Electronic Skin: Imagine a world where robots can feel the texture of a leaf, or where a prosthetic hand can sense a gentle tap or a warm cup of tea. Thanks to a new smart material breakthrough, this vision is rapidly becoming a reality. The latest advances in electronic skin (e-skin) technology are set to revolutionize not only robotics and human prosthetics, but also wearable health monitoring, gesture control, and much more.
This article explores how this new smart material is changing the landscape, what it means for professionals and everyday users, and how you can prepare for the exciting future of touch-sensitive technology.
Electronic Skin
| Feature/Statistic | Details |
|---|---|
| Breakthrough | Self-healing, ultra-thin, flexible e-skin with real-time sensing and magnetic field detection |
| Healing Speed | Recovers over 80% functionality in 10 seconds after damage |
| Resolution | 1mm spatial resolution for precise gesture and touch mapping |
| Applications | Robotics, prosthetics, healthcare, sports, human-machine interfaces |
| Market Growth | Rapid expansion in Asia-Pacific; strong adoption in healthcare and robotics |
| Official Resource | Science Advances Journal |
The development of a new smart material for electronic skin is a game-changer for robotics, prosthetics, and wearable health technology. With its self-healing, ultra-thin, and highly sensitive design, e-skin brings us closer to a future where machines can feel, prosthetics can sense, and health can be monitored seamlessly and non-invasively.
As the technology matures, we can expect to see e-skin integrated into more aspects of our daily lives, from advanced medical devices to intuitive human-machine interfaces. Whether you’re a professional in robotics, healthcare, or simply fascinated by the future of technology, now is the perfect time to get acquainted with this exciting innovation.
