Picture a world where your phone recognizes your face in milliseconds, your car avoids accidents before you sense danger, your smartwatch alerts you to health issues instantly—all without sending your private data to the cloud. This is no longer a fantasy. It’s happening today, thanks to Edge AI. In 2025, Edge AI is reshaping the way artificial intelligence interacts with our world, powering devices and systems both big and small with real intelligence—right where the action happens.

Edge AI means that smart, decision-making programs (artificial intelligence) run directly on the devices themselves—smartphones, security cameras, factory machines, wearables, even agricultural sensors—instead of relying on distant cloud servers. This local processing makes devices smarter, faster, more private, and often much more energy-efficient. As industries and consumers demand ever-faster, private, and reliable technology, Edge AI is rapidly becoming the cornerstone of modern digital life.
In this guide, you’ll discover what Edge AI is, how it works, why it’s exploding in popularity, and how it’s changing industries and careers. You’ll find clear analogies, real-world examples, practical advice, and actionable insights—all written so a 10-year-old can follow along, but designed to offer value to professionals, entrepreneurs, and students alike.
Table of Contents
New AI Strategy Brings High-Powered Intelligence to Low-Energy Edge Devices
| Aspect | Details & Stats | Professional Insights |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Artificial intelligence algorithms run directly on local devices—smartphones, cameras, sensors, machines, etc. | Edge AI is driving real-time, low-power, privacy-first strategies for businesses and consumers. |
| Market Impact | 2025 is being called “the year of edge AI”—up to 75% of enterprise data could be processed outside centralized clouds. | Career paths in Edge AI span hardware design, software optimization, IoT, and AI governance. |
| Key Benefits | Instant decisions, stronger privacy, major energy and cost savings, reliability even without cloud connection. | Balance between model accuracy and resource constraints is key; edge-cloud hybrid models are trending. |
| Industry Use Cases | Autonomous vehicles, manufacturing, healthcare, smart cities, agriculture, energy, consumer tech. | Adoption is accelerating in sectors needing speed, safety, and sustainability—Industry 4.0, smart grids. |
| Technology Enablers | Specialized chips (NPUs, ASICs, accelerators), compact AI models (quantization, pruning), lightweight frameworks. | Hardware-software co-design is crucial for performance; federated learning is emerging for privacy. |
| Challenges | Hardware diversity, model complexity, deployment at scale, ethics and explainability, sustainability concerns. | Solutions include hybrid approaches, standardization, and emphasis on fairness, transparency, and recycling. |
Edge AI in 2025 is transforming how we live and work by making everyday devices smarter, faster, and more private. From life-saving medical gadgets to energy-saving smart cities, the impact is enormous—and this is only the beginning. Whether you’re curious about how your phone works, or you’re a professional looking to build the next big thing, Edge AI offers exciting opportunities for everyone.
Edge AI is more than a buzzword—it’s the foundation for a future of instant, personal, and responsible artificial intelligence. As hardware and software continue to advance, and as ethical and environmental concerns shape its growth, Edge AI will become even more essential—and accessible—to us all.
If you want to explore further, consider starting with a simple project, experimenting with a Raspberry Pi or smartphone, or diving into a career in this fast-growing, innovation-driven field. The future of AI is local, efficient, and in your hands.
What is Edge AI? A Simple, Everyday Explanation
Edge AI isn’t about flying robots or talking computers (at least, not yet!). It’s about ordinary gadgets getting smart enough to make decisions on their own—without always asking a “cloud brain” for help. Think of your smartphone recognizing your face to unlock, a security camera spotting an intruder instantly, or a factory robot detecting a faulty part all by itself, without sending video or data back to a server.
