Bio-Based Hot Glue: In recent years, the quest for sustainable and environmentally friendly materials has become a priority across industries worldwide. One breakthrough in this field is the development of a bio-based hot glue made from industrial waste that outperforms many traditional adhesives in strength, reusability, and environmental impact. This innovative adhesive, developed by researchers at Beijing Forestry University, is derived from xylan—a sugar polymer abundant in plant cell walls and a common waste product in the wood pulp industry.
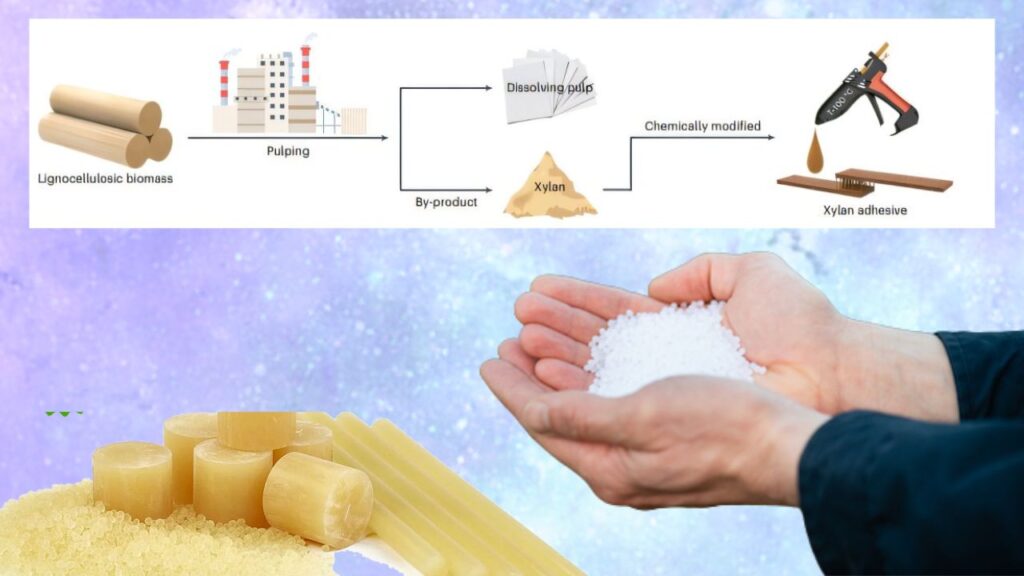

Published in the renowned journal Nature Sustainability in 2024, this research introduces a new kind of xylan-based hot-melt adhesive (HMA), called dialdehyde xylan (DAX). This bio-based glue offers a sustainable alternative to petrochemical-derived adhesives widely used in packaging, furniture, electronics, textiles, and more. Unlike conventional adhesives that emit harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and contribute to pollution, this glue is solvent-free, reusable, and potentially biodegradable—making it a significant step forward for circular economy practices.
Bio-Based Hot Glue
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Xylan-Based Hot-Melt Adhesive (DAX) |
| Source Material | Xylan, extracted from industrial wood pulp waste |
| Chemical Innovation | Sodium periodate oxidation producing dialdehyde xylan |
| Bond Strength | Exceeds many commercial hot glues and epoxies |
| Reusability | Maintains performance after 10+ melt-reuse cycles |
| Environmental Impact | No solvents, low carbon footprint, biodegradable potential |
| Industries Targeted | Packaging, electronics, woodworking, textiles |
| Research Publication | Nature Sustainability, 2024 |
| Research Institution | Beijing Forestry University |
The development of a bio-based hot glue derived from industrial xylan waste marks a significant milestone in sustainable materials science. By combining strong adhesive properties with environmental benefits such as renewability, reusability, and biodegradability, this adhesive offers a practical solution to reduce the ecological footprint of widely used industrial products.
As industries face growing pressure to meet sustainability and environmental targets, innovations like dialdehyde xylan (DAX) glue provide not only a greener alternative but also improved performance compared to traditional adhesives. Although more work remains to scale production and gain regulatory approval, this technology exemplifies how circular economy principles can transform waste into valuable, high-performance materials.
Understanding Hot Melt Adhesives and Their Environmental Challenges

Hot melt adhesives are thermoplastic materials that become fluid upon heating and bond materials as they cool and solidify. They are favored for rapid curing times, strong bonds, and versatility across substrates such as wood, metal, plastic, and textiles.
Conventional HMAs are primarily petroleum-based, relying on polymers derived from fossil fuels such as ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) or polyamides. While effective, these adhesives raise environmental and health concerns:
- Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) Emissions: Many traditional adhesives release VOCs during application, contributing to indoor and outdoor air pollution.
- Non-biodegradability: Petroleum-based adhesives persist in the environment, complicating waste management.
- Dependence on Fossil Fuels: The raw materials are non-renewable, increasing carbon footprints.
