Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the world rapidly, and at the core of this revolution is the race to build the most powerful AI computing machines. Among the latest breakthroughs is Huawei’s CloudMatrix 384 AI system, a groundbreaking supercomputing cluster designed to directly challenge Nvidia, the long-time global leader in AI hardware. This article offers an in-depth look at Huawei CloudMatrix 384 — what it is, how it works, why it matters, and practical insights for professionals and enthusiasts alike.

Table of Contents
What is Huawei CloudMatrix 384?
Unveiled in 2025 at the World Artificial Intelligence Conference (WAIC) in Shanghai, the Huawei CloudMatrix 384 is a supercomputer constructed using 384 of Huawei’s Ascend 910C AI chips (known as NPUs — Neural Processing Units), combined with 192 Kunpeng CPUs, creating a massive, rack-scale AI computing system. The cluster achieves approximately 300 petaFLOPS (PFLOPS) of BF16 dense computing power — this means it can perform 300 quadrillion AI operations per second.
To put that into perspective, Nvidia’s flagship AI system, the GB200 NVL72, delivers around 180 PFLOPS. Huawei’s CloudMatrix 384 system outperforms Nvidia’s in several key aspects such as throughput, memory capacity, and bandwidth, although it consumes more power and comes at a higher cost.
Huawei CloudMatrix 384
| Feature | Huawei CloudMatrix 384 | Nvidia GB200 NVL72 |
|---|---|---|
| Number of AI Chips (NPUs) | 384 Ascend 910C | 72 B200 |
| Compute Performance | 300 PFLOPS (BF16 dense compute) | ~180 PFLOPS |
| Memory Capacity | 49.2 TB High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2E) | 13.8 TB HBM |
| Memory Bandwidth | 1229 TB/s | 576 TB/s |
| Interconnect Technology | Fully optical mesh network (6912 optical transceivers) | Copper wiring |
| Power Consumption | ~559 kW | ~145 kW |
| System Cost | Approx. $8 million | Approx. $2.5 million |
| Deployment | Operational on Huawei’s cloud platform | Globally deployed in enterprise AI centers |
Huawei’s CloudMatrix 384 is a landmark in AI supercomputing, effectively challenging Nvidia’s longstanding dominance by emphasizing system-level innovation, impressive compute scaling, and advanced optical networking. It delivers significantly higher compute power, memory capacity, and throughput than Nvidia’s GB200 system, although with higher energy needs and cost.
For AI professionals and enterprises, CloudMatrix offers a new, powerful platform for handling demanding AI models, marking a shift in the global AI computing ecosystem shaped by technology, industry needs, and geopolitical realities. As AI continues to evolve, innovations like CloudMatrix 384 will be pivotal in defining the future of computing infrastructure.
For official details, visit Huawei’s official website.
How Does the CloudMatrix 384 Work?
The design of the CloudMatrix 384 is innovative and tailored to maximize system-level performance through scale, connectivity, and memory optimization.
1. Massive Parallel Processing Power
Huawei’s philosophy emphasizes scaling out with a large number of AI processors rather than relying on a few extremely powerful chips. Although each Ascend 910C chip is individually less potent than Nvidia’s GPUs, Huawei’s approach integrates 384 chips in a tightly coordinated cluster, dramatically increasing total throughput.
2. Supernode Architecture and Optical Interconnects
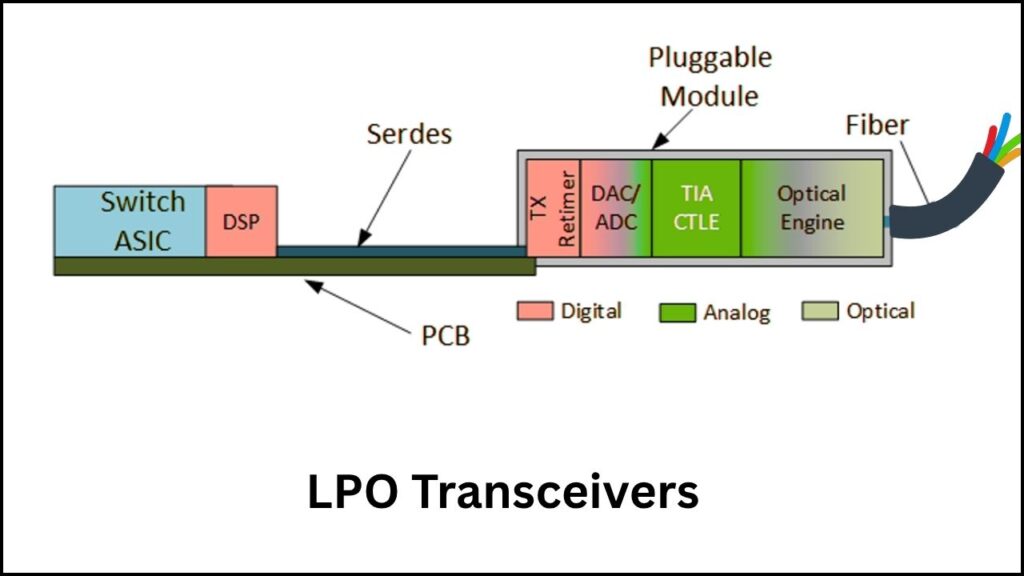
A standout feature is the fully optical mesh network interconnecting all 384 chips. Using 6,912 linear pluggable optical (LPO) transceivers, Huawei replaces traditional copper wiring with light-based communication. This allows data to flow at more than 5.5 petabits per second with ultra-low latency, overcoming bottlenecks common in electric connections and enabling near-instantaneous communication among chips.
