Navigating new places can seem like an impossible challenge if you are unable to see. Yet today, thanks to AI navigation tools for vision loss, millions worldwide are experiencing a revolution in how they move, live, and explore—with greater independence and dignity. This article delves deeply into the advances powering these life-changing technologies, showcases real-life examples, and provides a comprehensive, step-by-step guide for users, families, and professionals.

Table of Contents
AI Tool Helps People With Vision Loss
| Feature/Topic | Details & Data |
|---|---|
| People with vision impairment worldwide | Over 2.2 billion globally, with 253 million facing moderate to severe vision loss |
| AI navigation tool examples | Tools: Seeing AI, Envision Glasses, OrCam MyEye, Meta AI Glasses, smart canes, wearables |
| Measured navigation improvement | Up to 25% faster and safer movement with AI vs. cane alone in controlled studies |
| Market growth | Assistive tech device market expanding at ~8% yearly as of 2025 |
| Professional independence | AI tools support reading, moving freely, and joining job activities for vision-impaired |
| Cost range | Apps may be free/low-cost; smart hardware typically ranges from affordable to premium |
AI navigation tools for the blind and vision-impaired are transforming what’s possible for millions worldwide. By blending computer vision, language understanding, wearable design, and user-focused features, these innovations foster safety, connection, and dignity. For families, professionals, and caregivers, these tools aren’t just about high technology—they are about opening new worlds of independence, confidence, and opportunity.
Introduction: The Urgent Need
Imagine entering a crowded city intersection or a noisy shopping mall—but you can’t see crosswalks, signs, or even other people. For the 2.2 billion people living with some form of vision impairment, daily life includes difficult moments like these. Mobility and information are key to participation in society, yet traditional aids (like the white cane or guide dogs) have limits.
That’s where AI-powered navigation tools are breaking new ground, using real-time computer vision, smart audio feedback, and wearable designs to guide users safely and confidently—right when and where it’s needed.
The Technology: How AI Makes Navigation Possible
Easy-to-use devices and apps now rely on several kinds of artificial intelligence and smart engineering:
Computer Vision
Tiny cameras (in glasses, phones, or canes) “see” what’s around the user. Advanced AI instantly processes images, detects obstacles, and recognizes objects, faces, text, and even gestures.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
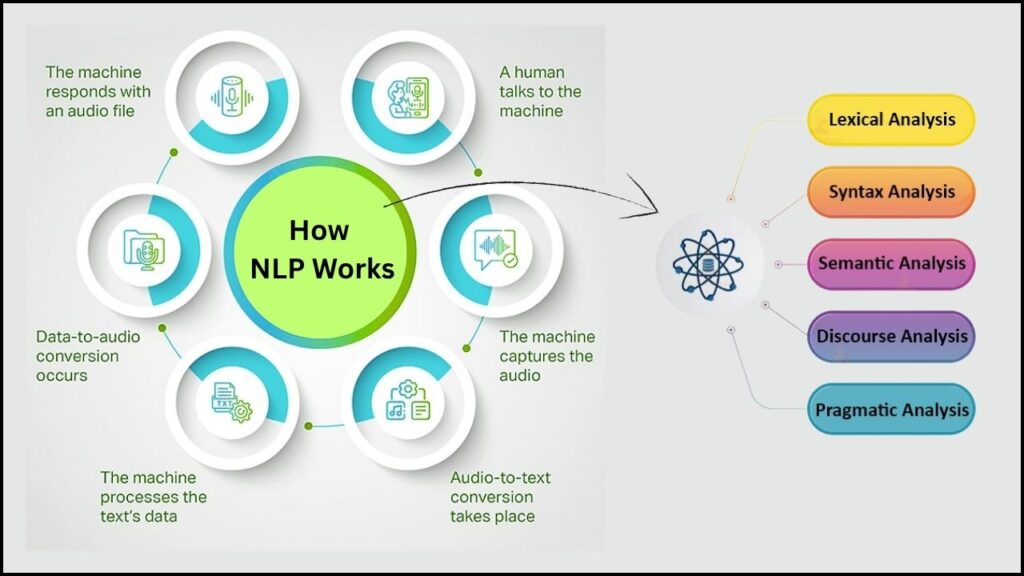
Users speak to their devices: “What’s in front of me?” or “Read this document.” The AI returns realistic, helpful answers aloud, describing the scene, reading menus, or answering travel questions.
