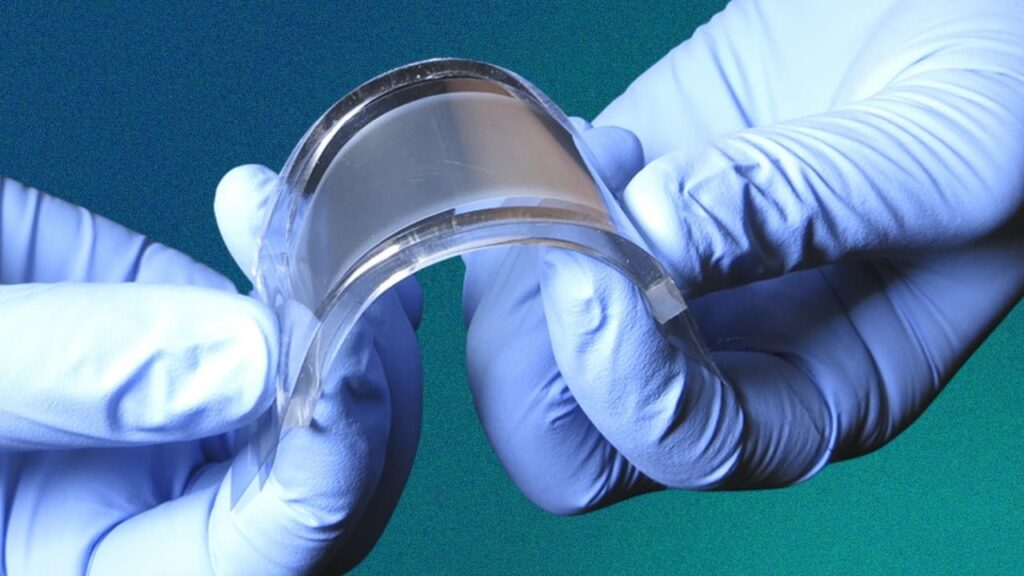

Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU), silicone, and other flexible plastics offer the elasticity and durability needed for comfortable, wearable designs. These materials can stretch, bend, and return to shape without compromising performance.
- Example: TPU is commonly used in smart compression sleeves that track muscle engagement during sports.
- Tip: Look for garments with these polymers if you’re seeking flexibility for athletic or rehab use.
- Professional Insight: Engineers prefer TPU because it’s lightweight, durable, and resistant to sweat.
3. Nanomaterials and Coatings
Nanomaterials provide superior functionality at microscopic levels. Textiles infused with carbon nanotubes, graphene, or nano-silver can deliver improved conductivity, thermal regulation, and antibacterial properties.
- Example: Graphene-laced fabrics regulate temperature by absorbing and redistributing heat.
- Environmental Note: Some nanocoatings are eco-friendly and can be applied using water-based processes.
4. Energy-Harvesting Fabrics
One of the biggest challenges in smart clothing is power. That’s where energy-harvesting fabrics come in. These fabrics can generate electricity from sunlight, body heat, or movement using solar cells, piezoelectric materials, and thermoelectrics.
- Example: A solar-charged hoodie that powers a wearable GPS or emergency beacon.
- Pro Tip: Hybrid energy systems (solar + motion) are the most reliable for continuous use.
5. Responsive and Adaptive Materials
Smart clothes can do more than just measure—they can react. Using shape-memory alloys, thermochromic and photochromic dyes, these fabrics change shape or color depending on temperature, light, or pressure.
- Example: Training apparel that shifts color as your body heats up—visual feedback for workout intensity.
- Advice: Newer generations of these materials offer improved washability and colorfastness.
- Bonus Insight: Responsive textiles are also being explored for mental health, providing mood-boosting visuals.
Practical Applications of Smart Clothing
Healthcare and Medical Monitoring
- Shirts embedded with ECG sensors for cardiac patients.
- Smart socks for diabetes patients to monitor circulation and pressure points.
- Wearable patches that detect dehydration, respiratory distress, or even early infection.
Sports and Fitness
- Compression clothing that gives real-time feedback on form and performance.
- Sensor-equipped insoles that guide runners to avoid injury.
- AI-powered fitness gear that adapts training based on fatigue levels.
Military and Tactical Use
- Smart uniforms that track vitals and hydration in combat zones.
- Embedded sensors to detect chemical exposure or injury in real-time.
- Navigation assistance via haptic feedback built into boots or belts.
Fashion and Everyday Use
- Jackets with LED lights for visibility and style.
- Adaptive coats that heat or cool based on outdoor temperature.
- Clothes with built-in NFC chips for secure access or contactless payments.
Workplace and Industrial Safety
- Smart vests that monitor worker fatigue in construction or mining.
- Real-time location tracking in hazardous environments.
- Garments that alert wearers about proximity to dangerous machinery.
Challenges in Smart Clothing Development
Despite its promise, smart clothing faces several roadblocks:
- Durability: Washing, stretching, and daily wear can damage integrated electronics.
- Power Supply: Reliable, flexible, and long-lasting power sources are still under development.
- Affordability: The cost of high-tech fabrics and manufacturing processes makes products expensive.
- Standardization: There’s a lack of universal guidelines for product safety, compatibility, and performance.
- Privacy: As garments collect more biometric data, privacy and data security become pressing concerns.
The Future of Smart Fabrics
Looking ahead, the integration of AI and machine learning into clothing will revolutionize personal health monitoring, fitness, and even mental well-being. Smart fabrics that “think” could adapt in real time to changing conditions or user behavior.
Researchers at top universities are developing textiles that serve as wearable computers—able to store and process data, not just transmit it. Meanwhile, startups are working on biodegradable electronics to reduce e-waste and support sustainable fashion.
As technology becomes more seamless and user-friendly, expect smart clothing to become as common as smartphones—integrated into our lives in ways we haven’t imagined yet.
LED Innovations: The Bright Future of Energy-Efficient Lighting
Breakthroughs in Flexible Solar Panels: The Future of Renewable Energy
Is the Era of Silicon Coming to an End? What’s Next in Semiconductor Tech
FAQs About Wearable Technology
Q1. Are smart clothes washable?
Most smart clothes are washable, but typically under specific conditions—such as hand-washing or using gentle machine cycles. Always follow the care instructions.
Q2. Do smart clothes need to be charged?
Yes, especially if they include electronics like sensors or heating elements. Some charge via USB, while others use wireless or solar methods.
Q3. Can I wear smart clothing every day?
Many smart garments are designed for daily use, especially in sports, health, and casual wear. Just be mindful of durability and battery life.
Q4. Is smart clothing safe for kids?
Yes, when designed with children in mind. Products made for kids usually comply with strict safety standards and focus on health and location tracking.
Q5. Where can I learn more about smart textiles?
Refer to reputable educational websites and academic journals for in-depth knowledge and the latest research.