What Is Electronic Skin and Why Does It Matter?
Electronic skin, or e-skin, is a thin, flexible material that mimics the properties of human skin. It can sense touch, pressure, temperature, and even magnetic fields. The goal is to give robots and prosthetic limbs a sense of touch, making them more lifelike and capable of delicate, precise movements.
Why Is This Important?
- For Robots: E-skin allows robots to interact safely and gently with humans and their environment. Imagine a robot that can pick up a fragile egg without breaking it or shake hands with a person without squeezing too hard.
- For Prosthetics: People with prosthetic limbs could regain the sensation of touch, improving their quality of life and their ability to perform everyday tasks.
- For Healthcare: E-skin can monitor vital signs, muscle activity, and fatigue in real time, offering new ways to track health without invasive procedures.
How Does the New Smart Material Work?
The Science Behind the Breakthrough
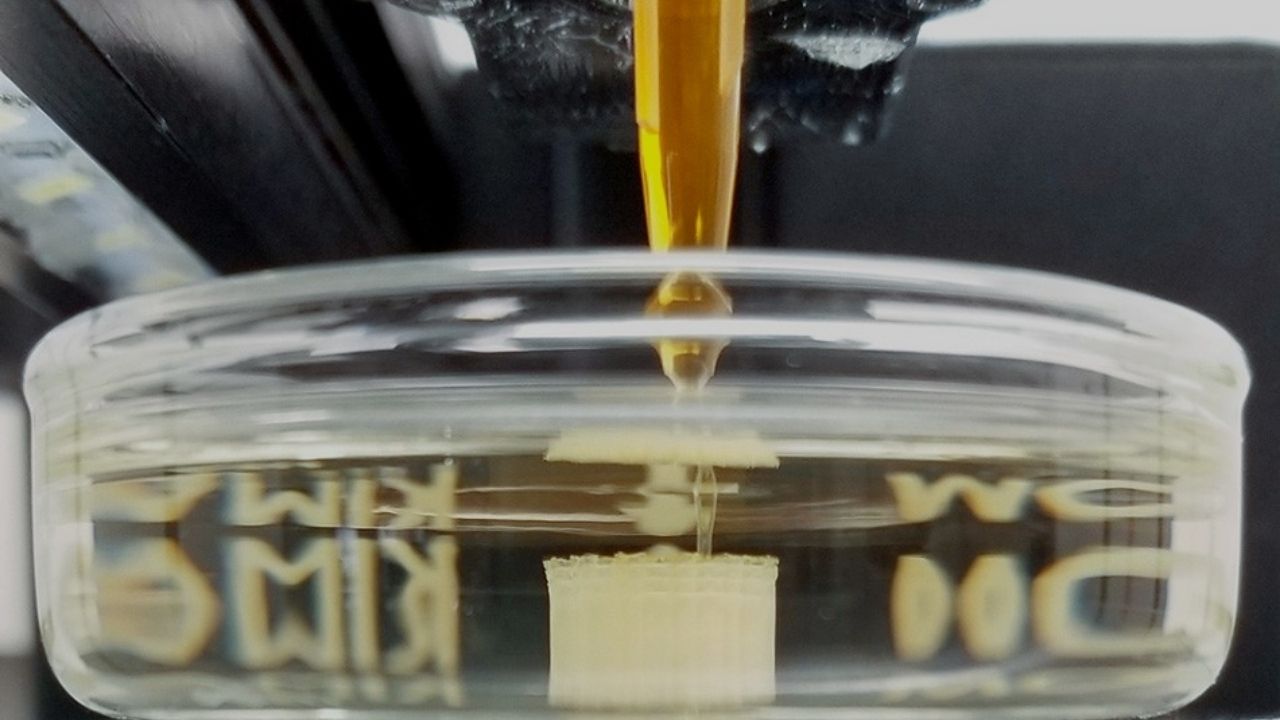
Recent research has led to the creation of self-healing, ultra-thin, and highly sensitive e-skin. Here’s what makes it special:
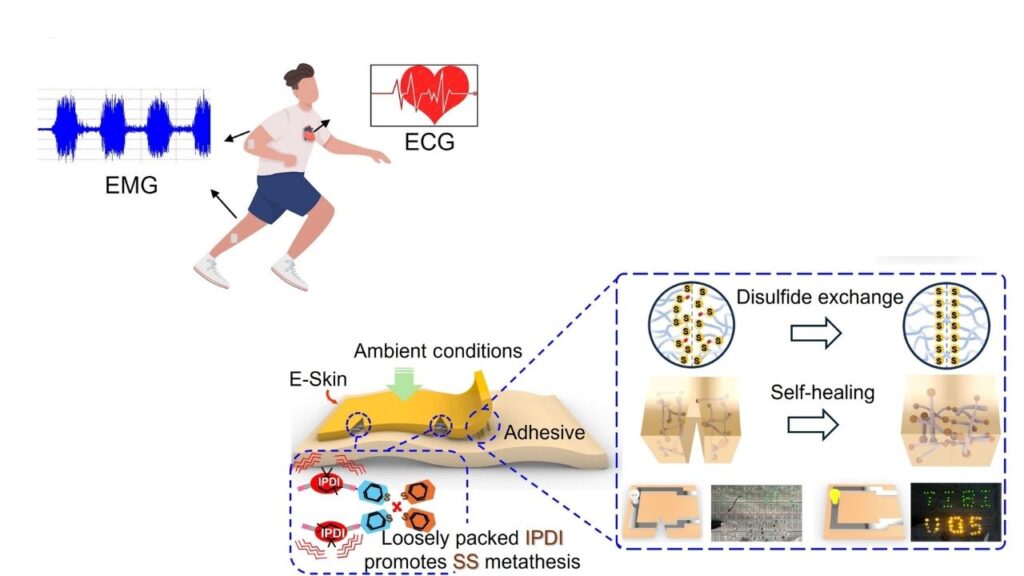
- Self-Healing: If the e-skin gets scratched or damaged, it can repair itself in just seconds, restoring over 80% of its original function. This is much faster than older materials, which could take hours to heal.
- High Sensitivity: The new e-skin can detect very small changes in pressure, temperature, and even magnetic fields, with a spatial resolution as fine as 1 millimeter.
- Flexible and Stretchable: It bends and stretches just like real skin, making it comfortable to wear or wrap around robotic limbs.
