Scientists Uncover Rare Brain Activity: What if the secret to understanding human consciousness—our ability to think, feel, dream, and be aware—was hidden deep inside the brain, waiting to be discovered? Scientists uncover rare brain activity that could unlock new frontiers in human consciousness is not just a headline; it’s a groundbreaking leap in neuroscience that could change how we see ourselves, treat brain disorders, and even design smarter machines.
For decades, consciousness has been one of science’s greatest mysteries. Where does it come from? How does the brain create our sense of self and awareness? Recent research, powered by advanced brain imaging and global collaboration, is finally providing some answers—and the results may surprise you.
Scientists Uncover Rare Brain Activity
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Discovery | Rare brain activity patterns linked to consciousness found in deep brain regions and sensory cortex |
| Major Brain Areas | Sensory cortex (back of brain), midbrain reticular formation, central thalamus, inferior frontal cortex |
| Techniques Used | fMRI, MEG, intracranial EEG, large-scale collaborative studies (250+ participants) |
| Theories Tested | Integrated Information Theory (IIT), Global Neuronal Workspace Theory (GNWT) |
| Clinical Impact | Potential for new treatments for coma, epilepsy, ADHD, and attention disorders |
| Official Resource | Allen Institute for Brain Science |
Scientists uncover rare brain activity that could unlock new frontiers in human consciousness is more than a scientific breakthrough—it’s a window into what makes us human. By discovering how sensory and deep brain regions work together to create awareness, researchers are paving the way for new medical treatments, smarter technology, and a deeper understanding of ourselves. The journey to fully unravel consciousness is just beginning, but these discoveries are a giant leap forward.
What Is Consciousness? Why Does It Matter?
Consciousness is what allows you to see, hear, dream, imagine, feel pain or joy, and be aware of yourself and the world. It’s at the core of human experience. But for a long time, no one knew exactly where in the brain consciousness “lives” or how it works.
Understanding consciousness isn’t just a philosophical puzzle. It has real-world importance:
- Medical care: Diagnosing and treating coma, epilepsy, and attention disorders.
- Technology: Building smarter, more human-like artificial intelligence.
- Ethics: Deciding which beings (animals, AI, even fetuses) might be conscious.
How Did Scientists Uncover Rare Brain Activity?
The Big Experiment
A global team of neuroscientists set out to answer three big questions:
- Where in the brain does conscious experience happen?
- How is it maintained over time?
- How do different brain regions work together to create consciousness?
To find out, they recorded electrical, magnetic, and blood flow activity in the brains of over 250 people across 12 labs in the US, Europe, and China. Participants looked at images, listened to sounds, and performed tasks while their brains were scanned using:
- fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging)
- MEG (magnetoencephalography)
- Intracranial EEG (for epilepsy patients)
This massive project tested two of the most famous theories of consciousness:
- Integrated Information Theory (IIT): Consciousness arises when information in the brain is highly connected and unified.
- Global Neuronal Workspace Theory (GNWT): Consciousness happens when important information is broadcast across a network of brain areas, especially the frontal cortex.
What Did They Find?
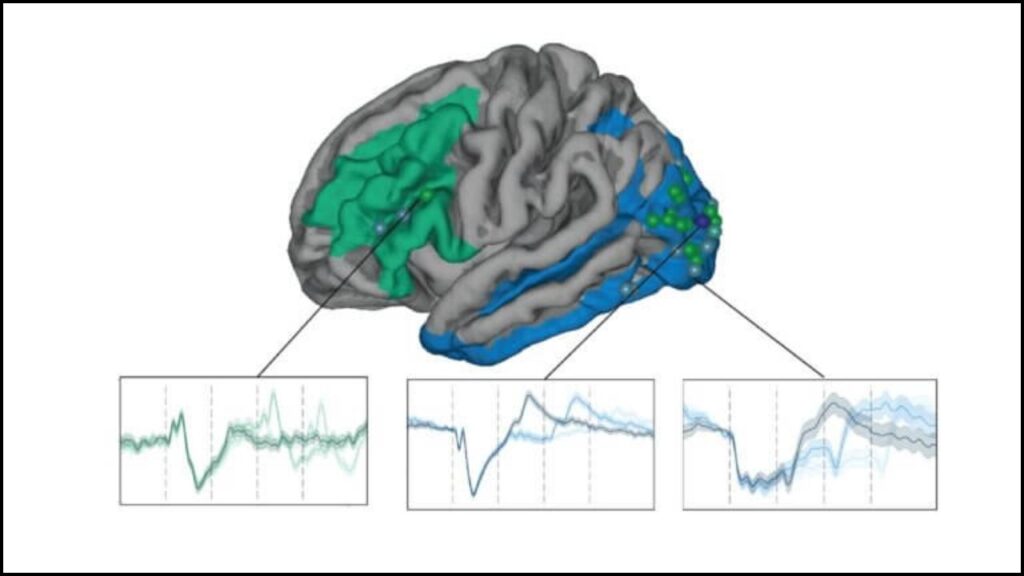
Surprisingly, consciousness may not come from the brain’s “smartest” parts (the frontal lobes). Instead, it seems to start in the sensory areas at the back of the brain, which process what we see and hear.
But that’s not all. When people focused their attention, deep brain regions—especially the midbrain reticular formation and the central thalamus—lit up, no matter which sense was being used (sight, sound, taste, or touch). These regions act like a switchboard, linking all senses to our conscious awareness.
“We were expecting to find activity on shared networks, but when we saw all the senses light up the same central brain regions while a test subject was focusing, it was really astonishing.”
