Imagine a world where your most secret online messages, bank transactions, and personal data could be cracked open in a few days. This isn’t science fiction—it’s a real possibility, thanks to rapid advances in quantum computing. Recently, a team of researchers in China made headlines by using a quantum computer to break RSA encryption, the same technology that keeps your chats, emails, and online shopping secure.

While the immediate threat is still small, this breakthrough is a big warning sign for everyone who cares about online security. Let’s break down what happened, why it matters, and what you can do to protect yourself and your business.
Understanding the Big News: China Breaks RSA with Quantum Computing
RSA encryption is one of the most important tools for keeping information safe online. It’s used by banks, websites, email providers, messaging apps, and even your favorite games and streaming services. The system works by using two very large numbers (called “keys”)—one to lock (encrypt) your data and another to unlock (decrypt) it. The security of RSA depends on how hard it is for anyone else to figure out those two numbers.
Quantum computers are a new kind of super-powerful computer that can solve certain problems much faster than regular computers. Until now, breaking RSA encryption with a quantum computer was just a theory. But in June 2025, researchers at Shanghai University used a D-Wave quantum annealer to factor a 22-bit RSA key—the first real demonstration of a quantum computer attacking this kind of encryption.
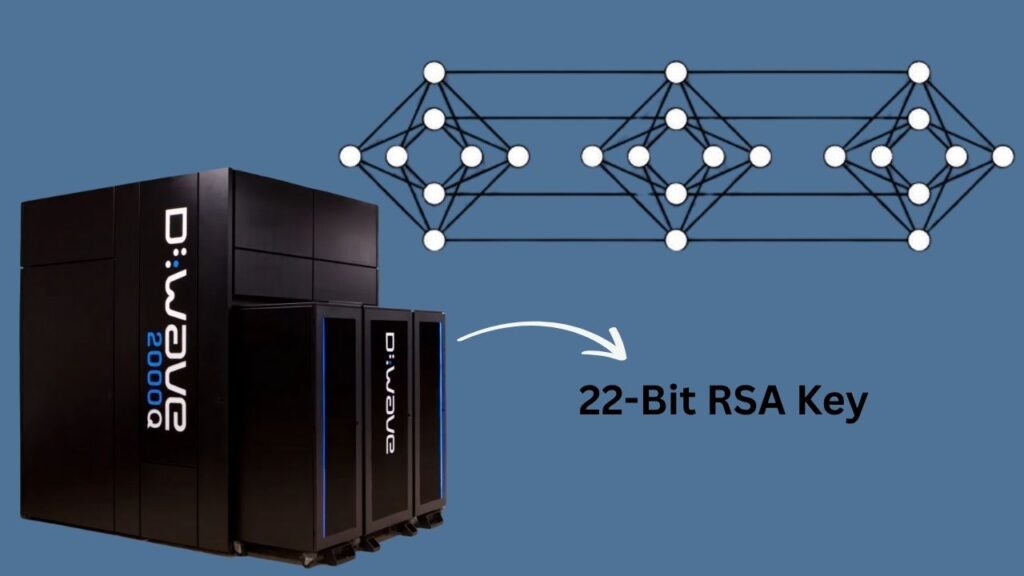
A 22-bit key is tiny compared to the 2048-bit keys used in real-world security today. But the real story here is that quantum computers are getting better at cracking codes, and experts are worried that bigger breakthroughs could be just around the corner.
China Uses Quantum Computer to Break RSA Encryption
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| What happened? | Chinese researchers broke a 22-bit RSA key using a quantum computer |
| What hardware was used? | D-Wave Advantage quantum annealer |
| Why is this important? | Shows quantum computers can attack real encryption, not just theory |
| How big are real-world RSA keys? | 2048-bit or 3072-bit keys are standard |
| Is RSA broken for good? | Not yet—current quantum computers can’t break real-world keys |
| What are experts saying? | Urging a switch to post-quantum cryptography |
| How soon could RSA be broken? | Possibly within a decade if quantum tech advances quickly |
| What should you do now? | Prepare for post-quantum security, especially if you handle sensitive data |
The news that China used a quantum computer to break RSA encryption is a wake-up call for everyone who uses the internet. While the immediate threat is still small, the rapid progress in quantum computing means that today’s encryption could become obsolete sooner than we think.
The best way to stay safe is to prepare now. Stay informed, support the switch to post-quantum cryptography, and make sure your personal and business data are protected for the future.
How Does RSA Encryption Work? (And Why Is It at Risk?)
To understand why this is such big news, let’s look at how RSA encryption works:
- Key Generation: Two large prime numbers are chosen and multiplied together. This product is used to make the “public key.”
- Encryption: Anyone can use the public key to lock (encrypt) a message.
- Decryption: Only the person with the matching “private key” (the original prime numbers) can unlock (decrypt) the message.