- Energy Efficient: The design uses advanced signal processing so it can run for long periods without needing much power.
How Is E-Skin Made?
The latest e-skin is made from layers of special materials:
- Top Layer: Ultra-thin, breathable membrane that lets air and moisture pass through.
- Middle Layer: Magnetosensitive or pressure-sensitive material that detects changes in the environment.
- Bottom Layer: A tiny computer chip that reads the signals and figures out what’s happening on the surface.
Real-World Applications: Where Will We See E-Skin?
1. Robotics
Robots equipped with e-skin can:
- Sense touch, pressure, and even gestures, making them safer and more adaptable.
- Perform delicate tasks, such as surgery or handling fragile objects, with greater precision.
- Recognize and respond to human gestures for more intuitive controls.
2. Prosthetics
For people with artificial limbs, e-skin offers:
- The ability to feel touch, temperature, and texture.
- Improved control and feedback, making prosthetics feel more like natural limbs.
- Enhanced safety, as users can sense when they’re pressing too hard or touching something hot.
3. Healthcare and Wearables
E-skin can be used in:
- Continuous health monitoring, such as tracking heart rate, muscle activity, and fatigue.
- Athletic training, by measuring muscle strength and performance in real time.
- Medical rehabilitation, helping patients recover from injuries with precise feedback.
4. Human-Machine Interfaces
E-skin enables:
- Touchless gesture control for computers, smart homes, and virtual reality.
- More natural and intuitive interactions with devices and machines.
The Market and Career Opportunities
The electronic skin market is booming, especially in Asia-Pacific, where countries like Japan, China, and South Korea are leading the way in research and adoption. The technology is expected to grow rapidly over the next decade, creating new opportunities in:
- Biomedical engineering
- Robotics and automation
- Wearable technology development
- Sports science and rehabilitation
- Consumer electronics
Industry experts highlight the potential for e-skin to revolutionize personalized medicine, prosthetics, and human-machine interaction, while also noting the challenge of making these materials durable and affordable for everyone.
Step-by-Step Guide: How E-Skin Technology Works
Step 1: Sensing
The e-skin’s sensitive layers detect changes in pressure, temperature, and magnetic fields. For example, if you tap the e-skin, it senses the pressure and location of your finger.
Step 2: Signal Processing
Tiny computer chips inside the e-skin read these signals and figure out what’s happening. Advanced algorithms help the system “learn” which signals are important and how to interpret them accurately.
Step 3: Healing
If the e-skin is scratched or torn, its self-healing materials bond back together in seconds, restoring most of its function.
Step 4: Feedback
The processed information can be sent to a robot, a prosthetic limb, or a wearable device, allowing it to react—such as gripping an object gently or warning the user of high temperature.
Step 5: Integration
The e-skin can be wrapped around robotic arms, prosthetic hands, or worn as a patch on the body. It’s lightweight, flexible, and comfortable for long-term use.
Satellite LiDAR and AI Enable Rapid Forest Carbon Mapping Breakthrough
Researchers Develop Metallic Materials Using Data-Driven Frameworks and Explainable AI
FAQs About Electronic Skin
Q: How durable is the new electronic skin?
A: The latest e-skin can heal itself in seconds after damage, restoring over 80% of its function. It’s designed to survive daily wear and tear, even in tough environments like underwater.
Q: Is e-skin safe for human use?
A: Yes, the materials are biocompatible and safe for use on human skin or in prosthetic devices. They’re also breathable and comfortable to wear.
Q: Can e-skin be used for sports and fitness?
A: Absolutely! E-skin can monitor muscle activity, fatigue, and performance in real time, making it valuable for athletes and trainers.
Q: How soon will we see e-skin in everyday products?
A: Some applications, like health monitoring patches, are already in development. More complex uses, such as robotic skin and advanced prosthetics, are expected to become mainstream within the next 5–10 years.
Q: Where can I learn more about e-skin research?
A: Visit the Science Advances Journal for the latest peer-reviewed studies and breakthroughs.