Quantum computers are the next giant leap in technology, and Denmark is about to become a global hub for this “quantum leap” with Magne—the world’s first commercially available Level 2 quantum computer. This is not just another tech story; it’s about redefining what’s possible in science, medicine, and business, and ensuring Europe stays at the forefront of the future.

Magne will be built in Copenhagen, a city already famous for green energy and groundbreaking science. It’s being developed by QuNorth, a new company created by EIFO (Denmark’s Export and Investment Fund) and the Novo Nordisk Foundation, each investing €40 million for a total of €80 million. The project is 100% Danish-owned, but with Microsoft and Atom Computing as world-leading partners—Microsoft providing the brain (software), and Atom Computing the brawn (hardware). Magne is not just big news for Denmark; it’s a game-changer for Europe and the world.
Denmark’s Magne
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Project Name | QuNorth |
| Computer Name | Magne (inspired by Thor’s son in Norse mythology) |
| Type | Level 2 Quantum Computer (logical qubits, advanced error correction) |
| Qubits | 50 logical qubits (over 1,200 physical qubits) |
| Ownership | 100% EIFO & Novo Nordisk Foundation (Denmark) |
| Major Partners | Microsoft (software), Atom Computing (hardware) |
| Investment | €80 million total (€40 million each) |
| Location | Innovation District Copenhagen |
| Construction Start | Autumn 2025 |
| Operational Date | Early 2027 |
| Key Applications | Drug discovery, materials science, logistics, finance, chemicals |
| Region’s Role | Nordic researchers and businesses get priority access; Magne aims to place Denmark and Europe at the forefront of quantum innovation |
| Significance | First operational commercial Level 2 quantum computer; full-stack integration (hardware, software, algorithms, control) |
| Official Project Site | www.qunorth.com (for latest updates and official information) |
Magne is more than a scientific milestone—it’s a statement that Denmark and Europe are serious about shaping the future. By building the world’s first commercially available Level 2 quantum computer in Copenhagen, Denmark is ensuring that Nordic researchers and companies have the tools they need to lead in medicine, materials, logistics, and beyond.
Magne is a leap ahead, but it’s also an open invitation: to scientists, students, startups, and businesses ready to solve the world’s toughest problems. With Magne, the quantum future isn’t just coming—it’s arriving, and Denmark is at the helm.
What Is a Quantum Computer—And Why Does Magne Matter?
A quantum computer isn’t just a faster version of your laptop. It works entirely differently, using “qubits” instead of the usual bits. A qubit is a tiny particle (like an atom or electron) that can be both “0” and “1” at the same time, thanks to a weird quantum effect called superposition.
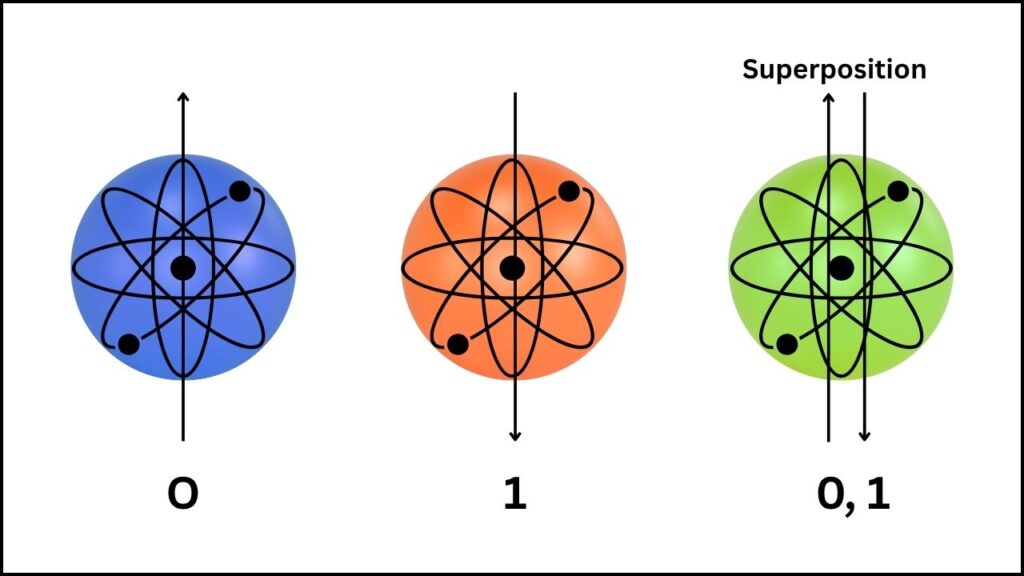
This lets quantum computers explore many possibilities at once, making them potentially millions of times faster for certain problems.
