The world of blockchain, AI, and Web3 is full of opportunity—but also danger. Right now, scammers are creating fake AI companies to trick Web3 developers into downloading malware that steals cryptocurrency and sensitive data. This isn’t just spam or phishing. These attacks are sophisticated, believable, and designed to bypass your instincts. Let’s break down what’s happening, why you’re a target, and—most importantly—how you can stay safe.

If you work in Web3, you’re likely used to exciting job offers, cool new tools, and opportunities to test the latest apps. But what if that “next big thing” is actually a trap? Cybercriminals are building entire fake companies, complete with professional websites, whitepapers, GitHub pages, and even fake teams on LinkedIn and Notion. They’re using AI to generate blogs, press releases, and social media posts that look just like the real thing. Their goal? To trick you into trusting them, downloading their “app,” and handing over your crypto—or worse, your entire digital life.
This is not just a nuisance. It’s a global, organized cybercrime wave, targeting both Windows and Mac users, and evolving faster than many traditional security measures can keep up. Let’s dive deep into how these scams work, who’s behind them, and the practical steps you can take to protect yourself and your assets.
Table of Contents
Fake AI Platforms Are Targeting Web3 Developers
| Topic | Key Facts & Stats | Professional Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Attack Method | Fake AI/Web3 startups, social media scams, job offers, “test our app” lures. | Targets devs, freelancers, crypto pros. |
| Malware Used | Info-stealers like Realst, Atomic Stealer, SparkKitty; targets wallets, browsers, credentials. | Loss of crypto, data, reputation damage. |
| Social Engineering | AI-generated content, fake teams, spoofed social media, fabricated partnerships. | Harder to detect, erodes trust. |
| Platforms Targeted | Windows, macOS; attacks via X, Telegram, LinkedIn, job boards, app stores. | Cross-platform risk. |
| Global Reach | Victims in multiple countries; scam infrastructure hosted globally. | No one is immune. |
| Defense Tips | Verify first, avoid unsolicited downloads, use hardware wallets, check domains, report scams. | Essential for career safety. |
The rise of fake AI platforms targeting Web3 developers is a serious and evolving threat. Scammers are using cutting-edge social engineering, AI-generated content, and professional branding to bypass your defenses and steal your crypto. But with vigilance, skepticism, and smart security habits, you can protect yourself and your digital assets.
How the Scam Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
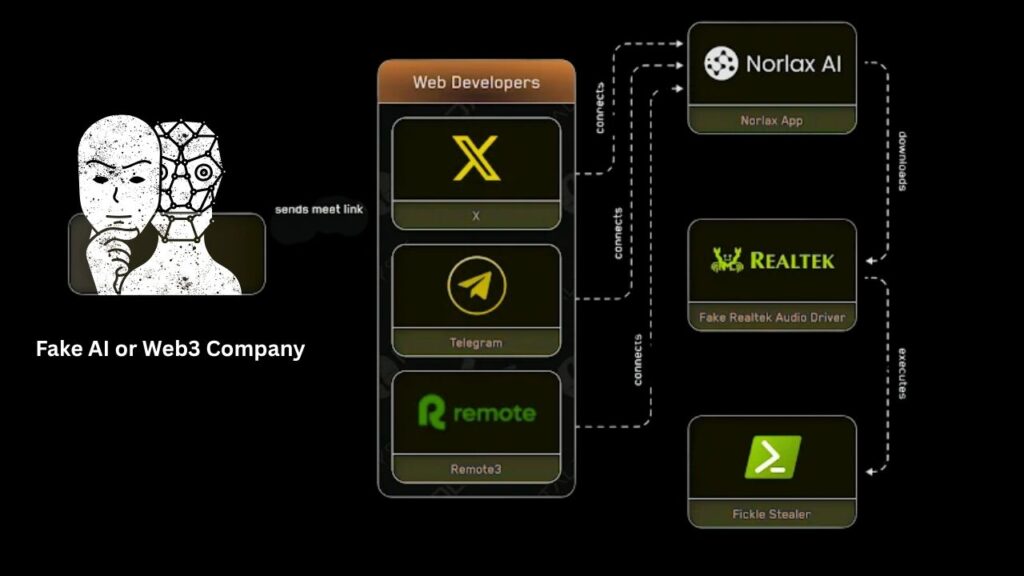
Step 1: Building the Illusion
Scammers create a fake AI or Web3 company—complete with a professional website, whitepapers, GitHub repos, and fake team profiles on LinkedIn and Notion. They might call it something like “Norlax AI,” “Luma Dream AI,” or even use names that sound similar to real, popular platforms. They go so far as to create fake press releases, product updates, and even “verified” social media accounts. All of this is designed to look exactly like a legitimate, innovative startup.
