In the global journey to make renewable energy reliable and accessible every hour of the day, Google has joined forces with Italian startup Energy Dome to pioneer an extraordinary new technology: the CO₂ battery. This innovation promises to transform energy storage and help power a cleaner, more sustainable future.
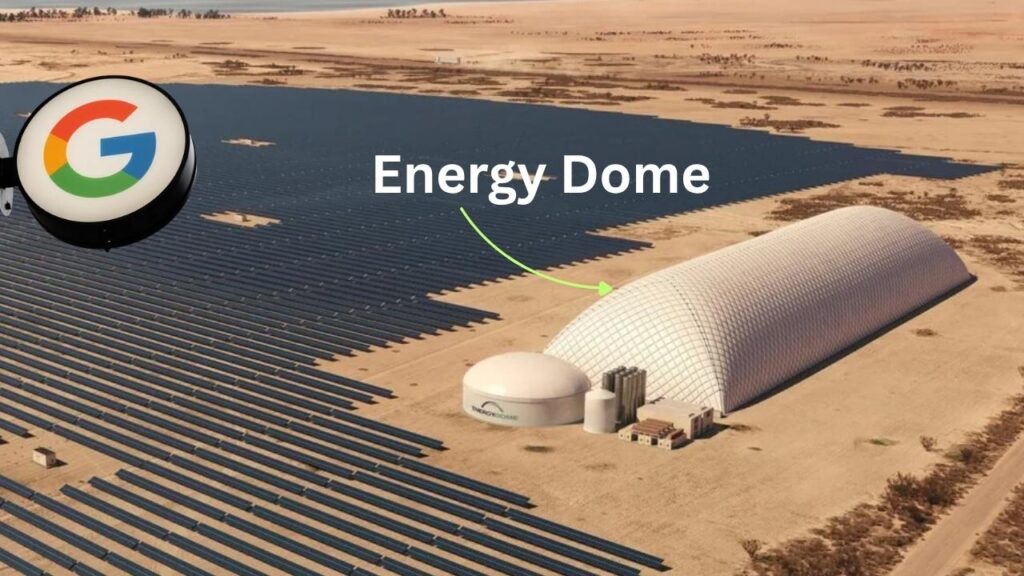

Renewable energy sources like solar and wind are brilliant but unpredictable. Sometimes the sun shines brightly, and the wind blows strong; other times, energy production dips. The challenge is how to store surplus clean energy when it’s abundant and release it efficiently when demand rises or renewables are quiet. Google’s CO₂ battery offers a powerful solution, providing long-duration energy storage (LDES) for 8 to 24 hours—much longer than most current batteries—bridging the supply and demand gap sustainably and affordably.
Table of Contents
Google’s CO₂ Battery Could Revolutionize Green Energy
| Key Highlights | |
|---|---|
| Technology | CO₂ battery stores energy by compressing and liquefying CO₂ gas in a closed-loop cycle. |
| Energy Storage Duration | Can dispatch electricity continuously for 8 to 24 hours. |
| Efficiency | Round-trip efficiency over 75%, competitive with lithium-ion batteries. |
| Materials | No lithium or rare metals; uses off-the-shelf industrial components. |
| Environmental Impact | Emission-free during operation; CO₂ is recycled within a sealed system. |
| Grid Benefits | Provides natural mechanical inertia to stabilize power grids. |
| Current Deployments | Operational commercial plants in Italy with expansion planned globally, including Europe, US, and India. |
| Google’s Goal | Power global data centers with 24/7 carbon-free electricity by 2030. |
| Official Website | energydome.com/co2-battery |
Google’s partnership with Energy Dome to scale the CO₂ battery represents a major step toward a clean, reliable, and economically viable energy future. By harnessing carbon dioxide in a clever closed-loop cycle, this technology offers long-duration, emission-free energy storage that surpasses current chemical battery limits.
With the potential to power grids continuously for up to 24 hours, reduce dependency on rare materials, and stabilize energy systems, the CO₂ battery stands poised to be a cornerstone of the global energy transition.
What Is the CO₂ Battery and How Does It Work?
The CO₂ battery is a thermo-mechanical energy storage system that uses carbon dioxide gas as the working fluid to store electricity. It captures surplus renewable power, stores it efficiently, and releases it again when needed—all while recycling the CO₂ in a closed, emission-free loop.