— Aya Khalaf, Yale School of Medicine
Breaking Down the Science: How Consciousness Works in the Brain
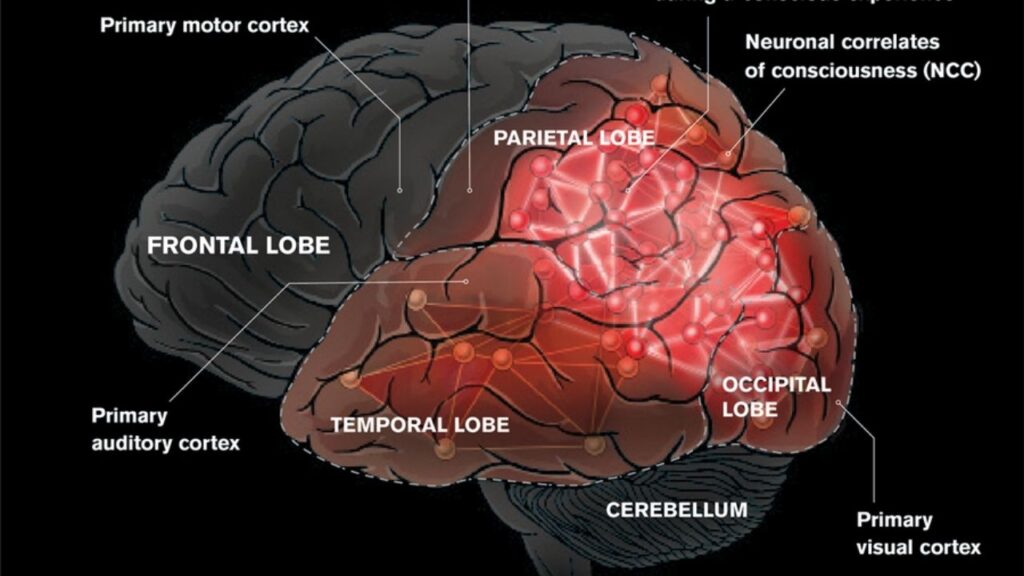
1. The Sensory Cortex: Where Awareness Begins
- Located at the back of the brain.
- Processes visual, auditory, and other sensory information.
- Shows sustained activity when we are consciously aware of something.
2. Deep Brain Regions: The Gatekeepers
- Midbrain Reticular Formation & Central Thalamus:
- Activated by all senses when attention is focused.
- Act as a hub, linking sensory input to conscious awareness.
- Crucial for sleep-wake cycles, attention, and arousal.
3. The Frontal Cortex: The Spotlight Operator
- Involved in higher-order thinking and decision-making.
- Works with deep brain regions to “broadcast” important information throughout the brain.
- Helps maintain and direct conscious experience.
4. Theories Put to the Test
- IIT: Predicts that consciousness is about how connected and unified information is in the brain.
- GNWT: Predicts that consciousness happens when information is widely shared across the brain, especially in the frontal cortex.
- Result: Neither theory is perfect. Consciousness involves both sustained activity in sensory regions and complex communication between the front and back of the brain.
Practical Advice: What Does This Mean for You?
For Patients and Families
- Hope for New Treatments:
Understanding these rare brain activity patterns could lead to better therapies for coma, epilepsy, ADHD, and attention disorders. Doctors may be able to use brain stimulation to restore or improve consciousness in the future.
For Professionals
- Better Diagnosis:
New brain imaging techniques could help doctors more accurately diagnose disorders of consciousness. - Targeted Therapies:
Medications or brain stimulation could be designed to target the deep brain regions that control attention and awareness.
For Everyone
- Ethical Questions:
As we learn more, we may need to rethink which beings are considered conscious and deserve rights—animals, AI, even unborn babies. - Personal Growth:
Understanding how attention and awareness work can help you focus better and be more mindful in daily life.
Clear Examples: How This Research Changes What We Know
- Example 1:
A person in a coma may have activity in their deep brain regions but not in their sensory cortex. By stimulating the right areas, doctors might help them regain consciousness. - Example 2:
Kids with ADHD might have trouble focusing because these deep brain regions aren’t working properly. New treatments could help them pay attention better. - Example 3:
When you suddenly notice a sound or a flash of light, your midbrain reticular formation and central thalamus “light up,” helping you become aware of the change.
Scientists Crack 500-Million-Year-Old Code That Controls the Immune System
Ocean-Like Fluids Reveal Tiny Porous Particles Sink Faster: A Surprising Discovery in Marine Science
FAQs About Scientists Uncover Rare Brain Activity
What is consciousness in simple terms?
Consciousness is your awareness of yourself and the world around you. It lets you think, feel, dream, and experience life.
Where in the brain does consciousness happen?
Recent studies show that consciousness mainly involves the sensory cortex at the back of the brain and deep brain regions like the midbrain reticular formation and central thalamus.
How do scientists study consciousness?
They use brain imaging tools like fMRI, MEG, and EEG to measure brain activity while people perform tasks or respond to stimuli.
Why does this research matter?
It could lead to better treatments for brain disorders, help us build more human-like AI, and answer big questions about who or what is conscious.
What are the main theories of consciousness?
- Integrated Information Theory (IIT): Consciousness comes from highly connected information in the brain.
- Global Neuronal Workspace Theory (GNWT): Consciousness happens when information is broadcast across many brain areas.
Can this research help people with brain injuries?
Yes! By understanding which brain regions control consciousness, doctors can develop new ways to diagnose and treat patients with brain injuries or disorders.