3. Exceptional Memory Capacity and Bandwidth
With 49.2 TB of HBM2E memory and 1229 TB/s of memory bandwidth, CloudMatrix 384 offers over 3.6 times the memory capacity and more than twice the bandwidth compared to Nvidia’s GB200 system. This massive, fast memory allows AI models to process huge datasets quickly and efficiently, speeding up both training and inferencing phases.
4. System Stability and Reliability
Huawei uses systematic engineering optimizations that make the cluster stable and efficient — in fact, the system runs as reliably as a well-configured PC despite its complexity. This means enhanced uptime during long AI training sessions and robustness in managing complex AI workloads.
Why CloudMatrix 384 Matters: Practical Insights
For AI Developers and Enterprises
- Faster Large-Scale AI Model Training: Thanks to its raw compute power and memory capacities, CloudMatrix 384 accelerates training for advanced AI models in areas such as natural language processing, computer vision, and recommendation systems.
- Scalable and Stable AI Infrastructure: Enterprises, particularly in China and regions affected by geopolitical restrictions, gain access to a robust and scalable AI computing alternative that is operational on Huawei’s cloud platform.
- Energy and Cost Considerations: The system’s power usage (~559 kW) is significantly higher than Nvidia’s, implying greater energy costs and cooling requirements. Organizations must prepare data center infrastructure accordingly.
For the Global AI Hardware Market
- Increasing Competition: Huawei’s aggressive innovation challenges Nvidia’s market dominance, fostering competition that can lead to faster technological advances and potentially more affordable AI solutions in the future.
- Geopolitical Impact: With U.S. restrictions limiting Chinese access to advanced AI chips, Huawei’s independent development of its CloudMatrix cluster exemplifies a resilient approach to technological sovereignty, influencing global AI hardware dynamics.
Understanding AI System Performance: A Simple Guide
Step 1: Know the Metrics
- PFLOPS (Peta Floating Point Operations per Second): Measures raw AI computing power.
- Memory Capacity & Bandwidth: More and faster memory means AI models can access and process data quickly.
- Interconnect Latency: Lower latency enables better synchronization between chips, crucial for efficient large-scale AI processing.
Step 2: Scale vs. Chip Power
- Traditional systems often focus on buying the most powerful single chips.
- Huawei’s approach emphasizes scalability — more chips operating efficiently in parallel.
Step 3: Energy Efficiency Matters
- Power consumption directly affects operational costs and environmental impact.
- CloudMatrix 384 trades efficiency for raw power, using more energy to achieve higher performance.
Step 4: Deployment Context and Cost
- High-performance AI systems require millions in investment.
- Infrastructure support and software ecosystem also influence return on investment.
The Cloud’s Hidden Cost: How Data Center Water Use Is Quietly Creating a Global Strain
Top Advantages of Cloud-Integrated Data Centers for Smarter Logistics Operations
Researchers Demonstrate Advanced Cooling in Data Centers to Cut Emissions 15–21%
FAQs About Huawei CloudMatrix 384
Q1: How is Huawei CloudMatrix 384 different from Nvidia’s AI systems?
Huawei’s CloudMatrix deploys many smaller Ascend 910C chips interconnected by ultra-fast optical networks versus Nvidia’s fewer but individually more powerful GPUs connected with copper wiring. This means higher total compute and bandwidth at the cost of more power consumption.
Q2: Is CloudMatrix 384 commercially available?
Yes, it is currently operational on Huawei’s cloud platform and primarily targeted at enterprise AI workloads, with a strong presence in China.
Q3: Does CloudMatrix 384 work only with Huawei’s AI software?
While optimized for Huawei’s AI stack, it supports mainstream AI frameworks and models, making it flexible for various AI applications.
Q4: What about power consumption and data center requirements?
CloudMatrix’s 559 kW power usage demands robust electrical infrastructure and advanced cooling systems, increasing operational costs compared to more energy-efficient systems.
Q5: Could Huawei’s CloudMatrix affect the global AI tech landscape?
Absolutely. It symbolizes that companies outside the U.S. can develop competitive, world-class AI hardware, potentially reshaping industry dynamics and supply chains.