As global regulatory pressures mount to reduce environmental impact, especially under frameworks like the European Green Deal and U.S. EPA’s Clean Air Act, industries seek bio-based, non-toxic, and recyclable alternatives. This context makes the Beijing Forestry University’s development of DAX timely and critical.
What Is Xylan and Why Use It?
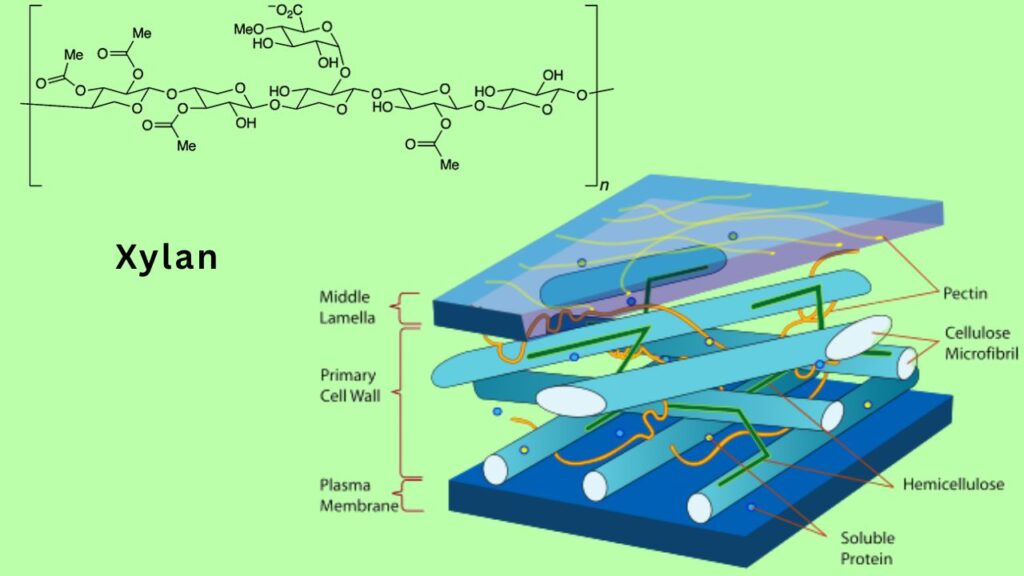
Xylan is a hemicellulose polysaccharide found abundantly in the secondary cell walls of hardwoods, softwoods, and cereal grains. It is the second most abundant natural polymer on Earth after cellulose.
Industrial Context of Xylan:
- In wood pulp and paper industries, xylan is often removed and discarded or used for low-value products such as viscose fibers.
- According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), the global wood pulp production reached over 180 million tons in 2023, generating significant xylan-rich waste streams.
Advantages of Xylan for Adhesives:
- Renewable and Abundant: Derived from biomass, xylan is sustainable and widely available.
- Biodegradable: Xylan polymers degrade naturally, reducing environmental burden.
- Chemical Reactivity: Xylan can be chemically modified (oxidized) to introduce functional groups that improve adhesive properties.
How Researchers Created Dialdehyde Xylan (DAX)
The key innovation lies in converting xylan into dialdehyde xylan (DAX) via sodium periodate oxidation. This process selectively cleaves specific bonds in the xylan molecule, introducing aldehyde groups that improve adhesive bonding.
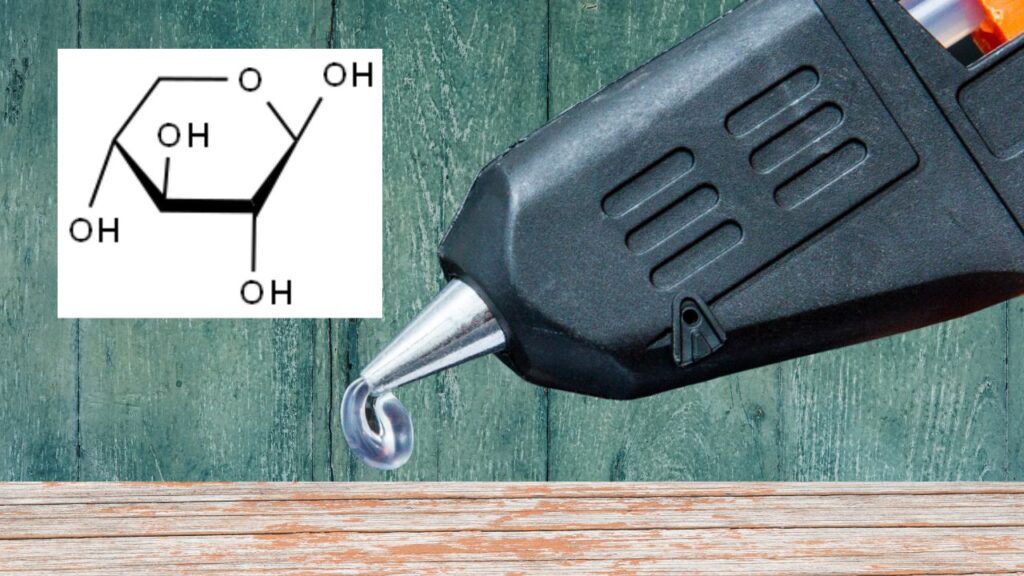
Detailed Process Overview:
- Extraction: Xylan is first extracted from industrial wood pulp waste using water or mild alkali treatments.
