AI Just Made 2D Materials Stronger: Imagine a material so thin it’s just a few atoms thick, yet so strong it can support hundreds of times its own weight. This is the world of two-dimensional (2D) materials—sheets of atoms that are revolutionizing everything from electronics to aerospace. Now, artificial intelligence (AI) is making these materials even stronger and more versatile, opening doors to technologies we once thought were science fiction.
In this article, we’ll explore how AI-driven advancements in 2D materials are reshaping material science. We’ll break down the science in simple terms, share real-world examples, and explain why these innovations matter for everyone—from curious kids to industry leaders.
AI Just Made 2D Materials Stronger
| Topic | Key Data/Stats/Insights | Professional/Career Impact |
|---|---|---|
| AI in 2D Material Design | 4.3% increase in stress uniformity; 23.1% reduction in stress concentrations | Faster R&D, new job roles in AI/material science |
| Strength of Optimized 2D-PHS | Tensile strength increase: 5.9 MPa to 6.6 MPa under 100% strain | Stronger, lighter aerospace components |
| AI-Enabled Discovery | Millions of material candidates screened in days, not years | Shorter time-to-market for new materials |
| Robotics & Automation | Robotic systems enable scalable fabrication of complex 2D/3D structures | New careers in robotics and automation |
| Twistronics & Moiré Systems | Controlled twist angles unlock exotic quantum states | Quantum computing, advanced electronics |
| Industry Applications | Aerospace, healthcare, energy storage, electronics | Cross-industry innovation and growth |
AI is transforming 2D materials, making them stronger, lighter, and more versatile than ever before. From airplanes to quantum computers, these innovations are opening up new possibilities for science, industry, and everyday life. By combining AI, robotics, and material science, we’re entering a new era of discovery—one where the materials of the future are being designed and built faster and smarter than ever.
What Are 2D Materials?
2D materials are ultra-thin sheets of atoms arranged in a single layer. The most famous example is graphene, a sheet of carbon atoms that’s stronger than steel, conducts electricity better than copper, and is nearly transparent. But there are many others, like molybdenum disulfide (MoS₂) and hexagonal boron nitride (hBN), each with unique properties.
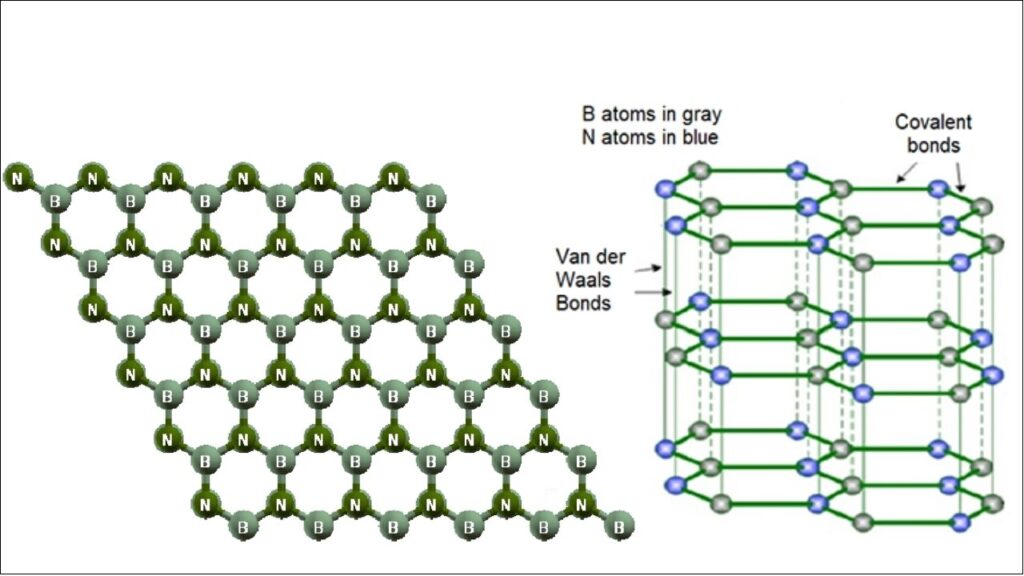
These materials are exciting because they’re lightweight, flexible, and can be stacked or twisted to create new electronic or mechanical behaviors—like making superconductors or ultra-efficient transistors.
Why Is AI Changing 2D Materials?