Step 2: The Bait—Job Offers and App Testing
Once the fake company looks real, scammers reach out to Web3 developers on X, Telegram, LinkedIn, Discord, or specialized job boards. The message could be a job offer, a request to review your portfolio, or an invitation to “test” a new game, wallet, or AI tool. Sometimes, they promise free crypto or early access to an exciting project. The key? The offer is always too good to pass up.
Step 3: The Trap—Download the Malware
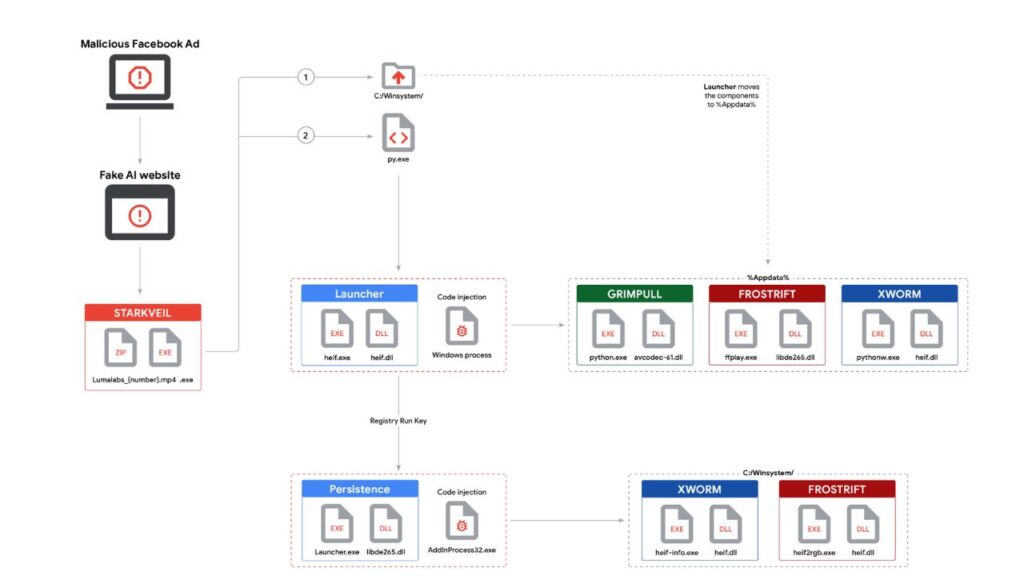
If you take the bait, you’ll be asked to download an app—maybe a new “meeting” platform, a “crypto wallet,” or an “AI video generator.” These apps have names like “Meeten,” “Meetio,” or something trendy and techy. The download link might come directly from the fake company’s website, or through a message. Once installed, the malware quietly steals your data—crypto wallet credentials, browser cookies, passwords, and even your photos (looking for screenshots of seed phrases).
Step 4: The Payoff—Your Crypto and Data Are Stolen
Within seconds or minutes, the malware is working. It can drain your crypto wallets, steal your logins, and grab sensitive files. Some malware, like Atomic Stealer or SparkKitty, is designed to work on both Windows and Mac, and some versions have even slipped into official app stores. The attackers can then use your information to steal your funds, impersonate you, or sell your data on the dark web.
Who Is Behind These Attacks?
These are not random hackers. Organized cybercrime groups—sometimes with ties to nation-states—are behind these campaigns. For example, groups like EncryptHub (aka LARVA-208, Water Gamayun) have a history of ransomware but have now switched to stealing crypto via these fake AI platforms. Other groups, like UNC6032, are linked to Vietnam and use fake “AI video generator” websites to spread their malware through social media ads. There are even signs that North Korean-linked actors may be involved in some campaigns, given their well-known focus on crypto theft.