But quantum computers have been noisy and error-prone—until now. Magne is what’s called a Level 2 quantum computer. That means it uses logical qubits, which are built from lots of physical qubits and include advanced error correction. This makes Magne stable, reliable, and ready for real-world tasks—a first for commercial machines.
Why Denmark? Why Now?
Denmark is a small country with a big reputation in science and green tech. But in the global race for quantum computing, the US and China have been racing ahead, while Europe risks falling behind. Danish leaders realized that without world-class quantum machines, Danish and Nordic researchers and businesses would miss out on the next wave of discovery.
Morten Bødskov, Denmark’s Minister of Industry, Business, and Financial Affairs, puts it clearly: The world is changing rapidly, and Europe must not be left behind. “With the investment in the world’s strongest quantum computer, we are making a solid shift in the global quantum race,” he said. “This will benefit all of Europe.”
How Will Magne Be Built and Who Will Use It?

Construction starts in autumn 2025, with Magne expected to be operational by early 2027. QuNorth will be a small, focused company with about 10 employees, plus four PhD/postdoc roles in partnership with Microsoft. Their job is to make sure Magne is used to its full potential by both researchers and businesses across the Nordics.
Priority access goes to Nordic users—scientists, students, startups, and companies working on hard problems in medicine, chemistry, logistics, finance, and advanced materials. Imagine a pharmaceutical company testing millions of drug combinations in minutes, or a logistics firm optimizing thousands of truck routes in seconds. Magne will make these possibilities real.
What Makes Magne So Powerful?
Magne’s strength comes from its 50 logical qubits, built from over 1,200 physical qubits.
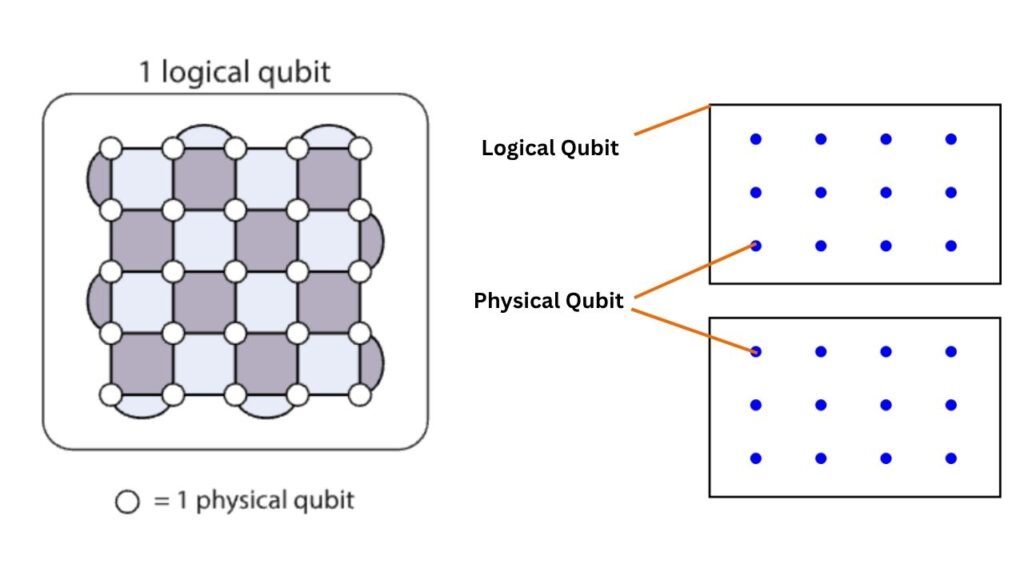
But it’s not just the number—it’s the quality. Logical qubits are error-corrected, meaning they can maintain information even when tiny mistakes happen (which is common in quantum systems). This reliability unlocks what’s called quantum advantage: the point where a quantum computer can solve a practical problem that’s impossible for even the biggest supercomputers.