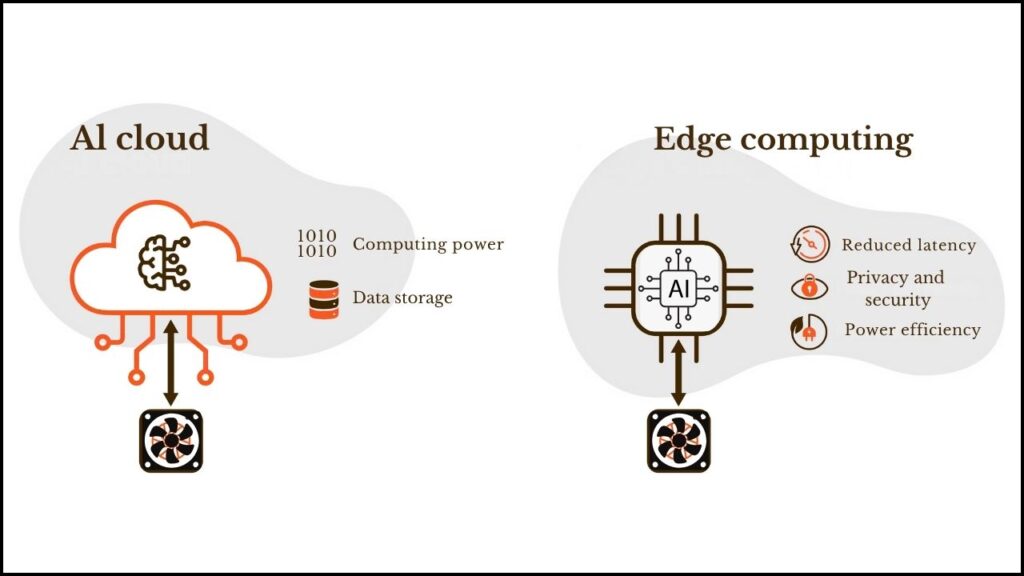
Traditional cloud-based AI works like this: your device collects data (like a picture), sends it to a giant remote computer (the “cloud”), the AI thinks, then sends an answer back. This takes time, uses energy, and means your data travels across the internet—raising privacy and security concerns.
Edge AI flips the script: the smart program lives right on your device. The device collects data, runs the AI, and makes decisions instantly—no waiting, no extra energy for cloud calls, and your data never leaves your hands. For tasks that need speed, privacy, or reliability, this local processing is a game-changer.
Why Does Edge AI Matter?
Imagine a self-driving car that must brake in a split second to avoid a crash. If it has to ask a faraway server for help, the delay could be deadly. With Edge AI, the car’s own “brain” makes the call instantly—saving lives, and keeping your location and driving habits private.
Or picture a hospital bedside monitor that detects a heart problem and alerts staff immediately—no need to send sensitive patient data to a cloud. In agriculture, soil sensors can water crops only where needed, saving water and energy, all without the internet. These are just a few of thousands of real-world uses for Edge AI.
How Does Edge AI Work? The Technology Behind the Scenes
Edge AI isn’t magic—it’s a mix of smart new hardware, clever software tricks, and fresh ways of building artificial intelligence. Here’s how it all comes together:
Specialized Chips: The AI Powerhouse Inside Your Device
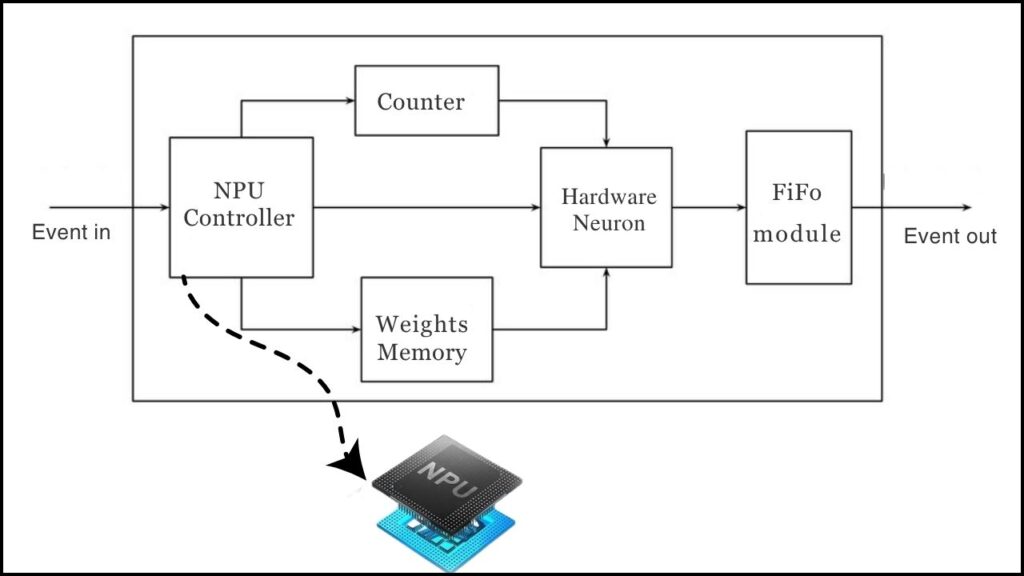
Modern gadgets are getting special “brains” just for AI called neural processing units (NPUs), application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs), or AI accelerators. These chips are designed to handle complex AI workloads—like recognizing images, understanding speech, or analyzing sensor data—much faster and with far less power than standard phone or computer chips. Companies like Apple, NVIDIA, and Qualcomm are at the forefront, packing these chips into phones, cameras, and even factory equipment. This hardware revolution is what makes Edge AI possible on everyday devices.