1. Charging the Battery: Compress and Liquefy CO₂
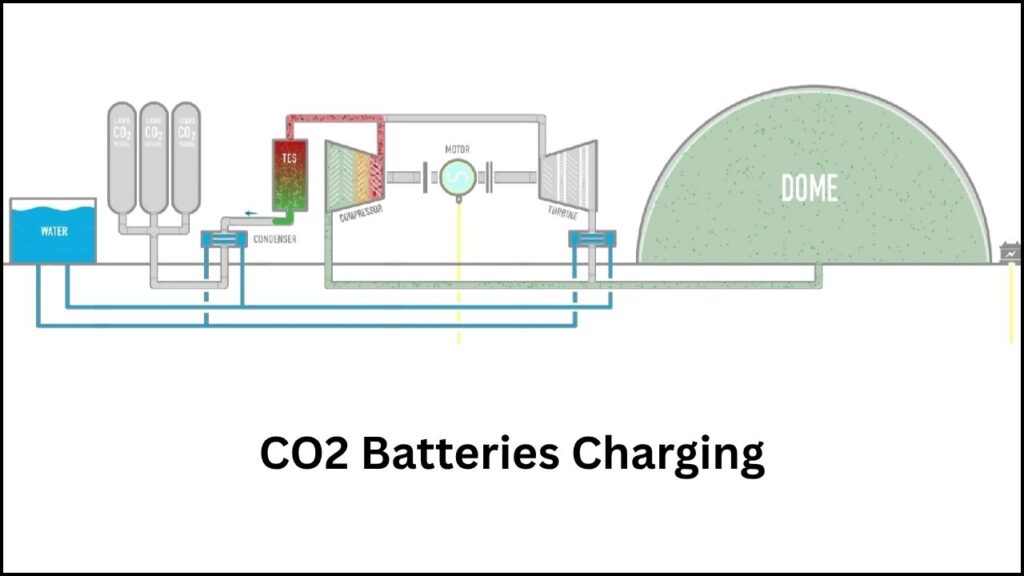
When the grid has extra solar or wind energy, this surplus electricity powers compressors that pressurize CO₂ gas, turning it into a liquid form. Unlike other energy storage methods requiring very cold temperatures, the CO₂ battery compresses CO₂ into its liquid state at ambient temperature, simplifying the technology and reducing costs.
2. Storing Energy: Liquid CO₂ in Sealed Tanks
The liquid CO₂ is stored under pressure inside dome-shaped tanks that keep the gas contained safely and efficiently until there is demand for electricity.
3. Releasing Energy: Expanding CO₂ Drives Turbines
When the grid needs more power, the liquid CO₂ is allowed to expand back into a gas, creating heat and pressure that spin turbines connected to generators. This process produces electricity similarly to how steam turbines operate in conventional power plants.
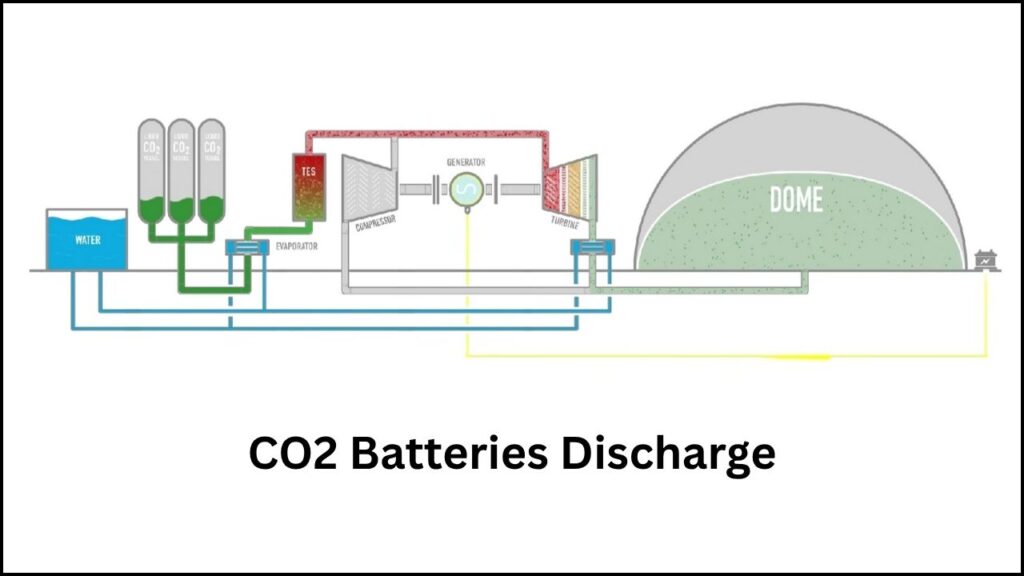
4. Closed-Loop System: Environmentally Safe and Sustainable
The CO₂ cycles continuously in this sealed system without leaks or emissions. Because no new CO₂ is released or absorbed, the entire process is carbon-neutral and emission-free during operation.
