Nanotech-Enhanced Fertilizer: Nanotech-enhanced fertilizer is rapidly gaining attention as a breakthrough in modern agriculture. By harnessing the power of nanotechnology, these fertilizers offer a smarter way to nourish crops, increase yields, and protect our environment. Whether you’re a student, a home gardener, or a professional farmer, understanding how nano-fertilizers work and their benefits can help you appreciate this innovative approach to sustainable farming.
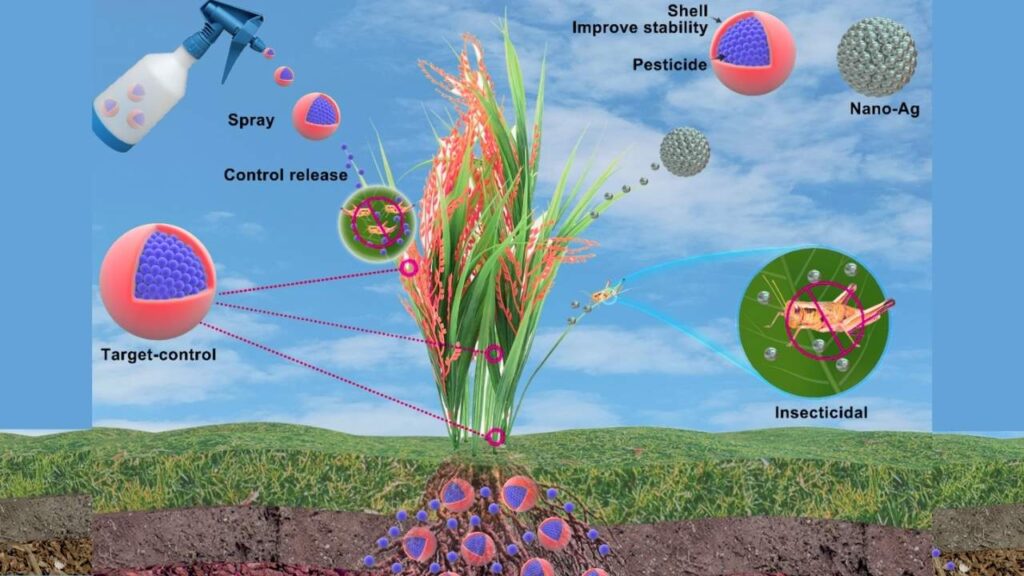
Table of Contents
What Are Nanotech-Enhanced Fertilizers?
Nanotech-enhanced fertilizers, commonly known as nano-fertilizers, are fertilizers engineered at the nanoscale—particles so tiny they measure less than 100 nanometers (about 1/1000th the width of a human hair). This incredibly small size allows nutrients to be delivered more efficiently to plants.
Unlike conventional fertilizers, which often release nutrients quickly and in large amounts, nano-fertilizers are designed to release nutrients slowly and precisely, matching the plant’s needs over time. This precision reduces nutrient losses to the environment and increases nutrient uptake by plants.
Why Does Size Matter?
The nanoscale size of these fertilizers increases their surface area dramatically. This means:
- Nutrients are more reactive and accessible to plants.
- They can penetrate plant tissues more easily.
- They adhere better to soil particles and roots, minimizing losses.
This technology represents a significant leap forward in how we feed crops.
Nanotech-Enhanced Fertilizer
| Feature | Details & Data |
|---|---|
| Yield Increase (Wheat) | 20–55% higher with nano-fertilizers compared to conventional fertilizers |
| Yield Increase (Maize, Rice, Potato) | Maize: 20–40%; Rice: 13–25%; Potato: 20–35% |
| Fertilizer Use Reduction | Up to 50% less fertilizer needed while maintaining or increasing yields |
| Nutrient Release Time | Nano-fertilizers: 40–50 days; Conventional: 4–10 days |
| Market Value (2024) | USD 1.1 billion for cereals & grains segment; 13.8% CAGR expected through 2034 |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced nutrient runoff, lower water and soil pollution, improved sustainability |
| Professional Opportunity | Increased profitability for farmers, new roles in precision agriculture, R&D, and sustainable farming |
| Official Resource | Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) |
Nanotech-enhanced fertilizers represent a promising leap forward in agricultural science. By delivering nutrients more efficiently and reducing environmental harm, they offer a sustainable path to feeding the world’s growing population. With proven yield improvements, cost savings, and ecological benefits, nano-fertilizers are poised to become a key tool in modern farming. As research advances and adoption spreads, they will help build a greener, more productive future for agriculture.