Real-Time Mapping and Navigation
Some tools use inbuilt sensors and GPS to create digital maps of surroundings—indoors or outside. Others identify steps, ramps, escalators, or street corners, providing audio or vibration cues for safer movement.
Haptic Feedback
Wearables, such as wristbands or smart canes, offer gentle vibrational alerts—so users keep their hands and ears free for other tasks and can instantly adjust their path.
Personalized Learning
Machine learning tailors responses over time, remembering user preferences, landmark locations, and common routes to make each journey safer and more efficient.
Everyday Examples: The AI Tools Changing Lives
Seeing AI
A free app, this tool reads out printed text, describes objects, recognizes faces, and even tells users about their environment—like whether there’s an empty seat nearby or what color an item of clothing is.
Envision Glasses
Wearable smart glasses with a discreet camera, designed to read text, recognize faces, deliver scene descriptions, and respond to spoken commands—all hands-free and continuously updated.
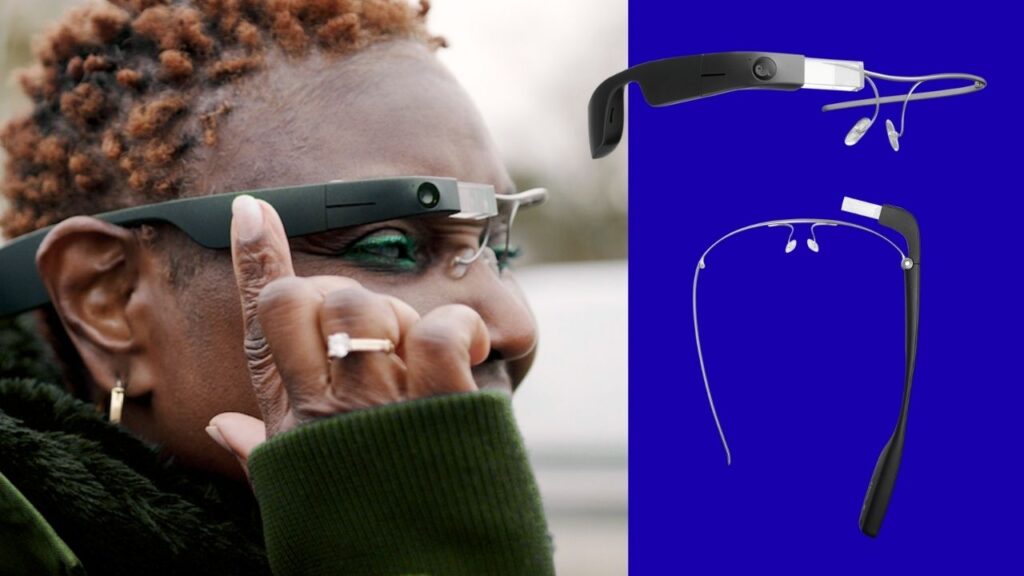

OrCam MyEye
A small device that clips onto glasses, reading printed or digital text aloud in real time, recognizing products and faces, and working indoors or outdoors.
Meta AI Glasses
Combining Ray-Ban eyewear with embedded cameras and AI, these allow for spoken translation, live scene description, object identification, and connection to a human volunteer when extra support is needed.
Smart Canes & Wearable Navigation Bands
Modern “intelligent” canes and wearable wristbands offer obstacle detection (via echoes or AI sensors), haptic alerts, and can even connect to smartphones for real-time GPS and navigation.
