Solar panels have become more affordable than ever—their cost has dropped by over 99% since the 1970s. This monumental reduction is enabling more homes, businesses, and communities worldwide to adopt solar power, helping reduce reliance on fossil fuels and advance renewable energy adoption. But what exactly sparked these dramatic price drops, and how did innovations from many different fields come together to make it happen?

A groundbreaking study by researchers at MIT reveals that the dramatic decrease in solar panel costs wasn’t just a matter of improving solar technology itself. Instead, it resulted from a complex web of innovations spanning diverse industries such as semiconductor fabrication, metallurgy, glass manufacturing, construction, and even legal and permitting processes. These cross-industry advancements improved both the core solar modules and the supporting systems, making solar power cheaper and more accessible.
Let’s break down these exciting insights and explore how knowledge from seemingly unrelated fields has helped solar panels become significantly more affordable—and what this means for the future of renewable energy.
Surprisingly Diverse Innovations Have Led to Dramatically Cheaper Solar Panels
| Topic | Details |
|---|---|
| Solar Panel Cost Reduction | Over 99% decrease in cost since the 1970s |
| Major Innovation Sources | Semiconductor fabrication, metallurgy, glass manufacturing, oil and gas drilling, construction, legal domains |
| Number of Innovations Identified | 81 unique innovations affecting solar photovoltaic system costs |
| Balance-of-System (BOS) Cost | Includes mounting, wiring, inverters, influenced by software and permitting innovations |
| Future Drivers of Cost Reduction | Robotics, AI, automated permitting, digital tools |
| Research Published In | PLOS ONE (2025) |
| Official MIT Study | MIT News Article |
The incredible drop in solar panel costs over the past five decades is a testament to the power of diverse innovations crossing industrial and disciplinary lines. Thanks to advances in semiconductor manufacturing, metallurgy, construction, software, and government reforms, solar power is now more affordable and accessible than ever.

Appreciating this complex web of progress helps industry professionals optimize technology development and enables policymakers to create supportive environments. With emerging technologies like AI and robotics poised to make an impact, the future for cheap, efficient solar energy looks brighter than ever.
How Did Solar Panels Become So Cheap?
Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic cells.
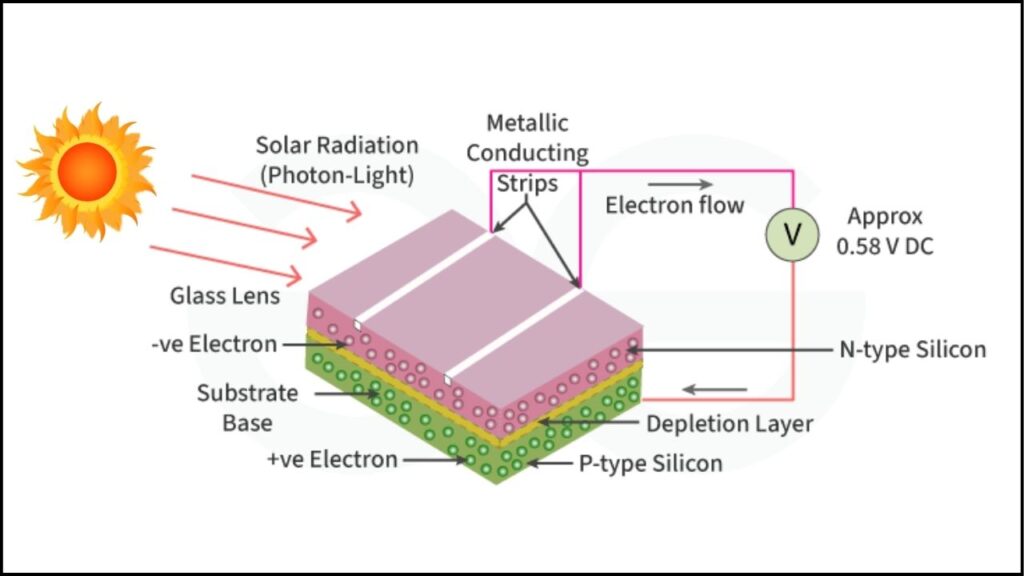
Since their invention, both the technology and manufacturing processes for these cells have evolved tremendously. The MIT study reveals that the cost decline was not a straightforward path of improving solar cell efficiency alone, but rather a giant collaborative leap driven by innovations from a variety of industries.
Researchers analyzed 81 key breakthroughs since 1970 that affected the materials, manufacturing methods, and deployment procedures of photovoltaic systems. For example:
- Enhancements in antireflective coated glass allowed panels to capture more sunlight.
- Introduction of wire sawing techniques in the 1980s reduced silicon waste and increased production efficiency, saving about $5 per watt in total system costs.
- Advances in semiconductor fabrication helped boost solar cell efficiency while lowering production expenses.
- Innovations in metallurgy and glass manufacturing improved material quality and durability.
- Development of software tools enabled automated permitting systems and streamlined installation processes.
These technical improvements all drew from advances in diverse sectors such as electronics, oil and gas, construction, and local government agencies.