Why Is the CO₂ Battery a Game-Changer?
The CO₂ battery offers multiple advantages that address the limitations of current energy storage technologies and enable a cleaner, more stable energy grid:
- Longer Energy Storage Duration: It can discharge power continuously for 8 to 24 hours, making it ideal for bridging daily gaps when renewable production is low.
- No Critical or Scarce Materials Needed: The system uses common, industrial-grade components and CO₂—abundant and inexpensive—bypassing the supply risks and environmental issues of lithium, cobalt, and rare-earth metals.
- Cost-Effective and Rapidly Scalable: Thanks to off-the-shelf components like steel tanks, compressors, and turbines, the CO₂ battery can be built quickly and affordably. Its modular design allows great flexibility for deployment worldwide.
- High Durability and Longevity: The battery experiences minimal degradation, promising a lifespan of over 30 years, compared to the 10–12 years typical for lithium-ion batteries.
- Grid Stability and Safety: Unlike chemical batteries, the CO₂ battery’s rotating machinery adds natural mechanical inertia to the grid, helping to stabilize frequency and smooth out sudden changes—critical as fossil fuel plants retire and renewable sources increase.
- Environmental Impact: Since the CO₂ is contained and reused inside the battery, no greenhouse gases are emitted. This closed-loop design helps support carbon reduction goals.
Google’s Strategic Role in Scaling the Technology
Google is aggressively pursuing its goal to run all its data centers and operations on 24/7 carbon-free electricity by 2030. Achieving this demands reliable, long-duration energy storage solutions capable of balancing the intermittent nature of solar and wind power.
By partnering with Energy Dome and investing in their CO₂ battery technology, Google aims to:
- Accelerate deployment of proven commercial-scale CO₂ battery systems in major markets including Europe, North America, and Asia-Pacific (such as India).
- Reduce costs and demonstrate rapid scalability of long-duration storage, enabling wider adoption beyond tech companies.
- Enhance grid resilience through the natural inertia provided by the battery’s turbines.
- Support broader clean energy policies by showcasing a reliable alternative to fossil fuels and traditional battery storage.
Maud Texier, Google’s Director of EMEA Energy, emphasizes that this technology will deliver “affordable, reliable, and clean electricity to communities everywhere” while advancing the global transition to sustainable energy.
Practical Implications for Energy Professionals and Consumers
This battery technology opens new pathways to maximize the potential of renewable energy and build resilient power grids:
- For Grid Operators: The CO₂ battery adds flexibility and inertia, easing integration of renewables and reducing dependence on fossil fuel backup plants.
- For Data Centers and Industry: Operators can secure continuous, carbon-free power without relying on volatile lithium markets or expensive battery replacements.
- For Policymakers: The CO₂ battery offers a scalable, sustainable solution to achieve decarbonization targets.
- For Consumers and Communities: It promotes stable electricity prices and steady access to clean energy, indirectly supporting a lower-carbon lifestyle.
New Building Materials Could Store 16 Billion Tonnes of CO₂ — A Climate Game-Changer
Breakthrough Catalyst Efficiently Converts CO₂ Into Methanol With High Precision
Simple Technique Improves CO₂ Conversion Efficiency in New Study
FAQs About Google’s CO₂ Battery Could Revolutionize Green Energy
1. Does the CO₂ battery emit carbon dioxide?
No. The battery operates as a closed system where CO₂ is compressed and liquefied, then expanded back to gas repeatedly without release, making the process emission-free.
2. How long can the CO₂ battery provide electricity?
It can continuously supply power for 8 to 24 hours, effectively covering daily periods without renewable generation.
3. How does the CO₂ battery differ from lithium-ion batteries?
The CO₂ battery uses abundant CO₂ and standard industrial parts; it lasts over 30 years with minimal degradation and offers longer duration storage. Lithium-ion batteries rely on scarce materials, have shorter lifespans, and typically discharge energy for only 4 to 6 hours.
4. Where are CO₂ batteries currently deployed?
Commercial-scale plants are operational in Italy, with projects underway or planned in Europe, the US, and India.
5. How does the CO₂ battery support grid stability?
Its rotating turbines provide natural mechanical inertia, smoothing grid frequency fluctuations especially important as traditional fossil fuel plants—which provided inertia—are phased out.