In 2025, the phrase chip-driven lending surge fuels growth of AI computing startups is reshaping how technology companies operate, innovate, and expand. This trend is not just a headline; it’s a fundamental shift in how emerging companies access capital, manage risk, and compete in the rapidly evolving world of artificial intelligence (AI). At the heart of this movement are AI chips—specialized hardware that powers everything from advanced chatbots to self-driving cars. These chips have become so valuable that startups now use them as collateral to secure major loans, fueling a new era of growth and competition.
This article will guide you through the mechanics of chip-backed borrowing, why it’s happening, who the major players are, and what this means for professionals and the broader tech industry. Whether you’re a curious student, a seasoned tech investor, or a professional looking to pivot into AI, this comprehensive guide will help you understand the landscape and make informed decisions.
Table of Contents
Chip-Driven Lending Surge Fuels Growth of AI Computing Startups
| Topic | Details |
|---|---|
| Total AI & ML Startup Funding (Q1 2025) | $73.6 billion across 1,603 deals |
| Global AI Chip Startup Investments (2025) | $11.6 billion, 140+ deals |
| AI Chip Revenue (2027 projection) | $83.25 billion |
| People Working in AI (2025) | 97 million globally |
| Largest AI Startup Funding Rounds | OpenAI ($157B valuation), xAI, Databricks, Anthropic |
| Top AI Chip Startups | Tenstorrent, Mythic AI, Cerebras, Untether AI, Esperanto Technologies |
The chip-driven lending surge is a powerful force reshaping the future of AI computing startups. By using high-value chips as collateral, startups can access the capital needed to innovate, scale, and compete in a fast-moving market. This trend is driving job creation, new business models, and a wave of technological breakthroughs. However, it also requires careful risk management and a deep understanding of both technology and finance. For professionals, investors, and entrepreneurs, this is an exciting and pivotal time to be involved in the AI revolution.
What Is Chip-Driven Lending and Why Is It Happening?
Chip-driven lending is a new financial strategy in which AI startups use their stockpile of high-value computer chips as collateral for loans. This approach is gaining traction because AI chips—like those made by Nvidia, AMD, and a new wave of startups—are in extremely high demand and short supply. These chips are essential for training and running AI models, and their value has skyrocketed as more companies race to build smarter, faster, and more capable AI systems.
Here’s why this is happening:
- Explosive AI Growth: The AI industry is expanding at a record pace. In just the first quarter of 2025, AI and machine learning startups raised over $73 billion in funding across more than 1,600 deals.
- Chip Scarcity: The supply of advanced AI chips can’t keep up with demand. This scarcity makes the chips themselves a valuable asset—almost like gold in a digital economy.
- Creative Financing: Traditional lending often requires real estate or cash as collateral. But for AI startups, their most valuable assets are often their chips. By using these chips as collateral, they can access much larger loans to fuel growth.
Why Are AI Chips So Valuable?
AI chips are not your everyday computer parts. They are designed to handle massive amounts of data and perform complex calculations at lightning speed. Here’s what makes them so important:
- Training AI Models: Building advanced AI—like large language models or image recognition systems—requires enormous computing power.
- Running Real-Time AI Applications: From voice assistants to autonomous vehicles, AI chips enable real-time decision-making and data processing.
- Enabling Innovation: The more powerful the chip, the more innovative and efficient the AI system can be.
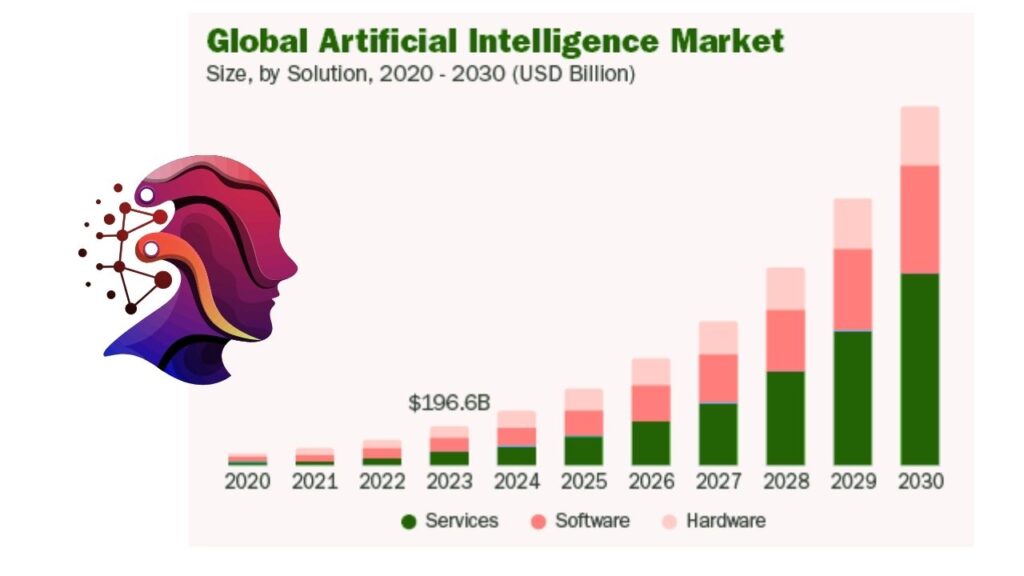
As a result, the global market for AI chips is projected to reach over $83 billion by 2027, with demand expected to continue climbing for years to come.
How Does Chip-Backed Borrowing Work?
Let’s break down the process in a simple way:
- Acquiring Chips: A startup purchases a large quantity of high-end AI chips.
