The Future of Displays: Display technology is evolving rapidly, and MicroLED is emerging as the next big breakthrough poised to outshine OLED technology.
Whether you are a tech enthusiast, a professional in electronics or design, or simply a consumer searching for the best screen technology, understanding MicroLED is crucial. This article explains what MicroLED is, compares it to OLED, and explores why it’s shaping the future of displays—with clear explanations and expert insights.
Table of Contents
The Future of Displays
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Technology | MicroLED uses inorganic micro-scale LEDs that emit light independently. |
| Brightness | Up to 10,000 nits, compared to OLED’s 800–1,000 nits. |
| Contrast & Color | Perfect blacks and higher contrast than OLED due to self-emissive pixels. |
| Durability | No burn-in risk; lasts significantly longer than OLED displays. |
| Power Efficiency | Up to 50% more efficient than OLED. |
| Industry Support | Backed by Samsung, Apple, Foxconn, Sony, and others. |
| Release Timeline | Mass production expected by late 2025, with devices coming in 2026. |
MicroLED represents the future of display technology with its unparalleled brightness, perfect blacks, energy efficiency, and durability. Supported by major industry players, MicroLED is poised to outshine OLED technology across a variety of applications from TVs to AR/VR. While challenges remain in production and cost, the technology’s benefits promise a revolution in how we experience digital screens.
A Brief History of Display Technologies
Understanding MicroLED is easier when viewed in the context of the evolution of display technologies:
- Cathode Ray Tube (CRT): Dominated screens for decades but bulky and heavy.
- Liquid Crystal Display (LCD): Revolutionized flat panels with backlighting.
- Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED): Introduced self-emissive pixels with superior contrast and thinner panels.
- MicroLED: Now promising to combine the best features of both OLED and LCD while minimizing their weaknesses.
Each step brought improvements in size, image quality, and power consumption, and MicroLED is the latest leap.
What Is MicroLED Technology?
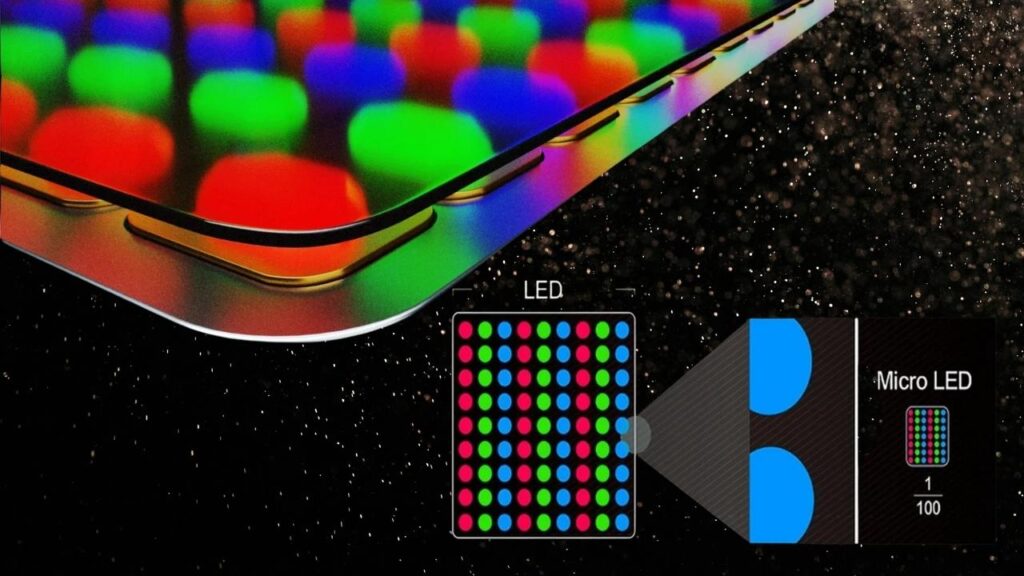
MicroLED displays consist of millions of microscopic inorganic LEDs that emit light individually. Unlike LCDs, which rely on a backlight, or OLEDs that use organic materials, MicroLED pixels light up independently, creating vibrant images with brighter colors, deeper blacks, and improved efficiency.
How MicroLED Works (Simple Breakdown)
- Pixels: Each pixel is a tiny LED (micrometer scale).
- Light Emission: LEDs produce their own light without needing filters or backlights.
- Color Production: By combining red, green, and blue micro LEDs, the display produces full-color images.
- Control: Each LED is independently controlled, allowing perfect blacks when turned off.
MicroLED vs. OLED: The Detailed Comparison
| Feature | OLED | MicroLED |
|---|---|---|
| Light Source | Organic compounds emit light | Inorganic micro-LEDs emit light |
| Brightness | ~800-1,000 nits max | Up to 10,000 nits peak |
| Burn-In Risk | Yes, possible with static images | No risk of burn-in |
| Lifespan | ~30,000–50,000 hours | >100,000 hours |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate | Up to 50% more efficient |
| Color Accuracy | Excellent | Superior contrast & color fidelity |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Established | High but improving rapidly |

Real-World Use Cases and Applications
MicroLED technology is not just for TVs and smartphones. Its features open up exciting applications across industries:
- Consumer Electronics: TVs, monitors, smartphones, smartwatches.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): High brightness and low latency make MicroLED perfect for AR/VR headsets.
- Automotive Displays: Robustness and brightness allow use in dashboards and HUDs.
- Commercial Digital Signage: Outdoor visibility and durability.
