Windows are the eyes of a building—letting in sunlight, providing views, and connecting us to the outside world. But did you know that windows are also one of the biggest culprits when it comes to energy loss in homes and offices? Even the best double-glazed windows can let precious heat escape in winter or allow unwanted warmth in during summer. This is why scientists and engineers are always looking for new ways to make windows more energy-efficient.

Recently, a boron nitride coating for glass has emerged as a promising breakthrough. Developed by a team of materials scientists, this innovative technology could dramatically reduce energy loss through glass, improve insulation, and make buildings more comfortable and sustainable. Let’s explore what this means for homeowners, building professionals, and the future of green construction.
Table of Contents
Boron Nitride Coating Promises to Cut Energy Loss in Glass
| Feature/Stat | Details |
|---|---|
| Material | Carbon-doped boron nitride (BN-C) transparent nano-coating |
| Energy Savings | 2.9% improvement over current commercial alternatives in cold climates |
| Durability | Resists scratches, moisture, UV light, temperature swings; suitable for outdoor use |
| Annual Window Installations (US) | Over 4 billion sq. ft. of new windows installed each year |
| Manufacturing | Room-temperature pulsed laser deposition; scalable to commercial production |
| Cost | Boron nitride is less expensive than silver or indium tin oxide used in current coatings |
The boron nitride coating for glass represents a significant leap forward in building technology. By combining advanced materials science with practical manufacturing techniques, this innovation offers real benefits: lower energy bills, greater comfort, and a more sustainable future. Whether you’re a homeowner, builder, or manufacturer, adopting this technology can help you stay ahead in the quest for energy-efficient, resilient, and beautiful buildings.
Why Energy Efficiency in Windows Matters
The Problem with Traditional Windows
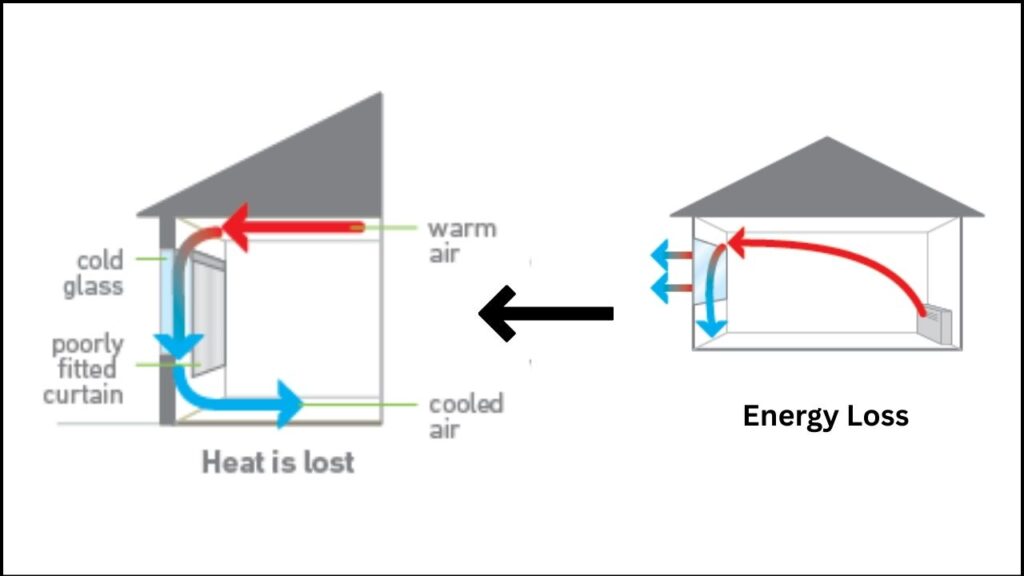
Windows are essential for comfort and aesthetics, but they’re also a major source of energy loss. According to building energy studies, up to 30% of a building’s heating and cooling energy can be lost through its windows. This not only leads to higher utility bills but also increases the carbon footprint of homes and commercial spaces.