Step-by-Step Guide: How Users and Families Can Benefit
1. Accessing and Starting AI Tools
- Download a Free App: Getting started can be as simple as downloading a trusted app like Seeing AI on a smartphone and following on-screen instructions.
- Trying Hands-Free Wearables: Devices like Envision Glasses or OrCam MyEye can be tried at local vision centers or through official vendor demos.
- Setup and Personalization: Users learn to set feedback types (audio, vibration), select language, and connect accessories like bone-conduction headphones for clear, private listening.
2. Moving Through New Environments
- The device “sees” surroundings, describing objects, doors, steps, people, or hazards in real time.
- Indoors, the system can help identify room layouts, desks, or elevators. Outdoors, it navigates sidewalks, crosswalks, and public transportation.
- Dynamic guidance means the user gets updates instantly if their environment changes.
3. Reading and Information Retrieval
- Scan and read documents, signs, or displays—at work, school, or while shopping.
- Some tools allow for “reading mode,” where the user just points to a page or package, and the device reads it aloud.
- Professionals can participate more confidently by reading presentations, reports, or email independently.
4. Social Confidence and Independence
- Facial recognition and scene description help identify friends, locate busy areas, or pick a seat in a restaurant.
- Users can request summaries of entire scenes or ask detailed questions about unfamiliar settings.
- When needed, some devices connect to sighted volunteers for additional help.
Trusted Data & the Science Behind the Impact
Scope of Vision Loss
- Globally, 2.2 billion people live with some level of impaired sight; 253 million are blind or have severe impairment.
- Age is a major factor: most affected are over 50, yet children and working-age adults also benefit greatly from AI navigation solutions.
- The economic impact includes billions lost annually due to reduced employment and extra care needs.
Technology Adoption and Measured Benefits
- Controlled studies consistently show AI users complete navigation tasks up to 25% faster and with fewer errors compared to those using traditional tools alone.
- User satisfaction surveys show high confidence and improved feelings of safety, social inclusion, and autonomy.
- The assistive tech market is seeing robust growth, driven by improvements in technology and wider societal focus on accessibility.
Choosing the Right Solution: Practical Advice
Individual Needs Assessment
- Reading: Is text access (digital, print, labels) most important?
- Mobility: Is real-time guidance (indoors or outdoors) a top priority?
- Social and Work Participation: Is recognizing faces, giving presentations, or attending meetings a regular need?
Comparison Shopping
- Basic apps are free or low cost—an accessible starting point for most families.
- Smart glasses and wearable devices vary in price, so always compare features for your lifestyle and needs.
Training & Support
- Vision rehabilitation services often offer both device demos and practical skills training at little or no cost.
- Many governments, nonprofits, and workplaces provide funding or subsidies to make devices affordable.
- Online and local resources offer community support and user tips.
AI Careers and Professional Access
- AI-powered accessibility tools allow people with vision loss to pursue a much wider range of careers in education, technology, government, and business.
- Users can read, travel, give presentations, and connect with colleagues independently.
- Companies increasingly hire and support employees with disabilities, helping develop and test even better technology for all.
Meta Launches New AGI Lab to Dominate the Future of Artificial Intelligence
FAQs About AI Tool Helps People With Vision Loss
How accurate and reliable are AI tools for navigation?
Modern devices, built and trained on extensive real-world data, offer impressive accuracy—especially in well-lit, familiar settings. However, users should still apply traditional skills and always be alert to unusual hazards.
Do these tools work everywhere?
Most perform well both indoors and outdoors. Navigation features may work best in urban areas or where digital maps are available, but obstacle detection works nearly anywhere the cameras can see.
How affordable are AI navigation solutions?
While free apps abound, hardware (like smart glasses or canes) ranges from several hundred to a few thousand dollars. Many organizations offer financial assistance.
Are these devices safe to trust?
They dramatically boost independence but are best used to supplement—not replace—common sense and mobility training.
Can children use these tools?
Absolutely. Many products are suitable for children under adult guidance, with child-friendly modes and supervised settings.