Summer Solstice 2025: The Summer Solstice 2025 marks the official start of Northern Hemisphere summer, bringing with it the longest day and shortest night of the year. This astronomical event, celebrated across cultures and continents, is not just about extra daylight—it’s a fascinating demonstration of Earth’s unique place in the solar system. Whether you’re a curious student, a weather enthusiast, or a professional in climate science, understanding the summer solstice offers valuable insights into our planet’s rhythms and the science behind the seasons.

As the sun reaches its highest point in the sky, the Northern Hemisphere enjoys extended daylight, warmer temperatures, and the unmistakable arrival of summer. But what exactly causes the summer solstice? Why does the date shift each year? And how can you make the most of this special day, both personally and professionally? Read on for a comprehensive, easy-to-understand guide.
Summer Solstice 2025
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Date & Time (2025) | June 20, 2025, 10:42 p.m. EDT (June 21, 02:42 UTC) Official NASA Solstice Information |
| Significance | Longest day and shortest night in the Northern Hemisphere |
| Sun’s Position | Directly overhead at the Tropic of Cancer (23.5°N latitude) |
| Daylight Variance | Up to 16 hours in northern cities (e.g., Seattle); nearly 15 hours in Washington, D.C. |
| Opposite in South | Shortest day and longest night in the Southern Hemisphere |
| Cultural Impact | Celebrations worldwide: Stonehenge sunrise, Sweden’s Midsummer, bonfires in Norway |
| Why Date Shifts | Due to Earth’s orbit and leap years |
| Professional Relevance | Affects agriculture, energy, tourism, and scientific research |
The Summer Solstice 2025 is more than just the start of summer—it’s a remarkable astronomical event that shapes our seasons, influences global cultures, and impacts everything from farming to energy use. By understanding the science and significance behind the solstice, you can appreciate the rhythms of our planet and make the most of the year’s longest day.
What Is the Summer Solstice?
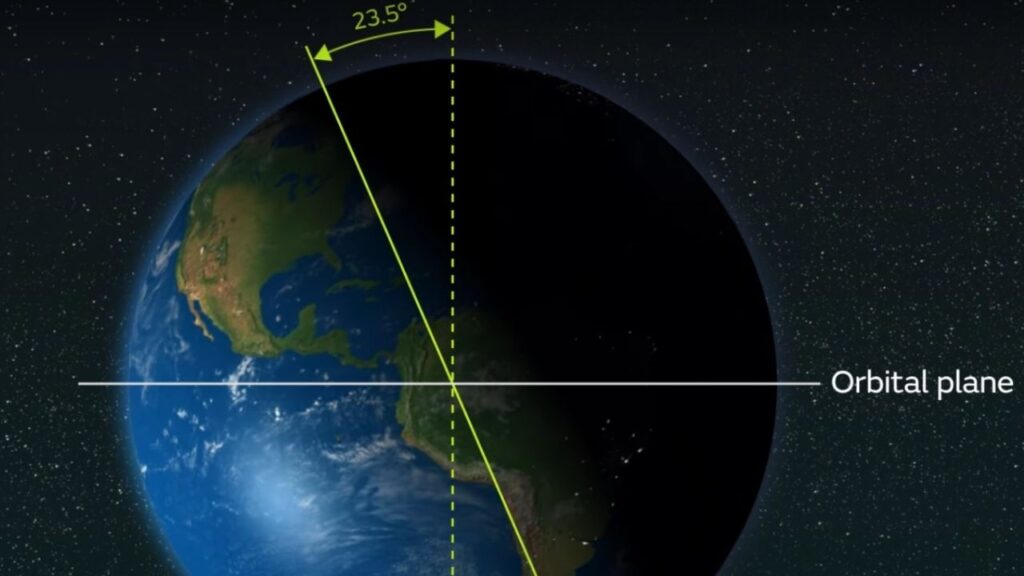
The summer solstice is the exact moment when the Earth’s Northern Hemisphere is tilted most directly toward the sun. This year, it occurs on Friday, June 20, 2025, at 10:42 p.m. Eastern Daylight Time. At that moment, the sun appears directly overhead at the Tropic of Cancer, an imaginary line circling the globe at about 23.5 degrees north of the equator.
This tilt—about 23.5 degrees—is the reason we have seasons. As Earth orbits the sun, the angle of sunlight hitting different parts of the planet changes, causing variations in day length and temperature throughout the year.
Why Is the Summer Solstice the Longest Day?