The Role of Low-Emissivity (Low-E) Coatings
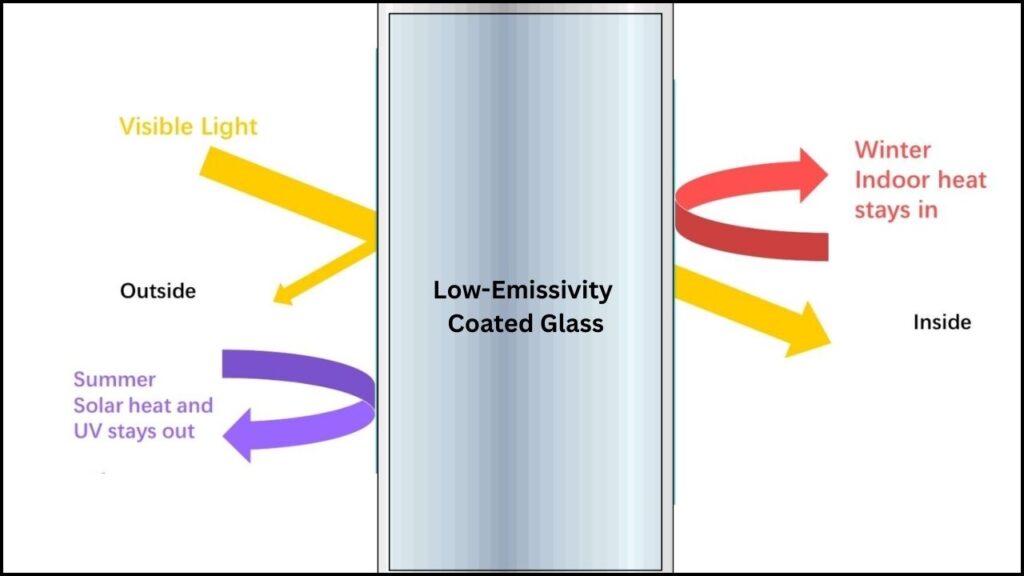
To combat this, low-emissivity (low-E) coatings were introduced. These are ultra-thin metallic layers applied to glass surfaces to reflect infrared energy (heat) while allowing visible light to pass through. Low-E coatings have become a standard feature in modern energy-efficient windows, but they have limitations:
- Durability Issues: Many low-E coatings degrade over time, especially when exposed to humidity, UV light, and temperature fluctuations.
- Installation Constraints: Most must be installed on the inside of windows to protect them from the elements.
- Material Costs: Some use expensive materials like silver or indium tin oxide, increasing the cost of production.
What Makes Boron Nitride Coating Revolutionary?
The Science Behind Boron Nitride
Boron nitride is a compound made of boron and nitrogen atoms, known for its exceptional hardness, chemical stability, and resistance to heat. When used as a coating, especially with a small amount of carbon added (creating BN-C), it forms a transparent, ultra-thin layer that is both tough and effective at reflecting heat.
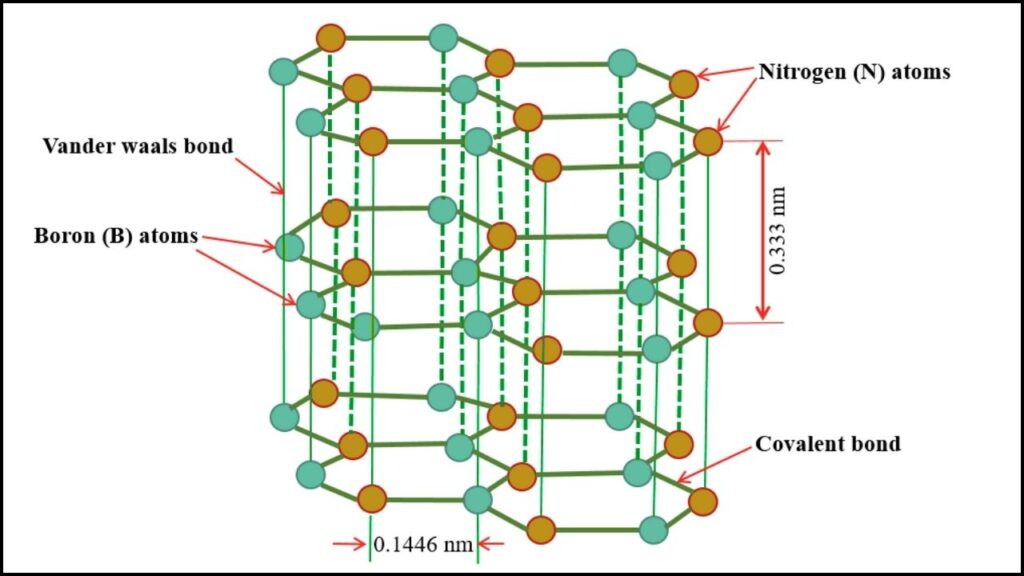
Key Advantages
- Low Emissivity: The carbon-doped boron nitride coating has a much lower emissivity than plain glass, meaning it reflects more heat and allows less to escape.
- Weather Resistance: It resists scratches, moisture, UV light, and temperature extremes, making it ideal for exterior use.
- Transparency: The coating is optically clear, so it doesn’t change the appearance of windows or reduce natural light.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Boron nitride is more affordable than precious metals used in traditional coatings.
