Universe’s Basic Building Blocks Exploded Into Existence: Have you ever gazed up at the night sky and wondered, “Where did all this come from?” The answer, according to physicists, begins with a mind-bending event called the Big Bang. This isn’t a Hollywood explosion—it’s a scientific model that explains how the universe, and all its basic building blocks, started from an unimaginably tiny, hot, and dense point about 13.8 billion years ago. Today, the Big Bang Theory is the most widely accepted explanation for the origin of the universe, and it’s supported by a mountain of evidence—from the glow of the cosmic microwave background to the way galaxies are racing away from each other.
The journey from that initial spark to the vast cosmos we see today is a story of transformation, discovery, and mystery. As a physicist, I’ve spent years studying these cosmic origins, and I’m excited to share how the universe’s basic building blocks—matter, energy, and even the mysterious dark stuff—came to be. Whether you’re a curious 10-year-old or a professional in the field, let’s explore this cosmic adventure together.
Universe’s Basic Building Blocks Exploded Into Existence
| Topic/Keyword | Key Data/Stats/Insight | Career/Professional Info |
|---|---|---|
| Big Bang Theory | Universe began 13.8 billion years ago | Most credible scientific explanation |
| Cosmic Microwave Background | Remnant glow from early universe (about 2.7 Kelvin) | Evidence for Big Bang |
| Nucleosynthesis | First nuclei formed within minutes | Source of light elements (H, He, Li) |
| Recombination | Atoms formed at ~380,000 years | Universe became transparent |
| Dark Matter & Dark Energy | Make up ~95% of universe’s mass-energy | Still major mysteries in physics |
The story of the universe’s basic building blocks is one of the most fascinating journeys in science. From a tiny, hot point to the vast cosmos filled with stars, galaxies, and planets, the Big Bang Theory provides the best explanation we have for how it all began. By studying the cosmic microwave background, the expansion of galaxies, and the behavior of particles, physicists continue to uncover new insights into the universe’s origins and evolution.
What Is the Big Bang Theory?
The Big Bang Theory is the leading scientific explanation for the origin of the universe. It describes how everything—space, time, matter, and energy—began from a single point of infinite density and temperature, then rapidly expanded to form the cosmos as we know it today. This model is supported by observations like the cosmic microwave background radiation and the redshift of distant galaxies, which show that the universe is still expanding.
A common misconception is that the Big Bang was an explosion in space. Actually, it was the rapid expansion of space itself, everywhere at once. Imagine inflating a balloon: as you blow it up, every point on the balloon’s surface moves away from every other point. The universe works in a similar way.
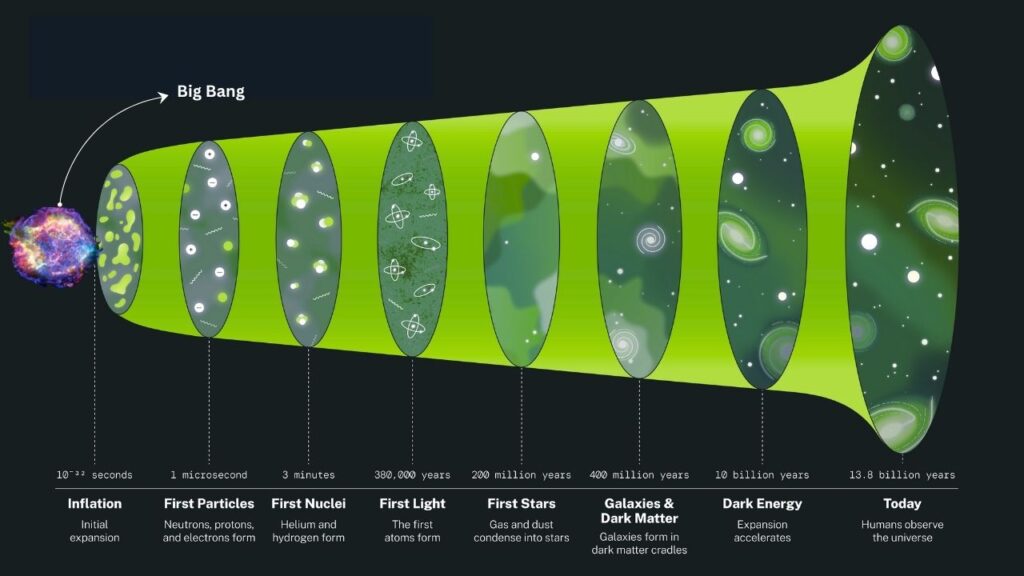
The Cosmic Timeline: From Singularity to Stars
Let’s break down the universe’s history into easy-to-follow steps:
1. The Beginning: A Hot, Dense Point
About 13.8 billion years ago, the universe was smaller than a grain of sand, but unimaginably hot and dense. This state is called a singularity. At this point, the laws of physics as we know them didn’t apply. As the universe began to expand, it cooled and the first particles formed.
2. The First Particles: Quarks, Electrons, and More
Within the first fraction of a second, the universe was a soup of quarks, electrons, and other fundamental particles. As it cooled, quarks combined to form protons and neutrons, the building blocks of atomic nuclei.
3. Big Bang Nucleosynthesis: Making the First Elements
A few minutes after the Big Bang, the temperature dropped enough for protons and neutrons to fuse, creating the first atomic nuclei—mostly hydrogen and helium, with a tiny bit of lithium. This process is called Big Bang nucleosynthesis.
