China is making bold moves in the world of artificial intelligence (AI) by planning to install over 115,000 Nvidia AI chips in a network of new data centers built across its vast desert regions. This ambitious project is part of China’s strategic push to become a global leader in AI, harnessing the power of advanced hardware and innovative infrastructure. But what does this mean for the world, and how is China overcoming the significant challenges involved? Let’s explore the details in a way that’s easy to understand, yet packed with valuable insights for professionals and curious minds alike.

Table of Contents
China’s Ambitious AI Expansion Targets 115,000 Nvidia Chips for Desert-Based Data Centers
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Project Scope | Over 115,000 Nvidia H100/H200 chips planned for 39 new data centers in Xinjiang & Qinghai deserts |
| Purpose | Train advanced AI models, boost China’s AI self-sufficiency, and compete globally |
| US Export Ban | H100/H200 chips banned from export to China since 2022 due to national security concerns |
| Feasibility Issues | Unclear how chips will be acquired legally; US and China silent on sourcing strategies |
| Domestic Alternatives | China accelerating development of Huawei Ascend chips as a backup |
| Strategic Initiative | Part of “East Data West Computing”—using western China’s cheap land, renewable energy, and cool climate |
| Industry Impact | Could support AI models on par with DeepSeek; still smaller than US hyperscalers (Meta, Google, AWS, xAI) |
| Professional Relevance | Opens new opportunities in AI R&D, data center management, and chip manufacturing |
China’s plan to install 115,000 Nvidia chips in desert-based data centers is a landmark project in the global AI race. Despite facing significant challenges from US export controls, China is pushing forward with massive investments in infrastructure, domestic chip innovation, and strategic use of renewable energy. This ambitious initiative not only signals China’s determination to achieve AI self-sufficiency but also opens new opportunities for professionals in technology, data management, and research. As the world watches, China’s desert data centers could become a defining symbol of the next era in artificial intelligence.
Understanding China’s AI Expansion
What Is China Doing?
China is investing heavily in AI infrastructure by building massive data centers in the remote deserts of Xinjiang and Qinghai. These facilities are designed to house over 115,000 Nvidia H100 and H200 chips, which are among the most powerful processors available for AI training and inference. The goal is to create a computing backbone capable of supporting the next generation of AI models—ranging from large language models to advanced image and data processing systems.
This expansion is part of a national strategy called “East Data West Computing,” which aims to move data processing and storage from China’s crowded eastern cities to the resource-rich western provinces. The western regions offer several advantages: cheaper land, abundant renewable energy (especially solar and wind), and cooler climates that help reduce the cost of cooling the data centers.
Why the Focus on Nvidia Chips?
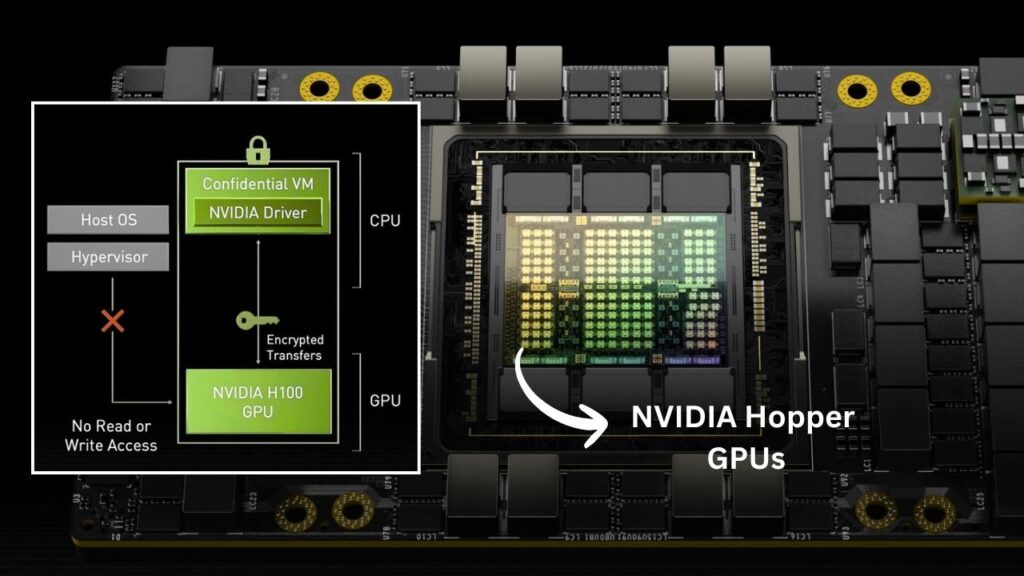
Nvidia’s H100 and H200 chips are considered the industry standard for high-performance AI computing. These chips are essential for training large and complex AI models, which require vast amounts of data to learn patterns, language, and decision-making processes. The chips’ advanced architecture allows for faster processing, greater efficiency, and the ability to handle the massive datasets used in modern AI research.
The Challenge: US Export Controls
In 2022, the US government imposed strict export controls on advanced AI chips, including Nvidia’s H100 and H200, citing national security concerns. These controls prohibit US companies from selling such chips to Chinese firms without a special license, which has not been granted for these products. This move was designed to slow China’s progress in AI and supercomputing, given the technology’s potential military and strategic applications.
Despite these restrictions, Chinese companies and government agencies have outlined plans to use these very chips in their new data centers. How they intend to legally acquire such a large quantity of restricted hardware remains unclear, and both US and Chinese officials have declined to comment on the specifics.
The Strategic Importance of Desert-Based Data Centers
Why Build Data Centers in the Desert?
