Hydrogen Fuel at Half the Cost: Imagine a world where cars, buses, and even factories run on a fuel that’s as clean as water and as powerful as gasoline—but costs half as much to make as it does today. That’s the promise behind the latest breakthrough in hydrogen fuel technology from South Korea. Scientists there have developed a new catalyst that could slash the cost of green hydrogen production, making this clean energy source more accessible than ever before.

Hydrogen has long been hailed as the fuel of the future: it’s clean, efficient, and packs a punch when it comes to energy storage. But until now, making hydrogen—especially the eco-friendly kind—has been expensive and complicated. Thanks to a team of brilliant researchers at Hanyang University, that’s about to change. Their new catalyst could transform not just the energy industry, but the entire way we power our world.
Hydrogen Fuel at Half the Cost
| Feature/Fact | Details & Data |
|---|---|
| Breakthrough | New catalyst for green hydrogen production cuts costs by up to 50% |
| Material | Cobalt phosphide-based nanomaterials, tailored with boron and phosphorus using MOFs |
| Efficiency | Twice as efficient as previous catalysts; yields 0.528% hydrogen per gram of oxide |
| Stability | Maintains performance for over 100 hours in alkaline electrolyzers |
| Environmental Impact | Enables large-scale, zero-carbon hydrogen production, reducing global emissions |
| Commercialization Potential | Uses earth-abundant materials, making green hydrogen more affordable and scalable |
| Official Resource | Hanyang University Official Website |
The development of a new, affordable catalyst by South Korean scientists could be the tipping point for green hydrogen. By slashing production costs and boosting efficiency, this innovation brings us closer to a future where clean, powerful hydrogen fuel is available to everyone. Whether you’re a student, a business leader, or just someone who cares about the planet, this is a breakthrough worth celebrating.
What Is Green Hydrogen, and Why Does It Matter?
Green hydrogen is hydrogen produced using renewable energy sources like wind or solar power. Unlike “grey” hydrogen (made from fossil fuels), green hydrogen doesn’t release carbon dioxide or other pollutants. When used, its only byproduct is water vapor. This makes it a key player in the fight against climate change and a potential replacement for fossil fuels in everything from transportation to heavy industry.
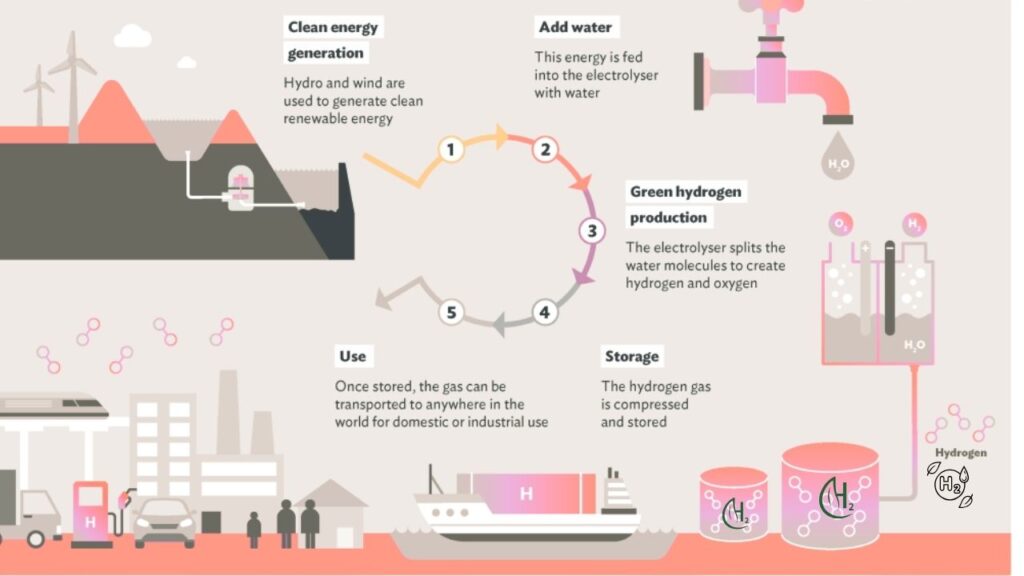
But there’s a catch: producing green hydrogen has been much more expensive than traditional fuels. The main reason? The catalysts used in the process are often made from rare, costly metals like platinum and iridium. These materials drive up costs and limit how much hydrogen we can produce.
The South Korean Breakthrough: A Catalyst for Change
How Does the New Catalyst Work?