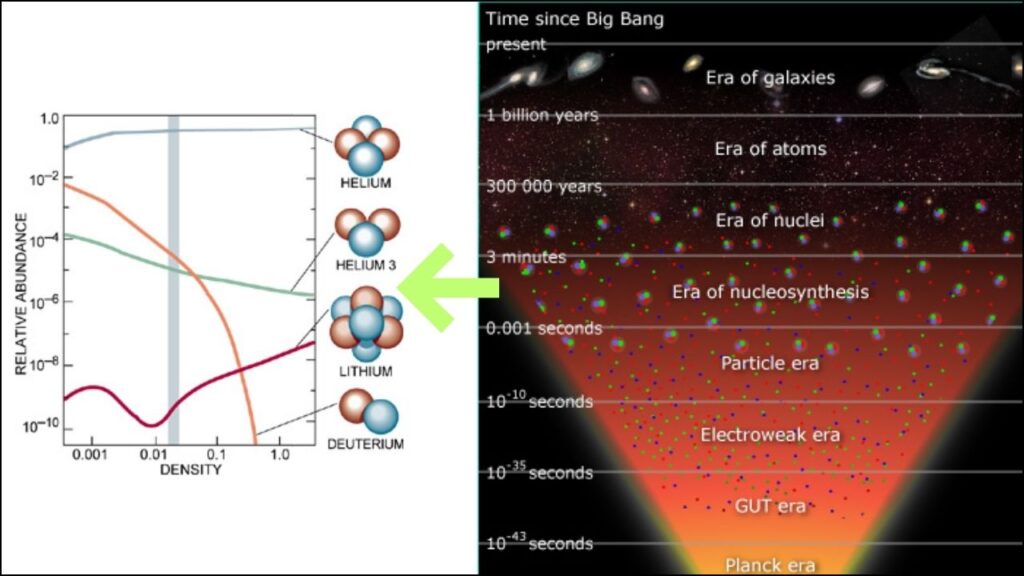
4. Recombination: Atoms Form and Light Shines
About 380,000 years after the Big Bang, the universe cooled enough for electrons to combine with nuclei to form the first stable atoms—mostly hydrogen. This event, called recombination, made the universe transparent for the first time. The light released at this moment is still visible today as the cosmic microwave background.
5. The Birth of Stars and Galaxies
Over millions and billions of years, gravity pulled atoms together to form clouds, which collapsed to form the first stars and galaxies. Inside stars, nuclear fusion created heavier elements like carbon, oxygen, and iron. When stars died in supernova explosions, they scattered these elements into space, seeding the universe with the ingredients for planets and life.
The Universe’s Building Blocks: What Are They?
The universe is made up of several key ingredients:
- Normal Matter: The stuff we can see—atoms, stars, planets, and people. This makes up only about 5% of the universe.
- Dark Matter: An invisible substance that doesn’t emit, absorb, or reflect light, but whose gravity holds galaxies together. It makes up about 27% of the universe.
- Dark Energy: A mysterious force causing the universe’s expansion to accelerate. It accounts for about 68% of the universe.

Practical Examples and Fun Facts
- Cosmic Microwave Background: You can think of this as the “afterglow” of the Big Bang. It’s a faint glow of light that fills the universe and is detected by radio telescopes.
- Redshift: When astronomers look at distant galaxies, the light is shifted toward the red end of the spectrum. This shows that the universe is expanding, just as the Big Bang Theory predicts.
- Element Formation: The hydrogen in your body was made in the Big Bang. The carbon, oxygen, and iron were forged in stars and scattered by supernovae.
How Do We Know All This? The Evidence
Scientists use several powerful tools to study the universe’s origins:
- Telescopes: Observe distant galaxies and the cosmic microwave background.
- Particle Accelerators: Recreate conditions from the early universe to study how particles behave.
- Mathematical Models: Use Einstein’s theory of relativity and quantum physics to predict how the universe evolved.
Step-by-Step Guide: How the Universe’s Building Blocks Came to Be
- The Big Bang: Everything starts from a hot, dense point.
- Expansion and Cooling: The universe expands and cools, forming the first particles.
- Nucleosynthesis: Protons and neutrons fuse to make the first atomic nuclei.
- Recombination: Electrons join nuclei to form atoms; the universe becomes transparent.
- Star and Galaxy Formation: Gravity pulls matter together to form stars and galaxies.
- Element Creation: Stars create heavier elements, which are scattered by supernovae.
- Planet and Life Formation: These elements become the building blocks for planets and life.
Researchers Discover New Method to Stabilize Ultra-Thin Materials for Next-Gen Electronics
Johnson & Johnson Reveals Smart Contact Lenses That Push Optical and Material Science Limits
Scientists Develop Breakthrough Copper Composite With Superior Strength and Conductivity
FAQs About Universe’s Basic Building Blocks Exploded Into Existence
Q: What caused the Big Bang?
A: We don’t know for sure. The Big Bang Theory describes what happened after the universe began, but not what caused it.
Q: Is the Big Bang Theory proven?
A: It’s the most widely accepted scientific explanation, supported by strong evidence like the cosmic microwave background and the expansion of the universe.
Q: What is dark matter?
A: Dark matter is an invisible substance that makes up about 27% of the universe. We detect it through its gravitational effects on galaxies.
Q: Will the universe keep expanding forever?
A: Observations suggest the universe’s expansion is accelerating due to dark energy, so it will likely keep expanding.
Q: How old is the universe?
A: The universe is about 13.8 billion years old.