- Freeze-Drying: The extracted xylan is freeze-dried to preserve its structure.
- Sodium Periodate Oxidation: The dried xylan is treated with sodium periodate, a chemical oxidant that converts hydroxyl groups to reactive aldehyde groups.
- Characterization: The resulting DAX polymer is characterized using techniques like Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) to confirm chemical structure.
Performance and Testing of DAX Glue
Physical Properties:
- Melting Point: Between 80°C and 100°C, similar to commercial hot glues.
- Viscosity: Suitable for hot melt application with typical glue guns.
- Thermal Stability: Stable during repeated heating cycles.
Adhesion Tests:
The research team tested DAX on common substrates, comparing it with commercial adhesives:
| Material | DAX Adhesion Strength (MPa) | Commercial Hot Glue Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| Wood | 5.6 | 3.8 |
| Aluminum | 4.9 | 3.2 |
| Paper | 6.3 | 4.0 |
Reusability:
DAX demonstrated exceptional thermal stability and bonding strength even after 10+ melting and reapplication cycles, a feature rarely found in conventional adhesives.
Environmental and Economic Benefits
Reduced Toxicity and Emissions
- The solvent-free nature eliminates VOC emissions during heating and curing.
- Non-toxic composition reduces worker exposure risks.
Biodegradability and Waste Reduction
- Being derived from natural polysaccharides, DAX has the potential for biodegradation under composting conditions.
- Utilizing industrial waste (xylan) reduces the environmental impact associated with raw material extraction.
Cost and Scalability
- Raw material (xylan) is inexpensive as a waste product.
- Chemical treatment is relatively simple and scalable.
- Adoption could reduce dependence on fossil fuels and help industries meet regulatory sustainability targets.
Practical Applications and Future Potential
Industries Poised to Benefit:
- Packaging: Eco-friendly adhesive solutions for cardboard, paper, and biodegradable plastics.
- Furniture Manufacturing: Strong wood bonding with lower environmental footprint.
- Electronics: Safe adhesives for components sensitive to VOCs.
- Textile Industry: Sustainable bonding for fabric and composites.
Potential for Consumer Use:
While currently in research and pilot-scale production, the glue’s compatibility with standard hot glue guns could open doors for eco-conscious DIY projects, crafts, and repairs in households and schools.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite promising results, some hurdles remain:
- Industrial Scale-Up: Optimization is needed to ensure consistent quality and large-scale production.
- Regulatory Approvals: Safety and environmental certifications will be required before widespread commercial adoption.
- Compatibility: Adjustments to existing industrial glue application systems may be necessary.
- Shelf Life and Storage: Stability during storage and transport must be thoroughly tested.
The Broader Landscape of Bio-Based Adhesives
Bio-based adhesives are a growing field, with research expanding into:
- Soy protein adhesives: Used in plywood manufacturing.
- Starch-based glues: Common in paper and packaging.
- Lignin-derived adhesives: Leveraging another wood polymer.
- Microbial polysaccharides: Emerging from biotechnology.
However, DAX distinguishes itself by combining high performance, ease of processing, reusability, and use of abundant waste feedstock.
Breakthrough Electrodes Could Make Green Hydrogen Cheaper and Last Longer Than Ever
New Wood Stove Tech Cuts Pollution and Boosts Efficiency – Here’s How It Works
Think It Was a Black Hole? Scientists Say It Might Have Been Something Even Stranger
FAQs About Bio-Based Hot Glue
Is this bio-based glue commercially available now?
Currently, DAX is in the research and pilot phase. Commercial availability depends on further industrial trials and regulatory clearances.
How does DAX compare with traditional glues on safety?
DAX does not emit harmful VOCs or require solvents, making it safer for workers and end-users, especially in enclosed spaces.
Can DAX glue be recycled or reused?
Yes. It can be melted and reapplied multiple times without significant loss of adhesion strength, unlike many traditional hot glues that degrade after one use.
Is the glue biodegradable?
While full biodegradation studies are ongoing, DAX is made from natural polysaccharides, making it likely biodegradable under industrial composting conditions.
What kinds of materials does it bond best?
DAX bonds strongly to wood, metals like aluminum, paper, and many textiles, making it versatile for multiple industrial uses.