How Do Nano-Fertilizers Work?
The Science Behind Nano-Fertilizers
Nano-fertilizers work by using nanoparticles to deliver essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, iron, and zinc in a form that plants can absorb more efficiently. These nanoparticles can either be:
- Nano-sized nutrient particles themselves, or
- Nutrients encapsulated in nano-carriers that release them slowly.
This slow and controlled release ensures that plants receive nutrients steadily over weeks, reducing the risk of nutrient loss through leaching or volatilization.
Controlled Nutrient Release and Targeting
One of the most exciting aspects of nano-fertilizers is their ability to release nutrients in response to environmental triggers such as soil moisture, pH, or root exudates. This responsiveness means that nutrients are available exactly when plants need them most.
Additionally, nano-fertilizers can be engineered to target specific parts of the plant, such as roots or leaves, improving uptake efficiency.
Environmental Benefits of Nano-Fertilizers
Reducing Nutrient Runoff and Pollution
Traditional fertilizers often lead to nutrient runoff, where excess nitrogen and phosphorus wash into nearby water bodies. This runoff causes eutrophication, leading to harmful algal blooms and dead zones in aquatic ecosystems.
Nano-fertilizers reduce this risk by:
- Minimizing excess nutrient application due to higher efficiency.
- Ensuring slow, steady nutrient release, reducing the chance of leaching.
- Improving nutrient retention in soil, which supports healthier plants and soil microbes.
Protecting Soil Health
Overuse of chemical fertilizers can degrade soil quality by disrupting microbial communities and causing acidification or salinization. Nano-fertilizers, by requiring lower application rates and releasing nutrients gradually, help maintain soil balance and promote long-term fertility.
Water Conservation
Because nano-fertilizers improve nutrient uptake, plants use water more efficiently. This means less irrigation is needed, which is critical in regions facing water scarcity.
Real-World Impact: Data and Examples
Crop Yield Improvements Across Major Crops
Studies have demonstrated significant yield improvements with nano-fertilizers:
- Wheat: Yield increases range from 20% to 55%, depending on soil and climate conditions.
- Maize: Gains of 20% to 40% have been recorded.
- Rice: Yield improvements between 13% and 25%.
- Potatoes: Increases of 20% to 35%.
These improvements translate into more food produced per hectare, helping address global food security challenges.
Economic Benefits for Farmers
Farmers benefit economically from nano-fertilizers by:
- Reducing fertilizer costs due to lower required quantities.
- Increasing crop quality and quantity, leading to higher market prices.
- Lowering environmental compliance costs as pollution decreases.
Moreover, nano-fertilizers are compatible with precision agriculture technologies, enabling farmers to optimize inputs further.
Types of Nano-Fertilizers and Their Applications
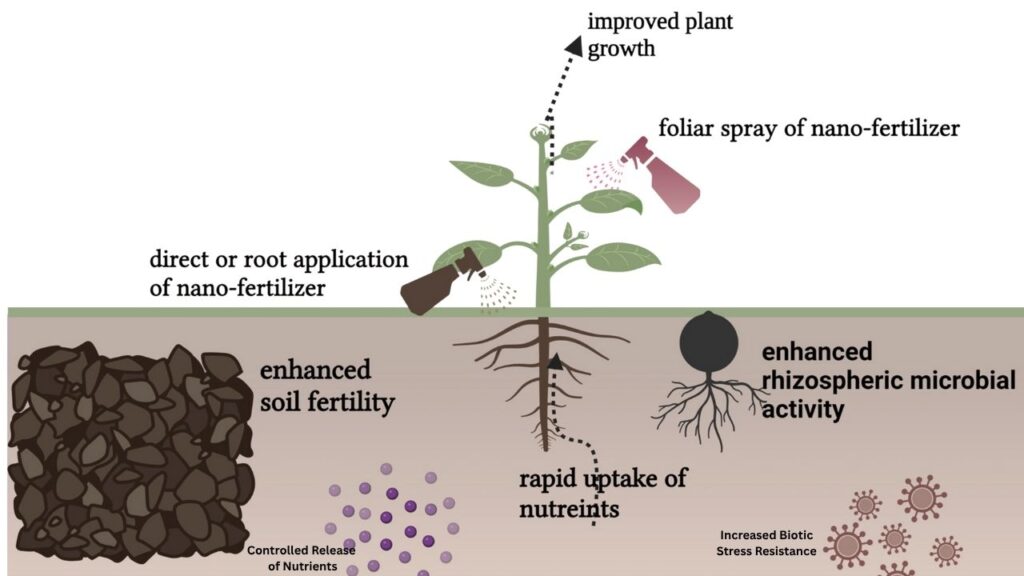
Common Varieties
- Nano-NPK Fertilizers: Contain nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in nanoparticle form.