Breaking Down Solar Costs: Modules vs. Balance-of-System (BOS)
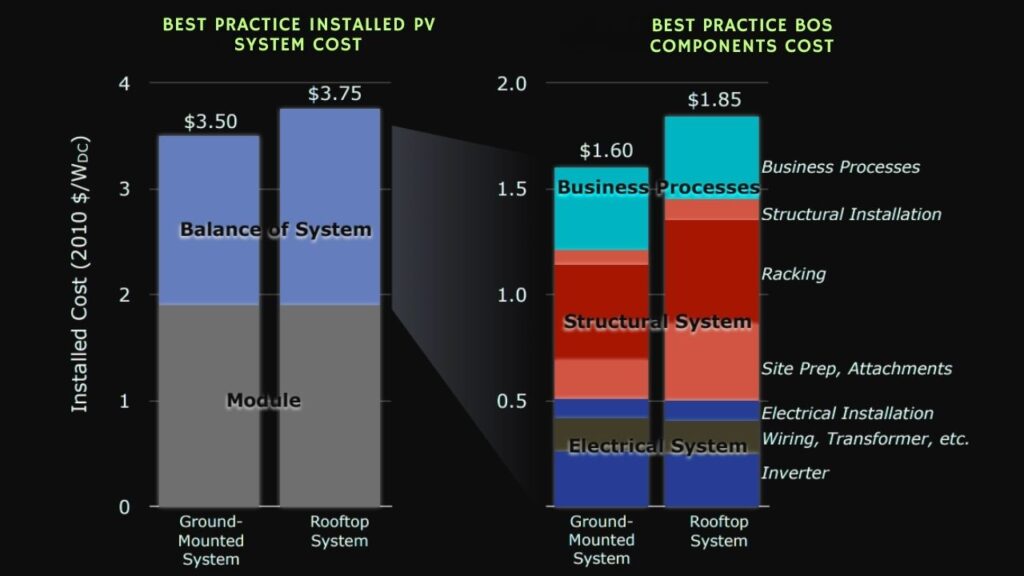
The MIT study separates solar costs into two main parts:
- PV Module Costs: The costs of the solar panels themselves, which consist of multiple solar cells wired together. These are often mass-produced and traded globally.
- Balance-of-System (BOS) Costs: Everything else needed to get a solar system up and running — including mounting infrastructure, wiring, inverters, installation labor, and permitting. These costs tend to be more localized and are influenced heavily by regulatory and administrative factors.
While the bulk of cost improvements for PV modules came from hardware and manufacturing advances, BOS costs saw significant reductions through software innovations and streamlined permitting processes. Examples include:
- Online permitting platforms that automatically approve grid-compliant systems.
- Improved construction workflows to minimize on-site delays.
- Enhanced coordination between utilities and installers via digital tools.
These soft technology improvements help reduce installation times and administrative overhead, making solar systems both faster to deploy and more cost-effective upfront.
The Role of Diverse Industries and Knowledge Transfer
One of the most striking findings is that many important innovations driving solar cost reductions originated outside the traditional solar industry. Contributions came from:
- The semiconductor industry, which developed fabrication processes critical for solar cell production.
- Metallurgy and glass manufacturing, which created better materials and coatings.
- Oil and gas drilling expertise, which informed precise manufacturing and installation techniques.
- The construction sector, which improved mounting and deployment methods.
- Legal and regulatory domains, which innovated in permitting systems and administrative streamlining.
This broad network of innovation highlights how knowledge spillovers from diverse sectors accelerated improvements in solar technology and cost structure.
What Does This Mean for the Future of Solar Power?
Looking forward, the MIT researchers point to exciting opportunities for continued cost reduction and performance improvement by leveraging emerging technologies such as:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and robotics for automating design, manufacturing, and installation.
- Digital engineering tools for remote assessments, engineering reviews, and predictive maintenance.
- Further software innovations to simplify permitting and utility interconnection approvals.
These developments have strong potential to reduce BOS costs, which historically have lagged behind module cost improvements. The study suggests that fostering cross-sector collaborations and embracing digital transformation will be key strategies for accelerating solar adoption.
Practical Advice for Solar Industry Stakeholders
For professionals in renewable energy, manufacturers, and policymakers, the study offers several actionable insights:
- Encourage cross-sector collaboration. Innovations often come from unexpected places, so partnerships across industries can unlock new breakthroughs.
- Focus on reducing BOS costs. Since module costs are nearing their practical minimums, addressing soft costs like permitting and installation efficiency offers major savings potential.
- Adopt digital tools. Automating routine technical and administrative tasks can reduce delays and overhead.
- Watch emerging technologies closely. AI, robotics, and advanced materials promise continued gains.
- Support policy reforms. Streamlining regulations and permitting processes will accelerate solar deployment.
Understanding Solar Panel Innovation for Everyone
If you are curious about how solar panels got so much cheaper, imagine building with LEGO bricks. At first, LEGO bricks were rare and expensive. Over time, inventors found better ways to make the bricks and faster ways to build houses. They even learned from other toy industries to make bricks cheaper and stronger. Computer programs helped builders avoid mistakes and speed up construction.
Solar panels followed a similar path. Many smart people from different fields learned from each other and worked together to make solar panels cheaper, better, and easier to use for everyone.
Innovative Composite Material Helps Solar Panels Stay Cooler and Work More Efficiently
MIT Researchers Develop Transparent Solar Panels for Windows and Mobile Devices
Breakthroughs in Flexible Solar Panels: The Future of Renewable Energy
FAQs About Surprisingly Diverse Innovations Have Led to Dramatically Cheaper Solar Panels
Q1: How much has the cost of solar panels dropped since the 1970s?
A1: The cost has dropped by over 99% since the 1970s, making solar power much more affordable worldwide.
Q2: Which industries contributed most to lowering solar panel costs?
A2: Innovations from semiconductor fabrication, metallurgy, glass manufacturing, oil and gas drilling, construction, and legal and regulatory fields all played key roles.
Q3: What does “Balance-of-System” (BOS) mean?
A3: BOS includes all components of a solar system other than the panels themselves — such as mounting, wiring, inverters, installation labor, and permitting.
Q4: Why are software and permitting innovations important?
A4: They help reduce installation times and administrative costs by automating approvals and streamlining processes, especially impacting BOS costs.
Q5: What future trends will drive solar cost reductions further?
A5: Robotics, AI, automated permitting, and advanced digital tools are expected to continue pushing costs down.