New Wood Stove Tech Cuts Pollution and Boosts Efficiency: Wood stoves have long been cherished for their ability to provide warmth and ambiance. However, traditional models have raised concerns due to their environmental impact and inefficiency. Enter the new generation of wood stove technology, which significantly reduces pollution and enhances efficiency, making wood stoves a more sustainable and eco-friendly heating option.

Whether you’re an eco-conscious homeowner, a heating professional, or someone exploring sustainable energy options, understanding these modern innovations is essential. The latest EPA-certified wood stoves reduce pollutants by up to 90% compared to traditional models, while also conserving wood and providing more effective heating.
New Wood Stove Tech Cuts Pollution and Boosts Efficiency
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Topic | New Wood Stove Technology: Pollution Reduction & Efficiency Boost |
| Main Benefits | Up to 90% less pollution, 30–50% higher efficiency, cleaner burns |
| Core Innovations | Catalytic combustion, secondary burn systems, air wash technology |
| Environmental Impact | Significantly lower particulate emissions |
| Energy Savings | Uses less wood for more heat |
| Target Audience | Homeowners, environmentalists, HVAC professionals |
| Official EPA Resource | EPA Burn Wise Program |
New wood stove technology is revolutionizing home heating by delivering cleaner air, better efficiency, and more sustainable energy use. Whether you’re upgrading an old unit or building a new eco-friendly home, choosing a modern EPA-certified stove is a smart investment for your wallet and the planet.
The Problem with Traditional Wood Stoves

Traditional wood-burning stoves and open fireplaces can emit substantial amounts of fine particulate matter (PM2.5), which poses health risks and contributes to environmental pollution. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), older, uncertified wood stoves can emit between 15 to 30 grams of smoke per hour, whereas modern EPA-certified models emit no more than 2.5 grams per hour.
These emissions contain harmful substances such as carbon monoxide (CO), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), all of which can adversely affect human health and the environment.
Innovations in Wood Stove Technology

Modern wood stoves have been redesigned to address the shortcomings of their predecessors. Key technological advancements include:
1. Catalytic Combustion
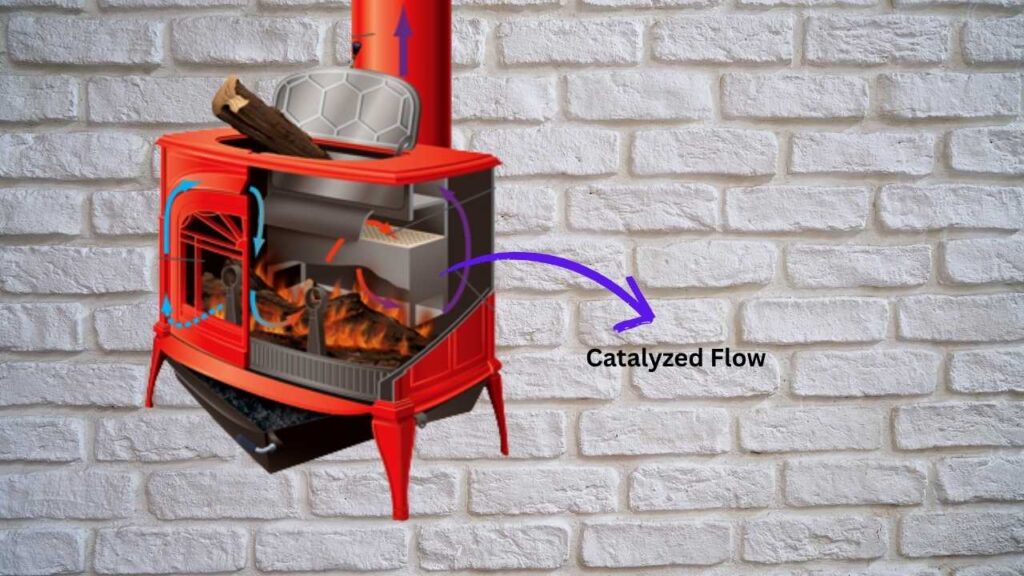
Catalytic stoves utilize a ceramic-coated honeycomb catalyst that ignites unburned gases and particulates at lower temperatures, resulting in cleaner emissions and improved efficiency. These stoves can achieve up to 90% reduction in harmful pollutants compared to traditional models.
2. Secondary Combustion
Non-catalytic stoves employ high-temperature zones and introduce fresh oxygen to ignite remaining gases, achieving nearly as clean burns as catalytic models without the need for a catalyst.
3. Air Wash Systems
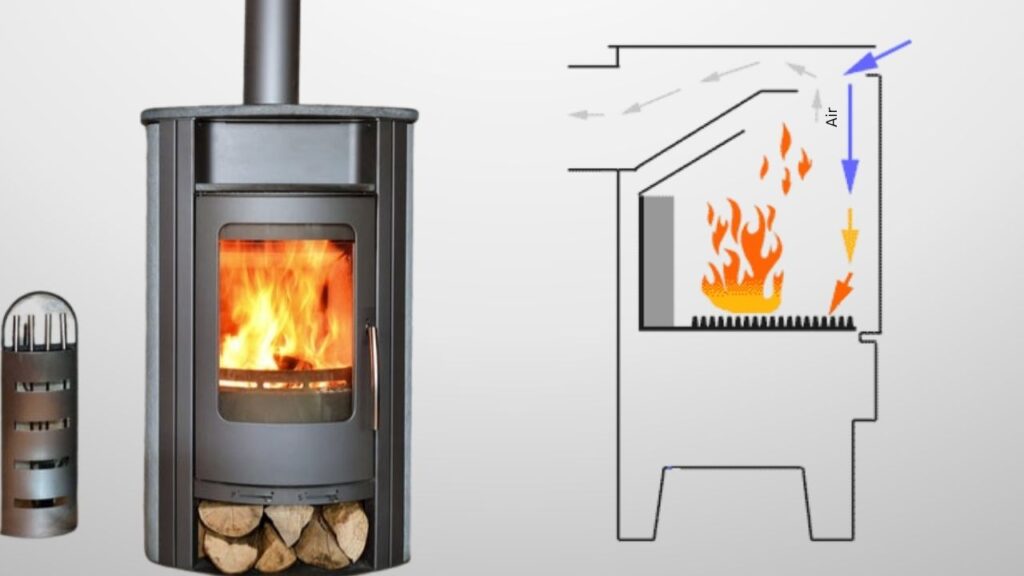