Traditionally, designing new materials involved lots of trial and error. Scientists would mix chemicals, heat them up, and test the results—a process that could take years. AI is changing this by analyzing huge amounts of data and predicting which materials will work best for specific jobs.
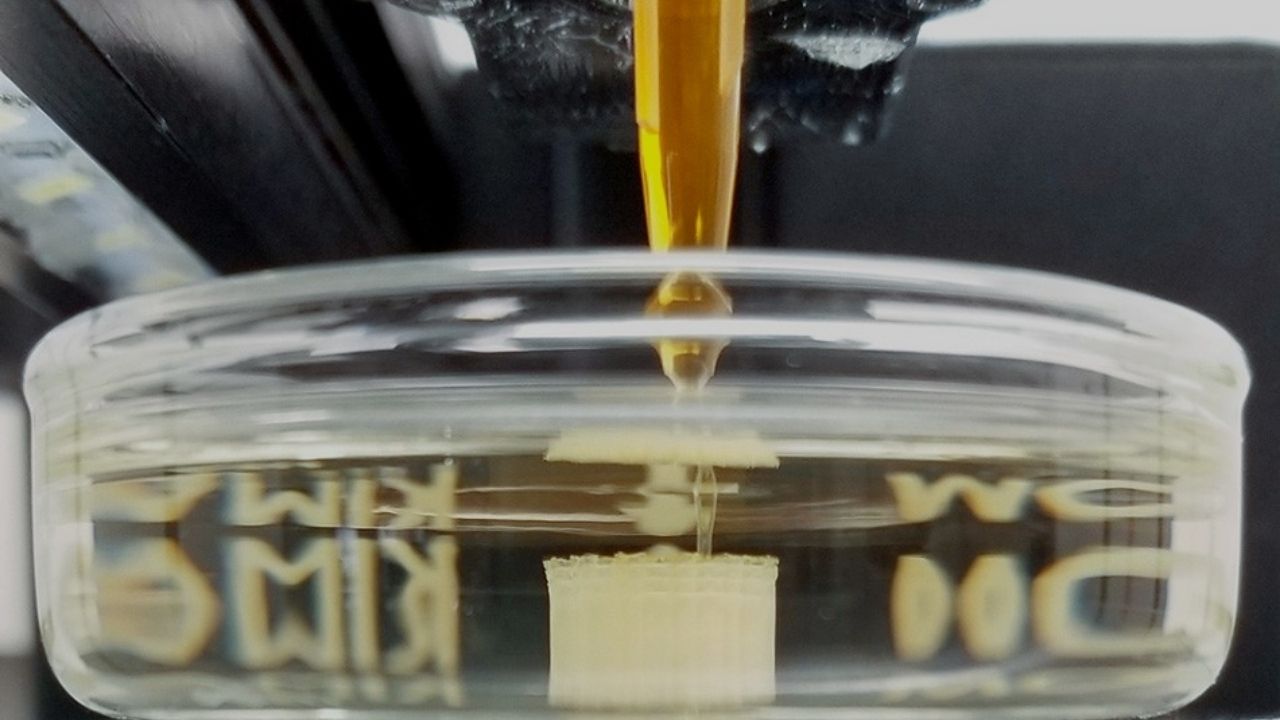
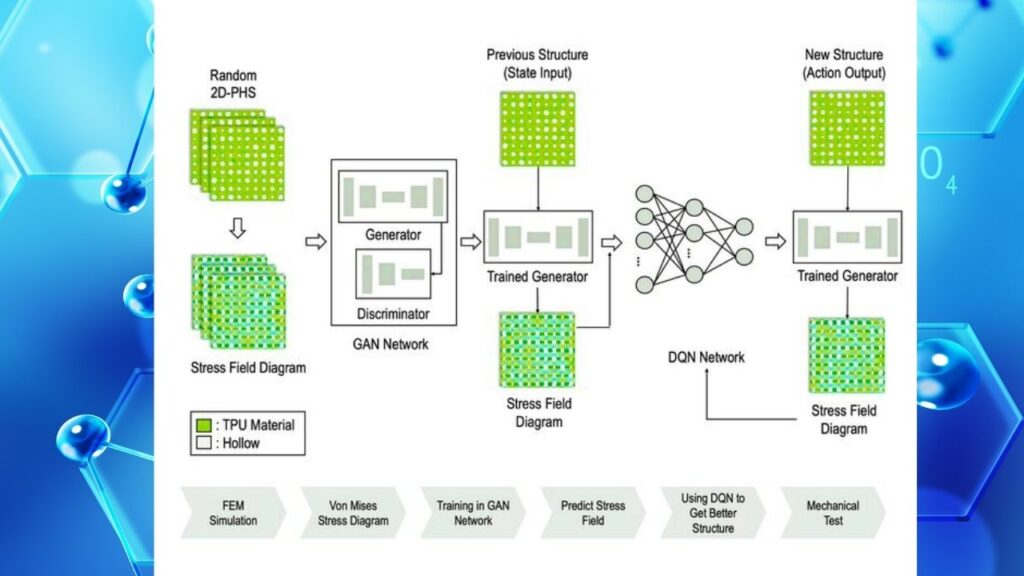
For example, researchers at ShanghaiTech University used an AI-driven framework to design two-dimensional patterned hollow structures (2D-PHS). These are special 2D materials with tiny, carefully placed holes that make them lighter and stronger. The AI helped scientists figure out the best arrangement, size, and shape for these holes, resulting in a 4.3% improvement in stress uniformity and a 23.1% reduction in maximum stress concentrations. The tensile strength of these materials also increased from 5.9 MPa to 6.6 MPa under 100% strain—meaning they can stretch further without breaking.
How Does AI Make 2D Materials Stronger?
Let’s break down the process step by step:
1. AI Analyzes Material Data
AI looks at thousands of experiments and simulations to learn what makes a material strong, flexible, or conductive. It uses machine learning models to find patterns in the data and predict how new materials will behave.
2. AI Designs New Structures
Using what it’s learned, AI can suggest new material designs—like where to put holes in a 2D sheet to make it lighter but still strong. This is called computational modeling.
3. AI Guides Experiments
Scientists use AI’s suggestions to make real materials in the lab. The AI keeps learning from these experiments, improving its predictions for next time.
4. AI and Robotics Work Together
Robots can now make these materials automatically, following AI’s instructions. This makes the process faster and more precise, so new materials can be tested and used much sooner.
Real-World Examples
- Aerospace: 2D-PHS materials are being used to make airplane wings and fuselage panels that are lighter but just as strong, helping planes use less fuel and fly farther.
- Healthcare: These materials can be used to make scaffolds for growing new tissues in the body, helping people recover from injuries.