- Medical Devices: Precise color and brightness for diagnostic displays.
Advantages That Make MicroLED a Game-Changer
Extreme Brightness and Superior Contrast
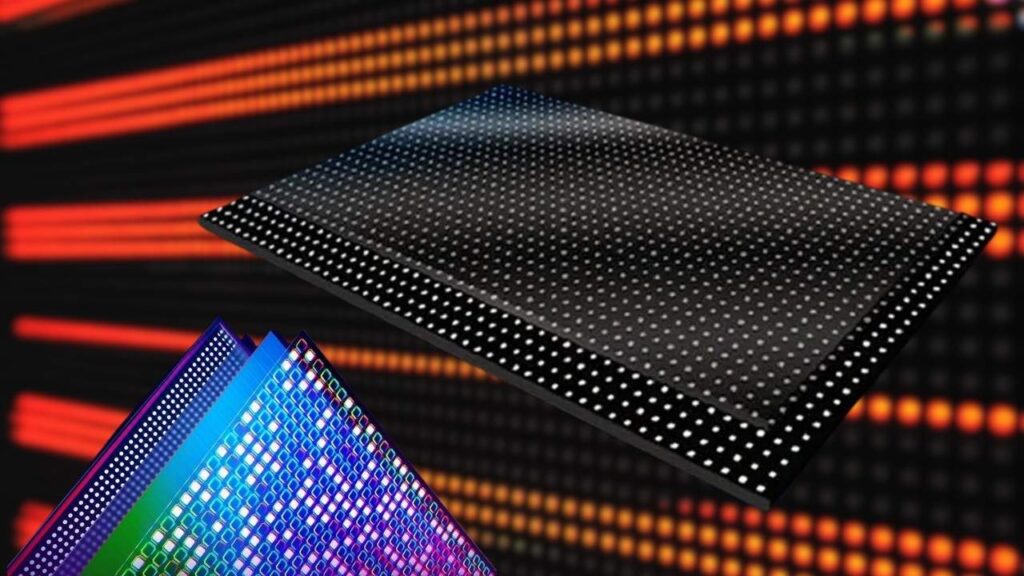

MicroLED can reach brightness levels up to 10 times higher than OLED, making screens visible even in bright sunlight. The ability to turn individual pixels off produces true black, delivering outstanding contrast that enhances picture quality dramatically.
Longevity and No Burn-In
Because MicroLEDs use inorganic materials, they degrade much slower than OLED’s organic compounds. This results in a longer lifespan, often more than double that of OLED, and no risk of burn-in—even with static images.
Energy Efficiency and Response Speed
MicroLED consumes significantly less power, especially when displaying bright content. It also has ultra-fast response times measured in nanoseconds, making it ideal for gaming and professional graphics work.
Challenges Still to Overcome
Despite its potential, MicroLED faces significant challenges:
- Manufacturing Complexity: Mass production requires precise placement of millions of tiny LEDs.
- Cost: Current production is expensive, but prices are expected to decrease with advancements in manufacturing.
- Yield and Size: Large displays without defects are difficult to produce, but modular display construction helps.
How Does MicroLED Compare to MiniLED and QLED?
It’s important to know the difference between MicroLED and other emerging display technologies:
- MiniLED: Uses thousands of tiny LEDs as a backlight for LCD panels. Better than traditional LCD but still requires backlight.
- QLED: Quantum Dot LCDs enhanced for color and brightness but rely on backlight and do not have perfect blacks.
- MicroLED: Self-emissive pixels that don’t require a backlight, delivering better contrast, brightness, and efficiency than both.
Environmental Impact of MicroLED
MicroLED’s longer lifespan and greater energy efficiency reduce electronic waste and power consumption. Additionally, its inorganic materials are generally more recyclable than OLED’s organic compounds. These factors make MicroLED a more environmentally sustainable option for future display tech.
Future Outlook and Innovations
Ongoing research focuses on:
- Improving manufacturing yield and reducing cost.
- Increasing pixel density for even sharper images.
- Flexible and transparent MicroLED displays for innovative device designs.
- Integration with AI and smart sensors to enhance display functions.
The next decade will likely see MicroLED technology become more accessible and integrated across multiple devices.
Practical Advice: When to Consider MicroLED
For Consumers
If you want the absolute best display quality and durability, wait for MicroLED TVs or monitors coming in 2025–2026. For now, OLED remains a fantastic choice for most users.
For Industry Professionals
Start integrating MicroLED research into your product development. Understand supply chains and potential applications—MicroLED will define premium electronics soon.
For Developers and Gamers
Watch for MicroLED monitors offering ultra-low latency and superb image quality, which can provide a competitive edge.
Light-Powered Computing: The Race to Build the First All-Optical Processor
Turning Heat into Power: New Thermoelectric Materials Could Revolutionize Waste Energy Use
Scientists Develop Self-Healing Materials for Electronics and Wearable Devices
FAQs About The Future of Displays
What makes MicroLED different from OLED?
MicroLED uses tiny inorganic LEDs that light independently, making it brighter, longer-lasting, and immune to burn-in.
When will MicroLED become widely available?
Mass production is expected by late 2025, with consumer products launching in 2026 and beyond.
Can MicroLED displays be flexible or transparent?
Yes, research is ongoing to produce flexible and transparent MicroLEDs for new device designs.
Are MicroLED displays better for the environment?
Yes, due to higher energy efficiency, longer lifespan, and better recyclability compared to OLED.