- Using Chips as Collateral: The startup offers these chips as collateral to a lender—like a bank or private equity firm—in exchange for a loan.
- Expanding Operations: With the loan, the startup can buy more chips, rent or build new data centers, and hire top talent.
- Scaling Rapidly: This allows the company to serve more customers, train better AI models, and stay ahead of competitors.
- Repaying the Loan: As the company grows and generates revenue, it repays the loan. If it fails, the lender can take the chips and resell them.
This model is similar to how businesses might use real estate or equipment to secure loans, but in this case, the chips themselves are the prized asset.
Who Are the Major Players?
Several companies are leading the charge in chip-driven lending and AI infrastructure:
- CoreWeave: Known for its rapid expansion, CoreWeave has raised billions using Nvidia chips as collateral to build massive data centers.
- Lambda Labs: This company has secured hundreds of millions to expand its cloud and AI infrastructure.
- Tenstorrent, Mythic AI, Cerebras, Untether AI, Esperanto Technologies: These startups are not only developing their own advanced chips but are also leveraging their hardware for financing and growth.
On the lending side, major financial institutions and private equity firms are entering the arena, seeing the value and relative safety in lending against such high-demand assets.
Why Are Investors and Lenders Interested?
- High Demand, High Value: AI chips are among the most sought-after assets in tech today. Their value is underpinned by real, growing demand.
- Potential for Rapid Returns: Startups that scale quickly in the AI space can achieve billion-dollar valuations within a few years.
- Collateral That’s Easy to Value: Unlike some intangible assets, chips have clear market prices and can be resold if necessary.
For investors, this means a chance to participate in the AI boom while managing risk. For lenders, it means making loans that are backed by assets with strong resale value.
What Are the Risks?
While chip-driven lending is fueling growth, it’s not without risks:
- Technological Obsolescence: AI chips can become outdated quickly as new generations are released. If a startup defaults, lenders might be left with chips that have lost value.
- Market Volatility: The AI chip market is subject to rapid changes in supply and demand, which can affect prices and collateral value.
- Overleveraging: Some startups may borrow more than they can realistically repay, especially if market conditions change or if competition intensifies.
- Economic Downturns: Broader economic challenges could reduce demand for AI services, impacting both startups and chip values.
How Is This Shaping the Future of AI and Tech Careers?
The surge in chip-driven lending is creating a ripple effect across the technology workforce:
- Job Creation: By 2025, nearly 100 million people globally are working in AI-related roles, from hardware engineering to software development, data science, and AI ethics.
- New Skill Demands: There’s a growing need for professionals who understand both AI software and the hardware that powers it.
- Specialization Opportunities: As AI applications become more industry-specific, there’s strong demand for experts in healthcare, finance, logistics, and more.
- Continuous Learning: The rapid pace of change means that professionals need to stay updated on the latest technologies, tools, and best practices.
The Most Promising AI Startups and Sectors
While general-purpose AI platforms are growing, some of the most exciting innovation is happening in specialized sectors:
- Healthcare: Startups are using AI chips to power medical imaging, diagnostics, and drug discovery.
- Finance: AI is transforming risk analysis, fraud detection, and customer service.
- Gaming and Entertainment: Real-time AI is enabling more immersive experiences.
- Aerospace and Defense: Advanced chips are powering autonomous systems and next-generation analytics.
Companies like Abridge (clinical AI), Synthesia (AI video), and others are reaching unicorn status by focusing on high-impact, industry-specific solutions.
Step-by-Step Guide: How Startups Use Chip-Driven Lending
- Identify Needs: Startups assess how much computing power they need to train and deploy their AI models.
- Source Chips: They purchase or lease high-end AI chips from manufacturers or secondary markets.
- Negotiate Loans: The chips are used as collateral to secure loans from banks or private investors.
- Build Infrastructure: Funds are used to expand data centers, hire talent, and develop new products.
- Launch and Scale: With more resources, startups can bring products to market faster and attract more customers.
- Monitor Risk: Companies must keep an eye on chip values, market trends, and their own financial health to avoid overextending.
- Repay or Refinance: As revenue grows, loans are repaid or refinanced to support further expansion.
Israeli Scientists Reveal the World’s First Brain-Like AI Chip That Teaches Itself
Amazon Unveils Project Rainier—Massive AI Chip Cluster to Train the Future of Machine Learning
China’s Ambitious AI Expansion Targets 115,000 Nvidia Chips for Desert-Based Data Centers
FAQs About Chip-Driven Lending Surge Fuels Growth of AI Computing Startups
Q: Why are AI chips used as collateral instead of traditional assets?
A: AI chips are in extremely high demand and have strong resale value, making them attractive and reliable collateral for lenders.
Q: Could chip-backed lending create a financial bubble?
A: While there are risks, the ongoing demand for AI chips and the underlying value of the technology provide a strong foundation. However, rapid changes in technology or market saturation could pose challenges.
Q: What skills are most valuable in the AI chip and lending ecosystem?
A: Hardware engineering, AI model development, data center management, and financial risk analysis are all in high demand.
Q: What happens if a startup defaults on a chip-backed loan?
A: The lender takes possession of the chips and can resell them. The risk is that if the chips have lost value, the lender may not recover the full loan amount.
Practical Advice for Professionals and Investors
- Stay Informed: Follow industry news and official reports to keep up with trends in AI hardware and financing.
- Build Relevant Skills: Whether you’re in engineering, data science, or finance, understanding the interplay between AI software and hardware is increasingly important.
- Network: Engage with communities, conferences, and online forums focused on AI and chip technology.
- Evaluate Risk Carefully: For investors, assess not just the technology but the financial health and strategy of startups using chip-backed lending.