- Electronics: Twisting two layers of graphene at a “magic angle” creates new electronic properties, leading to ultra-efficient transistors and even quantum computers.
Practical Advice: How Can You Get Involved?
If you’re interested in this field, here are some steps you can take:
- Learn the Basics: Start with simple science books or online resources about atoms, materials, and how computers work.
- Try Coding: AI and robotics are powered by code. Try learning a beginner-friendly language like Scratch or Python.
- Explore Science Clubs: Join a local science club or robotics team to get hands-on experience.
- Stay Curious: Follow news about AI and materials science to see what’s new and exciting.
The Future of AI and 2D Materials
The future looks bright for AI-powered 2D materials. Here’s what experts are excited about:
- Faster Discovery: AI can screen millions of possible materials in days, not years, speeding up innovation.
- New Jobs: There will be more jobs in AI, robotics, and material science as these technologies grow.
- Sustainability: Lighter, stronger materials mean less waste and energy use, helping the environment.
- Quantum Technologies: Twisted 2D materials could unlock new kinds of computers and electronics that are faster and use less power.
New Quantum State Discovery Set to Revolutionize Material Science Worldwide
FAQs About AI Just Made 2D Materials Stronger
Q: What are 2D materials?
A: 2D materials are sheets of atoms only one or a few layers thick, like graphene. They’re super strong, flexible, and have unique electronic properties.
Q: How does AI help make 2D materials stronger?
A: AI analyzes data from experiments and simulations to predict which material designs will be strongest. It then guides scientists and robots to make those materials in the lab.
Q: What are some uses for stronger 2D materials?
A: They can be used in airplanes, medical devices, electronics, and energy storage, making things lighter, stronger, and more efficient.
Q: Can AI and robotics make new materials by themselves?
A: Not entirely—AI suggests designs and robots help make them, but scientists are still needed to guide the process and check the results.
Q: Will this create new jobs?
A: Yes! There will be more jobs in AI, robotics, and material science as these technologies become more important.