How the Coating is Made
The boron nitride coating is applied using a process called pulsed laser deposition. Here’s how it works:
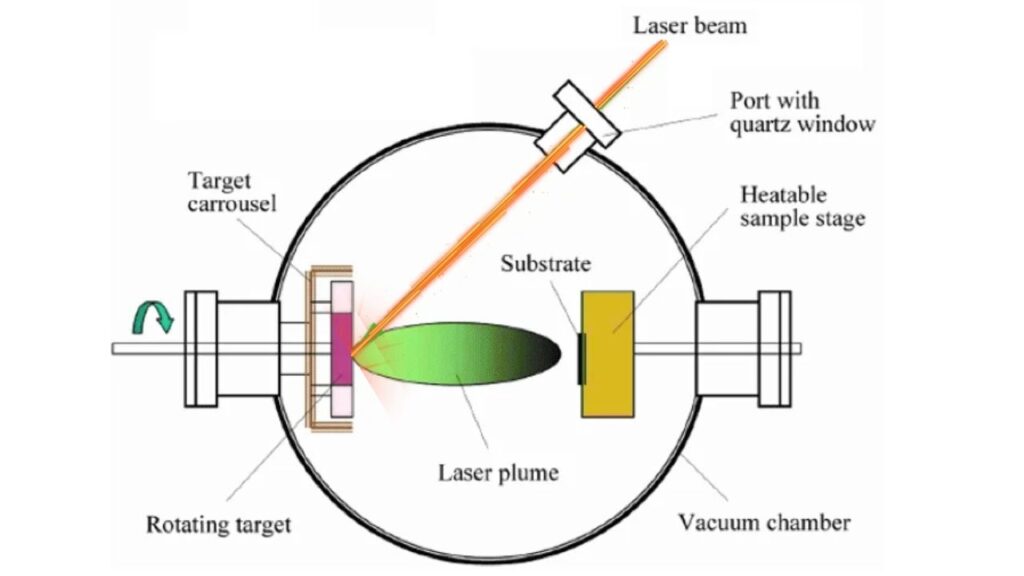
- Preparation: A solid boron nitride target is placed in a vacuum chamber.
- Laser Application: High-energy laser pulses vaporize the target, creating a plasma plume.
- Deposition: The vaporized material settles onto the glass, forming a uniform, thin film.
- Doping: Carbon is introduced during the process to enhance the coating’s heat-reflecting properties.
This process occurs at room temperature, which means it doesn’t damage the glass and can be easily scaled up for mass production.
Practical Benefits for Homeowners and Professionals
For Homeowners
- Lower Energy Bills: Improved insulation means less heat escapes in winter and less heat enters in summer, reducing heating and cooling costs.
- Year-Round Comfort: Rooms stay warmer in winter and cooler in summer, enhancing indoor comfort.
- Durable Windows: The tough coating protects against scratches and environmental damage, extending the life of your windows.
For Building Professionals and Architects
- Design Flexibility: The durability and exterior application of the coating allow for more creative window designs and placements.
- Sustainability: Enhanced insulation helps buildings meet green building standards and reduces environmental impact.
- Cost Savings: Lower material costs and improved energy efficiency make projects more economical over their lifespan.
For Manufacturers
- Easy Integration: The room-temperature process can be added to existing production lines without major changes.
- Competitive Edge: Offering windows with superior insulation and durability can set products apart in the market.
Real-World Impact: Data and Examples
Energy Savings at Scale
While a 2.9% energy savings per window may seem modest, consider the scale: With over 4 billion square feet of new windows installed annually in the United States alone, the cumulative energy and cost savings are massive. Over time, this could translate to millions of dollars in reduced utility costs and a significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
Durability in Harsh Environments
The boron nitride coating’s resistance to scratches, moisture, and UV light means it can be used in challenging climates—from salty coastal regions to high-altitude locations with intense sunlight. This durability ensures that windows maintain their insulating properties for years, reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
Supporting Green Building Initiatives
As cities and countries set stricter energy codes and sustainability targets, technologies like boron nitride coatings can help buildings achieve higher energy ratings and certifications, such as LEED or BREEAM. This not only benefits the environment but also increases property value and marketability.
How to Adopt Boron Nitride Coating in Your Project
Step 1: Assess Your Needs
- New Construction: If you’re building a new home or commercial property, specify boron nitride-coated glass in your window package.
- Renovations: Ask your contractor or window supplier about the availability of this technology for retrofit projects.
Step 2: Consult with Professionals
- Architects and Builders: Work with professionals familiar with advanced glazing technologies to ensure proper installation and performance.
- Manufacturers: Reach out to window manufacturers who have adopted the boron nitride coating process.
Step 3: Monitor Performance
- Track Energy Use: Compare your energy bills before and after installation to see the impact.
- Regular Maintenance: While the coating is highly durable, regular cleaning and inspection will keep your windows performing at their best.
MicroscopyGPT Uses AI to Describe Atomic Structures in 2D Materials with Unmatched Precision
Scientists Explore the Potential of MXenes in Revolutionizing Sustainable Ammonia Production
FAQs About Boron Nitride Coating Promises to Cut Energy Loss in Glass
What is boron nitride coating?
It’s a transparent, ultra-thin layer made by adding carbon to boron nitride, applied to glass to improve insulation and reduce energy loss.
How does it compare to traditional low-E coatings?
Boron nitride coating is more durable, can be applied to the outside of windows, and offers better long-term performance, especially in harsh environments.
Will the coating change the look of my windows?
No. The coating is optically clear and does not affect the appearance or transparency of the glass.
Can it be used on existing windows?
Currently, the technology is best suited for new windows, but research is ongoing to make it available for retrofitting in the future.
Is it cost-effective?
Yes. Boron nitride is less expensive than materials like silver, and the manufacturing process is energy-efficient and scalable.