- Nano-Urea: A nano-form of nitrogen fertilizer that releases nitrogen slowly.
- Nano-Micronutrients: Include essential trace elements like iron, zinc, and copper.
- Nano-Encapsulated Fertilizers: Nutrients enclosed in nanocarriers for controlled release.
- Nano-Zeolite Composites: Natural minerals combined with nano-nutrients to improve nutrient retention.
Application Methods
- Soil Application: Mixed with soil before or during planting.
- Foliar Spray: Applied directly to leaves for rapid absorption.
- Seed Treatment: Coated on seeds to enhance germination and early growth.
Each method has specific advantages depending on the crop and growth stage.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using Nano-Fertilizers
1. Assess Your Crop and Soil Needs
Conduct soil tests to identify nutrient deficiencies and select a nano-fertilizer formulation tailored to your crop’s requirements.
2. Select a Quality Product
Choose nano-fertilizers from reputable manufacturers that comply with safety and quality standards.
3. Follow Recommended Dosages
Use the manufacturer’s guidelines carefully. Nano-fertilizers are potent, so over-application can be wasteful or harmful.
4. Apply at the Right Growth Stage
Timing is crucial. Apply nano-fertilizers during critical growth phases such as seedling, vegetative, or flowering stages for maximum benefit.
5. Monitor Crop Response
Observe plant growth, leaf color, and overall health. Adjust fertilizer application based on observations and further soil testing.
6. Practice Safety and Environmental Care
Wear protective gear during application and store fertilizers safely. Avoid contamination of water sources.
7. Keep Records and Stay Updated
Maintain records of fertilizer use and crop performance. Stay informed about new research and technologies in nano-fertilizer development.
New Quantum Amplifier Could Revolutionize Secure Communications and Signal Detection
Is the Universe a Giant Computer? New Research Offers Clues About Quantum Gravity
New Quantum State Discovery Set to Revolutionize Material Science Worldwide
FAQs About Nanotech-Enhanced Fertilizer
Are nano-fertilizers safe for humans and the environment?
Current research indicates that nano-fertilizers are safe when used according to guidelines. However, ongoing studies aim to better understand their long-term environmental impact.
Can nano-fertilizers completely replace traditional fertilizers?
Nano-fertilizers are best used as part of an integrated nutrient management system, combining organic and conventional fertilizers to optimize crop nutrition.
How much can farmers save by using nano-fertilizers?
Farmers can reduce fertilizer use by up to 50%, which translates into significant cost savings, especially when combined with increased yields.
Are nano-fertilizers widely available?
While adoption is growing globally, availability varies by region. Many countries are investing in research and production to expand access.
What crops benefit most from nano-fertilizers?
Crops like wheat, maize, rice, and potatoes have shown substantial yield improvements, but research is expanding to fruits, vegetables, and cash crops.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Challenges
- Regulatory Frameworks: Governments are still developing policies to regulate nanomaterials in agriculture.
- Cost and Accessibility: Production costs remain relatively high, limiting access for smallholder farmers.
- Research Needs: More long-term studies are necessary to fully assess environmental and health impacts.
Future Prospects
With ongoing innovation, nano-fertilizers are expected to become more affordable and widely adopted. Integration with digital farming tools will further enhance precision agriculture, making farming more sustainable and productive.