China’s decision to build data centers in the deserts of Xinjiang and Qinghai is both practical and strategic:
- Abundant Renewable Energy: These regions have some of China’s largest solar and wind farms, providing a steady, low-cost, and environmentally friendly power supply.
- Cooler Climates: The natural climate helps keep servers cool, reducing the need for expensive air conditioning and lowering overall energy consumption.
- Lower Land and Construction Costs: Land is cheaper and more readily available in these remote areas, allowing for the construction of sprawling data center complexes.
This approach aligns with China’s broader environmental and economic goals, including reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable development.
The “East Data West Computing” Initiative
This initiative is a cornerstone of China’s digital infrastructure plan. By moving data processing to the west, China can:
- Reduce strain on eastern power grids
- Balance regional economic development
- Tap into underutilized renewable energy resources
- Create new jobs and industries in less developed regions
The Role of AI in China’s National Strategy
Why Is AI So Important for China?
AI is seen as a key driver of future economic growth, technological innovation, and national security. China’s leadership has made AI development a top priority, investing billions in research, education, and infrastructure. The country aims to lead the world in AI by 2030, with applications ranging from healthcare and transportation to manufacturing and defense.
Building Advanced AI Models
Training state-of-the-art AI models—such as large language models, image recognition systems, and autonomous vehicle algorithms—requires immense computing power. The more powerful the hardware, the faster and more accurately these models can be trained. By investing in advanced data centers equipped with high-end GPUs, China hopes to accelerate its progress and close the gap with leading US tech companies.
Overcoming the Chip Ban: China’s Multi-Pronged Approach
1. Sourcing Nvidia Chips

While the official path for acquiring Nvidia H100 and H200 chips remains unclear, Chinese companies are exploring every possible legal avenue. Some industry experts speculate that limited quantities may be sourced through third-party markets or existing inventories, but large-scale procurement remains a significant challenge under current US restrictions.
2. Accelerating Domestic Chip Development
Recognizing the risks of relying on foreign technology, China has dramatically increased investment in its domestic semiconductor industry. Companies like Huawei are developing high-performance AI chips, such as the Ascend 910C, which are now being adopted by leading Chinese AI firms. In early 2025, DeepSeek became the first major AI company to fully transition from Nvidia to Huawei chips for its production workloads, signaling a shift toward greater self-reliance.
3. Embracing Open-Source AI
Chinese companies are also leveraging open-source AI models, which are freely available and can be adapted to run on a variety of hardware platforms. This community-driven approach allows for rapid innovation and reduces dependence on proprietary Western technologies.
Step-by-Step Guide: How China’s AI Data Centers Are Built
Step 1: Site Selection
- Identify remote locations with access to renewable energy and favorable climate conditions.
- Assess infrastructure needs, such as power lines, water supply, and transportation links.
Step 2: Infrastructure Development
- Construct large-scale data center buildings, often spanning tens of thousands of square meters.
- Install advanced cooling systems, backup power supplies, and security measures.
Step 3: Hardware Installation
- Deploy thousands of high-performance GPUs, such as Nvidia H100/H200 or Huawei Ascend 910C.
- Integrate servers, storage systems, and networking equipment to create a scalable computing environment.
Step 4: AI Model Training
- Use the data center’s computing power to train large AI models, process big data, and support cloud services.
- Collaborate with research institutions and tech companies to develop cutting-edge applications.
Step 5: Scaling and Maintenance
- Monitor performance and energy consumption, optimizing systems for efficiency.
- Upgrade hardware and software as new technologies become available.
Practical Advice for Professionals
For Data Center Managers
- Prioritize Energy Efficiency: Leverage renewable energy sources and advanced cooling technologies to minimize costs and environmental impact.
- Plan for Flexibility: Design infrastructure that can accommodate multiple types of hardware, anticipating shifts in global supply chains and technology trends.
For AI Researchers and Developers
- Optimize for Available Hardware: Develop models that can run efficiently on both foreign and domestic chips, ensuring continuity in the face of supply chain disruptions.
- Engage with Open-Source Communities: Contribute to and benefit from global AI research, accelerating innovation through collaboration.
For Policy Makers
- Support Domestic Innovation: Invest in R&D and education to foster a robust local semiconductor industry.
- Monitor Global Trends: Stay informed about international regulations and market dynamics to anticipate challenges and opportunities.
China’s AI Chip War Strategy May Already Be Outpacing the West’s Response
China Unveils Quantum-Proof Blockchain Tech Designed to Survive the Next Cyber Era
China Unveils FuXi 2.0 AI-Powered Weather Forecasting Model: A New Era in Meteorology
FAQs About China’s Ambitious AI Expansion Targets 115,000 Nvidia Chips for Desert-Based Data Centers
Q1: Why does China want so many Nvidia chips?
China needs high-performance chips like Nvidia’s H100 and H200 to train advanced AI models, which are essential for competing in global technology and innovation.
Q2: How can China get these chips if they’re banned?
The official method for acquiring such chips is unclear. Chinese companies are exploring all legal avenues, while also accelerating domestic chip development.
Q3: What happens if China can’t get Nvidia chips?
China is investing heavily in domestic alternatives, such as Huawei’s Ascend chips, and some companies have already made the switch for their main AI workloads.
Q4: Are these data centers bigger than those in the US?
Even with 115,000 chips, China’s planned data centers are still smaller than those operated by US tech giants like Meta, Google, Microsoft, and AWS.
Q5: What is “East Data West Computing”?
It’s a national strategy to build data centers in western China, leveraging local renewable energy and resources to support the country’s digital economy.