The team at Hanyang University developed a cobalt phosphide-based nanomaterial catalyst. Here’s what makes it special:
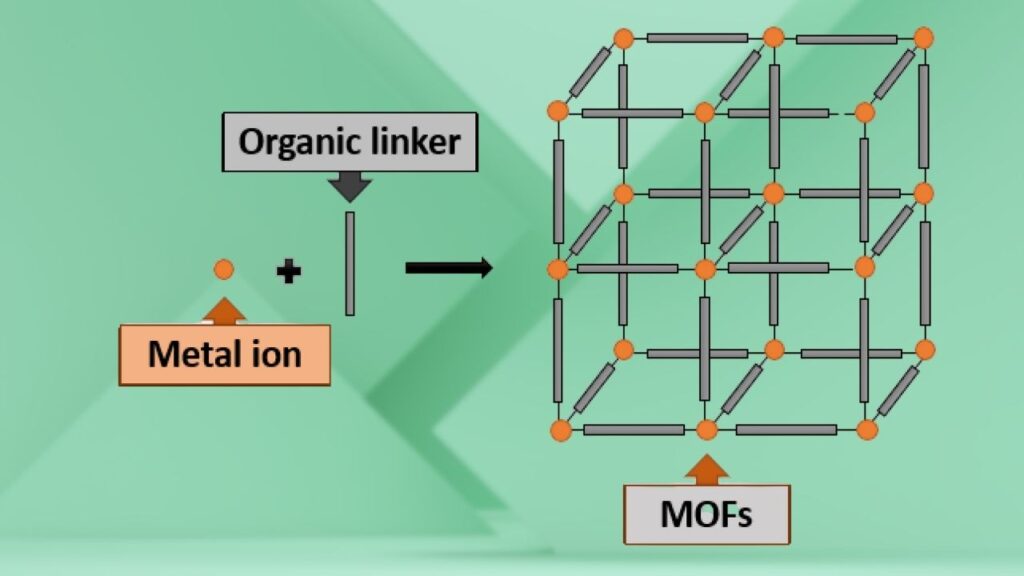
- Custom-Tailored with MOFs: By using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), the researchers could precisely control how much boron and phosphorus went into the catalyst. This fine-tuning made the catalyst more efficient and much cheaper to produce.
- Superior Performance: Unlike older catalysts that work well for only part of the hydrogen production process, this new material excels at both the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and the oxygen evolution reaction (OER)—the two key steps in splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen.
- Stability and Scalability: The catalyst stayed stable for over 100 hours in tough, alkaline conditions. That’s important for real-world use, where reliability matters.
Why Is This a Big Deal?
- Cost Reduction: Using earth-abundant materials instead of precious metals means hydrogen can be produced at half the cost—potentially making green hydrogen as cheap as, or even cheaper than, fossil fuels.
- Efficiency: The new catalyst produces twice as much hydrogen as the previous best materials, with a yield of 0.528% hydrogen per gram of oxide.
- Blueprint for Future Innovation: The researchers’ approach—using MOFs to design better catalysts—could lead to even more breakthroughs in clean energy technology.
How Does Hydrogen Production Work?
Let’s break it down step-by-step:
1. Electrolysis of Water
- Water (H₂O) is split into hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂) using electricity.
- The process needs a catalyst to speed things up and make it efficient.
2. Role of the Catalyst
- Traditional catalysts use platinum or iridium—expensive and rare.
- The new South Korean catalyst uses cobalt phosphide, boron, and phosphorus—much cheaper and more common.
3. Result
- Hydrogen gas is collected and can be used as a clean fuel.
- Oxygen is released as a harmless byproduct.
Practical Advice: What Does This Mean for You?
For Industry Professionals
- Lower Costs: Companies can produce green hydrogen more affordably, opening doors for wider adoption in transportation, manufacturing, and power generation.
- Scalability: The new catalyst’s stability means it can be used in large-scale plants, not just in labs.
- Investment Opportunity: As green hydrogen becomes cheaper, expect growth in hydrogen infrastructure and related industries.
For Everyday People
- Cleaner Air: More hydrogen-powered vehicles and factories mean less air pollution.
- Affordable Clean Energy: As production costs drop, hydrogen-powered devices and vehicles could become as common and affordable as gasoline ones.
- Job Creation: The shift to green hydrogen could create new jobs in science, engineering, and manufacturing.
Real-World Examples
- Buses and Trains: Cities like Seoul and Tokyo already use hydrogen-powered buses. Lower costs could bring these to more cities worldwide.
- Factories: Steel and chemical plants are testing hydrogen as a replacement for coal and natural gas.
- Power Plants: Some power stations are blending hydrogen with natural gas to cut emissions.
The Science Behind the Breakthrough
What Are Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs)?
- MOFs are like tiny scaffolds made of metal and organic molecules. They can be customized to hold different atoms in just the right places.
- In this case, MOFs helped the researchers add boron and phosphorus to cobalt phosphide, making the catalyst more effective and cheaper.
How Efficient Is the New Catalyst?
- The new catalyst is twice as efficient as the previous best, producing 0.528% hydrogen per gram of oxide, compared to 0.25% for older materials.
- It remains stable for over 100 hours in harsh, alkaline environments—crucial for industrial use.
Researchers Demonstrate Advanced Cooling in Data Centers to Cut Emissions 15–21%
FAQs About Hydrogen Fuel at Half the Cost
1. What is a catalyst, and why is it important in hydrogen production?
A catalyst speeds up chemical reactions without being used up itself. In hydrogen production, it makes splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen much faster and more efficient.
2. How much cheaper will hydrogen fuel be with this new catalyst?
Early estimates suggest production costs could drop by up to 50%, making green hydrogen competitive with fossil fuels.
3. Is this technology ready for commercial use?
The catalyst has shown great results in lab and pilot tests, and researchers are working to scale it up for industrial use.
4. Will this help fight climate change?
Yes! Cheaper, cleaner hydrogen can replace fossil fuels in many industries, reducing carbon emissions and improving air quality.
5. Are there other similar breakthroughs?
Yes. South Korean teams have also developed iron oxide-based catalysts that double the efficiency of thermochemical hydrogen production, and systems that turn plastic waste into hydrogen using sunlight.
What’s Next for Hydrogen Fuel?
The South Korean breakthrough is just the beginning. As more research teams around the world build on these findings, expect to see:
- More Affordable Green Hydrogen: Not just in labs, but in cars, buses, trains, and factories everywhere.
- Cleaner Cities: Less smog and pollution as hydrogen replaces fossil fuels.
- New Jobs and Industries: From catalyst manufacturing to hydrogen refueling stations.