This feature directs a flow of preheated air over the stove’s glass door, keeping it clean and aiding in the combustion of particulates, further reducing emissions.
4. Thermoelectric Generators
Innovations like BioLite’s HomeStove incorporate thermoelectric technology to convert heat into electricity, powering fans that improve combustion and reduce smoke. This approach not only enhances efficiency but also provides off-grid electricity for charging devices.
5. Rocket Mass Heaters
These stoves feature insulated combustion chambers and thermal mass components that store and slowly release heat, achieving fuel savings of up to 80–90% compared to conventional stoves.
Benefits for Homeowners
Cost Savings
Modern wood stoves burn wood more completely, allowing homeowners to use up to 50% less wood while achieving the same or better heat output.
Environmental Impact
Cleaner burns mean fewer trees are felled, less smoke is produced, and carbon-based emissions are reduced, contributing to better air quality and environmental conservation.
Ease of Maintenance
Advanced designs result in less creosote buildup, reducing the risk of chimney fires, and require less frequent ash disposal. Air wash technology also keeps the stove glass cleaner for longer periods.
Understanding Combustion Efficiency
Efficient combustion requires high temperatures (over 1100°F), adequate oxygen supply, and properly seasoned, dry wood with moisture content under 20%. Burning green or damp wood creates more smoke and less heat, wasting energy and increasing pollution.
Choosing the Right Wood Stove
When selecting a new stove, consider the following:
- EPA Certification: Ensure the stove is EPA-certified for optimal efficiency and reduced emissions.
- Appropriate Sizing: Choose a stove that matches the size of the space you intend to heat.
- Air Control Features: Look for models with adjustable air intake to optimize combustion.
- Installation Requirements: Ensure compatibility with your home’s chimney and ventilation systems.
Transitioning to Cleaner Heating
Step 1: Assess Your Current Stove
If your stove is over 20 years old, it’s likely not EPA-compliant and may emit significantly more pollution than newer models.
Step 2: Explore Incentives
Many regions offer rebates, tax credits, or trade-in programs for upgrading to cleaner stoves. For example, U.S. homeowners can qualify for a tax credit worth 30% of the cost, up to $2,000 per year, for upgrading to a new high-efficiency wood-burning stove.
Step 3: Professional Installation
Always work with certified professionals to ensure safety and compliance with local codes.
Think It Was a Black Hole? Scientists Say It Might Have Been Something Even Stranger
Physicists Create One of the Most Neutron-Deficient Isotopes Ever Observed in the Lab
Attosecond ‘Clock’ Measures Electron Tunneling Time With Unmatched Precision
FAQs About New Wood Stove Tech Cuts Pollution and Boosts Efficiency
Q1: Are new wood stoves carbon-neutral?
While burning wood releases CO₂, using sustainably harvested firewood makes the process close to carbon-neutral, especially compared to fossil fuels.
Q2: How often should I clean a modern stove?
Clean the ashpan weekly and inspect the flue every season. Catalytic units may require yearly maintenance.
Q3: What wood is best for clean burning?
Hardwoods like oak, maple, and hickory burn hotter and cleaner than softwoods. Always season wood for at least 6–12 months.
Q4: Can I install one in a smoke-controlled zone?
Yes, but only if the model is DEFRA-exempt in the UK or EPA-certified in the U.S. Always check local regulations.