Magne is a full-stack system: It has the hardware, the operating system, the software, the algorithms, and the control electronics—all integrated and ready to run real tasks. Microsoft is customizing its Azure quantum software for Atom Computing’s neutral atom hardware, making Magne a true turnkey solution for industry and research.
What Problems Will Magne Solve?
Medicine: Discover new drugs by simulating how molecules interact at the atomic level—something too complex for today’s computers.
Materials Science: Design stronger, lighter, or more efficient materials for batteries, solar panels, or airplanes.
Logistics: Optimize shipping and transport routes to save fuel, cut costs, and reduce pollution.
Finance: Model complex financial systems, detect fraud, or optimize investments in ways not possible today.
Chemistry: Unlock new chemical reactions or catalysts to make industrial processes cleaner and more efficient.
These are just a few examples. As researchers and companies start using Magne, we’ll discover even more ways quantum computing can change the world.
How Does Magne Compare to Other Quantum Computers?
Most quantum computers today are Level 1 (or “NISQ”—Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum). They can’t correct their own errors, so they’re mostly used for research and experiments. Level 2 machines like Magne are stable and reliable enough for real work. No other commercial quantum computer today offers this combination of scale and error correction.
Step-by-Step Guide: How Will Magne Change Science and Business?
Step 1: Understanding the Problem
Scientists and businesses face problems with so many possible answers that even supercomputers get stuck. These are called combinatorial problems—like finding the best way to arrange thousands of shipping containers, or simulating how a new drug molecule interacts with every cell in the body.
Step 2: Encoding the Problem for Magne
Experts translate real-world questions into quantum algorithms—special instructions Magne can understand. Microsoft’s software tools make this encoding easier for non-experts, too.
Step 3: Running the Computation
Magne uses its logical qubits to explore all possible solutions at once, thanks to superposition and entanglement. Its error correction keeps the answers reliable, even with lots of calculations.
Step 4: Analyzing the Results
Magne returns results in minutes or hours—not years. Researchers and companies get insights that would be impossible with today’s computers.
Step 5: Applying the Insights
New medicines are developed. Supply chains become more efficient. Financial models become more accurate. The possibilities are endless, and Magne will help Nordic innovators lead the way.
Microsoft Edge Gets Lightning-Fast Speed Boost—Here’s How It Beats Chrome Now
Microsoft Quietly Removes Key Password Management Feature, Sparking User Concerns
FAQs About Denmark’s Magne
Q: What is a quantum computer, and how is it different from a regular computer?
A: A quantum computer uses qubits, which can be in many states at once, making it millions of times faster for certain problems. Regular computers use bits that are only 0 or 1.
Q: Why is Magne special?
A: Magne is the first commercial Level 2 quantum computer, with error correction for reliable, real-world results. Most quantum computers today can’t do this.
Q: Who will get to use Magne?
A: Nordic researchers and businesses will have priority. QuNorth will help connect people to Magne’s power.
Q: When will Magne be ready?
A: Construction starts autumn 2025, with early operations expected by 2027.
Q: Why is this important for Europe?
A: Without quantum leadership, Europe risks falling behind the US and China. Magne ensures European scientists and companies can compete globally.
Q: Will Magne break internet security?
A: Not right away. Future quantum computers might break some encryption, but new “quantum-safe” security is already being developed—and Magne will help test these new systems.
Q: How is Microsoft involved?
A: Microsoft is providing Magne’s quantum software and has its largest quantum lab in Denmark. Their tools will help make Magne easy to use for everyone.