These groups use AI to automate and scale their attacks, making the scams harder to spot. They constantly change their tactics, branding, and infrastructure to avoid detection. This is a professional, global criminal operation—not a one-off scam.
Why Are Web3 Developers Targeted?
If you’re a Web3 developer, freelancer, or crypto professional, you’re a prime target. Here’s why:
- You have access to crypto wallets and smart contracts—often with significant value.
- You work independently or across multiple projects, so there’s no company IT department to protect you.
- You’re used to testing new tools and apps, making you more likely to download something “cool.”
- You’re active on social media and job boards, where scammers can easily find you.
- The hype around AI and Web3 makes you more likely to trust something that looks innovative.
In short: You have what they want (crypto), you’re easy to find, and you might be more trusting than the average person.
Real-World Examples
- Norlax AI: A fake platform that mimics real AI startups, luring developers with job offers and then infecting them with malware.
- Luma Dream AI: A fake text-to-video tool that delivers malware via a download button, no matter what the user does.
- Meetio/Meeten: A fake meeting app that steals credentials and crypto wallet info from both Windows and macOS users.
- SparkKitty: Malware found on official app stores, disguised as TikTok mods or crypto apps, scanning your photos for seed phrases.
- SoraAI.lnk: A malicious shortcut file distributed via GitHub, stealing browser cookies, passwords, and system info.
These are just a few examples. New brands and fake companies pop up every week, making it a moving target for security teams and users alike.
How to Protect Yourself: A Practical Guide
Here’s what you can do—right now—to reduce your risk and keep your crypto safe.
1. Verify Before You Trust
If you get a job offer, project invite, or app-testing opportunity from a company you’ve never heard of, do your homework. Check their website, social media, GitHub, and LinkedIn. Look for real people, real products, and a real history. If something feels off—trust your gut.
2. Never Download Unsolicited Apps
If someone asks you to download a new app to join a call, test a product, or get “free crypto,” be suspicious. Stick to well-known platforms like Zoom, Google Meet, Discord, or official app stores for meetings and downloads. If in doubt, don’t click.
3. Use Hardware Wallets for Crypto
For your most valuable crypto, use a hardware wallet like Ledger or Trezor. These are much harder for malware to compromise than browser or software wallets. Seed phrases should never be stored digitally—write them down and keep them safe.
4. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Use MFA everywhere you can—especially for email, crypto exchanges, and social media. This adds an extra layer of security if your password is stolen.
5. Check the Domain and Brand History
Look up the website’s domain registration. If it was created very recently, that’s a red flag. Search for news, reviews, or mentions of the brand—real companies have a footprint beyond their own website.
6. Keep Your Software Updated
Make sure your operating system, browser, and security software are always up to date. Many scams exploit known vulnerabilities that have already been patched.
7. Report Suspicious Activity
If you spot a scam, report it to the platform (X, Telegram, LinkedIn, etc.) and warn your community. Help others avoid the same trap.
8. Educate Yourself and Your Team
Stay informed about the latest scams and share what you learn. Awareness is your best defense.
WormGPT Is Back — And Its New AI Variants Are More Dangerous Than Ever
Mamona Ransomware: The Silent Offline Threat Everyone Should Take Seriously
GPUHammer Exploit Targets NVIDIA GPUs, Threatens AI Model Integrity With Memory Flaw
FAQs About Fake AI Platforms Are Targeting Web3 Developers
Q: What should I do if I downloaded a suspicious file?
A: Disconnect from the internet, scan your device with antivirus software, and change all your passwords—especially for crypto wallets and email. Consider transferring funds to a new, clean wallet.
Q: Can these scams affect Mac users?
A: Yes. Malware like Atomic Stealer and SparkKitty target both Windows and macOS users. No platform is immune.
Q: How do I know if a job offer is real?
A: Research the company. Look for a real team, verifiable products, and a history of activity. If the offer comes out of the blue, be extra careful.
Q: Are there tools to check if a website is malicious?
A: Services like VirusTotal can scan URLs for malware. Always double-check before clicking.
Q: Why are Web3 developers specifically targeted?
A: They often have access to valuable crypto assets, work independently, and are used to testing new tools—making them attractive and accessible targets.