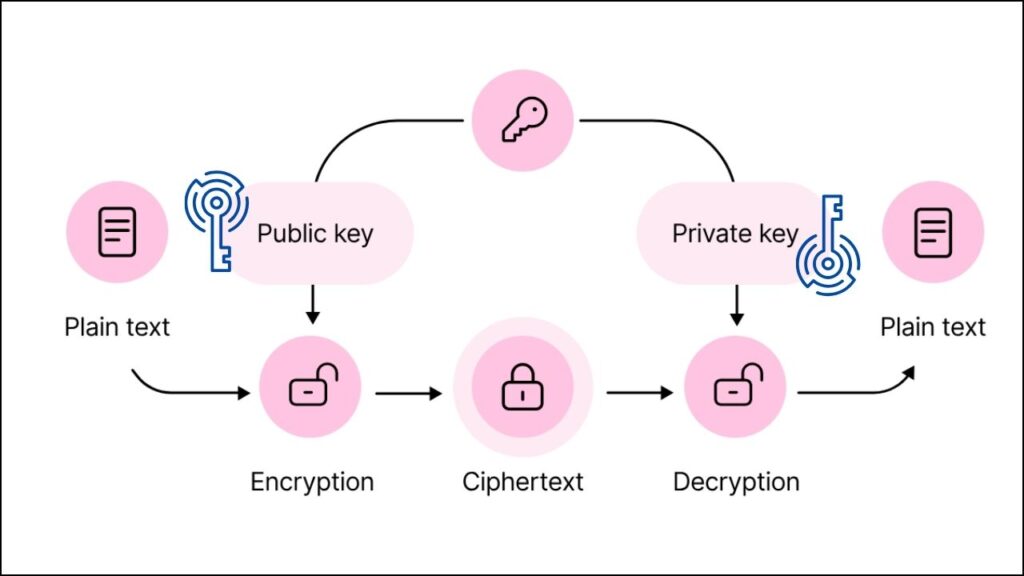
The security of RSA depends on how hard it is to figure out the original prime numbers from the public key. For regular computers, this is almost impossible for large numbers—but quantum computers can do it much faster using special algorithms like Shor’s algorithm.
What’s the Difference Between Classical and Quantum Computers?
Classical computers (like your laptop or phone) use bits that are either 0 or 1. Quantum computers use qubits that can be 0, 1, or both at the same time (a property called superposition). This lets them try many possible solutions at once, making them much faster at certain tasks—like factoring large numbers, which is exactly what’s needed to break RSA.
The Reality of the Threat: How Close Are We?
Right now, quantum computers are still in their early stages. The Chinese team broke a 22-bit key—but real-world RSA keys are 2048 or 3072 bits long. That’s like comparing a toy safe to a bank vault.
But experts are worried because quantum computers are getting better fast. Recent studies suggest that a quantum computer with one million noisy qubits could break a 2048-bit RSA key in less than a week. That’s a huge drop from earlier estimates of 20 million qubits.
Current quantum computers only have a few hundred to a few thousand qubits, so we’re still a long way from this scenario. But the trend is clear: the threat is real and getting closer.
What Is Post-Quantum Cryptography? (And Why Should You Care?)
Post-quantum cryptography (PQC) is a new type of encryption that’s designed to be secure even against quantum computers. Leading organizations are working to create and standardize these new algorithms.

Switching to PQC is a big job, but it’s essential for anyone who wants to keep their data safe in the future. Governments, banks, and tech companies are already starting to make the change.
Practical Steps: What You Can Do Right Now
Here’s how you can protect yourself and your business from the coming quantum threat:
- Stay Informed: Keep up with news about quantum computing and cybersecurity.
- Check Your Systems: Find out if your software and devices use RSA encryption.
- Plan for Upgrades: Talk to your IT team or service providers about switching to post-quantum cryptography.
- Watch for Warnings: Pay attention to alerts from organizations about new security standards.
- Educate Your Team: Make sure everyone knows about the risks and what’s being done to stay safe.
Real-World Examples: Who’s at Risk?
- Banks and Financial Services: Online banking, credit card payments, and stock trading all rely on RSA encryption.
- Tech Companies: Messaging apps, email providers, and cloud services use RSA to protect your data.
- Governments: Secure communications, classified information, and citizen data are all at risk if encryption is broken.
The “Harvest Now, Decrypt Later” Attack
One of the biggest worries is something called a “harvest now, decrypt later” attack. This means that hackers could steal encrypted data today, store it, and then decrypt it years later when quantum computers are powerful enough. That’s why it’s so important to switch to post-quantum cryptography as soon as possible.
How the Universe’s Basic Building Blocks Exploded Into Existence, According to a Physicist
Physicists Catch Light in Imaginary Time: What This Means for Science and You
AI Just Made 2D Materials Stronger—Here’s How It’s Changing the Future of Material Science
FAQs About China Uses Quantum Computer to Break RSA Encryption
Q: Is my online banking safe right now?
A: Yes, for now. Current quantum computers can’t break real-world RSA encryption, but experts warn that could change in the next decade.
Q: What is a qubit?
A: A qubit is the basic unit of information in a quantum computer. Unlike a regular bit (which is 0 or 1), a qubit can be both at the same time, making quantum computers much more powerful for certain tasks.
Q: How long until quantum computers can break RSA?
A: Estimates vary, but some studies say a quantum computer with one million qubits could break RSA-2048 in less than a week. Current quantum computers only have a few thousand qubits, so this is still years away.
Q: What is post-quantum cryptography?
A: Post-quantum cryptography is a new type of encryption that’s designed to be secure against attacks from both classical and quantum computers.
Q: Should I be worried about my personal data?
A: Not immediately, but it’s important to stay informed and support efforts to upgrade to post-quantum security.