On the solstice, the sun’s path across the sky is at its highest and longest for the year, resulting in the most daylight hours. For example, cities like Seattle experience nearly 16 hours of sunlight, while Washington, D.C., enjoys almost 15 hours. The farther north you go, the longer the day—near the Arctic Circle, the sun may not set at all, leading to the phenomenon known as the “Midnight Sun“.
Why Does the Date of the Summer Solstice Change?
You might notice that the solstice doesn’t always fall on the same date. Sometimes it’s June 20, other years it’s June 21. This variation is due to two factors:
- Earth’s Orbit: It takes Earth about 365.24 days to orbit the sun. Our calendar rounds this to 365 days, so we add a leap day every four years to catch up.
- Time Zones: The exact moment of the solstice is the same everywhere but falls on different local dates and times depending on your location. For instance, while it’s June 20 in the U.S., it will be June 21 in the UK and parts of Europe.
The Science Behind the Solstice
Earth’s Tilt and Orbit
The Earth is tilted at an angle of about 23.5 degrees relative to its orbit around the sun. This tilt is responsible for the changing seasons. During the summer solstice, the Northern Hemisphere is angled most directly toward the sun, resulting in longer days and warmer temperatures.
The Tropic of Cancer
On the solstice, the sun is directly overhead at noon along the Tropic of Cancer. This latitude line passes through countries like India, Mexico, Egypt, and China, making it a key reference point for understanding solar patterns and climate zones.
The “Sun Stands Still”
The word “solstice” comes from the Latin solstitium, meaning “sun stands still.” For a few days around the solstice, the sun’s apparent movement north or south pauses before reversing direction. This “pause” is most noticeable at high latitudes, where the change in daylight is dramatic.
How Does the Summer Solstice Affect Us?
Everyday Life
- More Daylight: Longer days mean more time for outdoor activities, from sports to gardening to evening walks.
- Warmer Weather: The increased sunlight warms the ground and air, leading to higher temperatures and the classic feel of summer.
- Cultural Celebrations: Many cultures celebrate the solstice with festivals, dances, and rituals. Examples include sunrise gatherings at Stonehenge in England, maypole dances in Sweden, and bonfires in Norway.
Professional Impact
- Agriculture: Farmers use the solstice as a marker for planting and harvesting schedules. Crops that need long days, like wheat and barley, thrive after the solstice.
- Energy: Longer days reduce the need for artificial lighting, affecting energy consumption patterns.
- Tourism: Destinations with unique solstice phenomena, such as the Midnight Sun, attract visitors from around the world.
- Science and Research: Meteorologists, astronomers, and climate scientists use solstice data to study weather patterns, solar energy, and Earth’s changing climate.
Practical Tips: Making the Most of the Summer Solstice
For Families and Kids:
- Plan a picnic or outdoor adventure to enjoy the extra daylight.
- Track sunrise and sunset times to observe how the day length changes.
- Try simple science experiments, like measuring the length of your shadow at noon.
For Professionals:
- Use the solstice as a benchmark for seasonal planning in agriculture, landscaping, or outdoor events.
- Monitor energy usage patterns and adjust lighting schedules for efficiency.
- Leverage the solstice in marketing campaigns for tourism and recreation.
For Enthusiasts:
- Photograph the sunrise or sunset on the solstice for a unique perspective.
- Visit a historical site known for solstice celebrations, such as Stonehenge or Chichen Itza.
- Join local or online communities to share observations and experiences.
Quantum Sensors Now Deliver Unmatched Precision For Medical And Aerospace Breakthroughs
Microsoft Declares the Beginning of the Logical Qubit Era in Quantum Computing
Ultralight 3D-Printed Antennas Cut Weight By 94 Percent With Breakthrough Multi-Material Design
FAQs About Summer Solstice 2025
Q: What exactly happens during the summer solstice?
A: The sun reaches its highest point in the sky at noon, and the Northern Hemisphere experiences the longest period of daylight for the year.
Q: Is the solstice always the hottest day of the year?
A: No. The hottest days usually occur a few weeks after the solstice, due to the time it takes for land and oceans to warm up—a phenomenon known as “seasonal lag.”
Q: Why do some places have 24 hours of daylight?
A: Near the Arctic Circle, the sun doesn’t set at all during the solstice, creating the “Midnight Sun.” This is because of the tilt of the Earth and the way sunlight reaches the poles.
Q: Does the solstice affect the Southern Hemisphere?
A: Yes, but in the opposite way. The Southern Hemisphere experiences its shortest day and the official start of winter.
Q: How can I find the exact time of the solstice where I live?
A: Check official resources such as NASA’s solstice information page for precise timings.