Optimized AI Models: Small, Fast, and Smart
Big AI models, like those behind ChatGPT or advanced image recognition, are usually too large and slow for phones or sensors. To make them work on the edge, engineers use clever techniques:
- Quantization: Reducing the precision of numbers in the AI model, making it much smaller and faster, with only a tiny loss in accuracy.
- Pruning: Cutting out unnecessary parts of the AI model—like trimming a bush to help it grow better.
- Compact Architectures: Designing new AI models from scratch for efficiency—examples include MobileNet for vision, TinyBERT for language, and SqueezeNet for ultra-lightweight tasks.
These optimized models can run smoothly on low-power chips, ensuring your device stays fast and your battery lasts longer.
Lightweight Frameworks: Software That Makes It Easy
Putting a smart AI model on your device isn’t just about hardware—you also need software that helps it all work together. TensorFlow Lite, PyTorch Mobile, and Edge Impulse are frameworks that let developers easily deploy AI models to phones, cameras, and tiny sensors. These tools handle compatibility issues, speed things up, and help you test and improve your edge AI applications—no PhD in computer science required.
Federated Learning: Smarter AI, Without Sharing Your Data
One of the biggest challenges in AI is privacy. Normally, to make an AI smarter, you need lots of data from many users—but that means sharing private information. Federated learning solves this by letting devices learn together without sending raw data anywhere. Your phone, for example, can improve its AI by learning from your habits, then send only a summary of what it learned to a central server, where all devices’ insights are combined. No one’s private data ever leaves their device.
Why Edge AI Is Exploding in 2025: Industry and Consumer Impact
2025 is being called “the year of edge AI” for good reason. Industries and everyday users alike are demanding AI that’s fast, private, efficient, and reliable—qualities the cloud can’t always deliver. Here’s why the shift is happening now:
- Instant Decisions: Real-time applications—like autonomous vehicles, industrial robots, healthcare monitors, and security systems—can’t afford cloud delays. Edge AI delivers these critical milliseconds.
- Privacy and Security: With growing concerns over data breaches and misuse, keeping sensitive information on-device is a major advantage for users, hospitals, governments, and businesses.
- Energy and Cost Savings: Sending less data over the internet means lower energy use and lower bills—some companies have reduced bandwidth costs by up to 90%.
- Reliability: Edge devices keep working even if the internet goes down. In emergencies, remote locations, or industrial settings, this can be the difference between safety and disaster.
- Scalability: Edge AI works for tiny sensors in a cornfield, powerful cameras in a city, and everything in between. There’s no “one size fits all,” so solutions are becoming more flexible and versatile.
Real-World Example: Smart Agriculture
On a “smart farm,” soil moisture sensors use Edge AI to check how much water plants need—right in the field. Each sensor decides when to water its own patch, without sending data to the cloud. This saves water, energy, and internet costs, and works perfectly even in remote areas with no internet connection.
Edge AI in Action: How Industries Are Using It Today
Let’s look at how Edge AI is transforming different areas:
- Healthcare: Wearable devices and bedside monitors use Edge AI to track heart rhythms, detect falls, or even predict serious health events—alerting patients and doctors instantly, without sending sensitive health data to a server. This enables faster, safer, and more private healthcare.
- Manufacturing: Machines on factory floors use Edge AI to listen for unusual sounds, spot defects in products, or predict when parts will fail—all in real time. This reduces downtime, saves money, and makes factories safer.
- Smart Cities: Traffic cameras count vehicles and adjust stoplights automatically, reducing congestion and pollution. Security cameras can identify suspicious activity and alert authorities immediately—without streaming sensitive footage to the cloud.
- Consumer Tech: Your phone’s camera uses AI to take better photos, and your smart speaker understands your voice commands instantly—no internet needed. This makes devices quicker, more private, and more useful even offline.
- Agriculture: Drones and sensors in fields use Edge AI to spot pests, diseases, or crops in need of water or fertilizer. Farmers can respond instantly, reducing waste and increasing yields.
- Energy: Smart grids use Edge AI to balance electricity supply and demand in real time, especially critical as renewable sources like wind and solar become more common. This keeps the power grid stable and efficient.
- Public Safety: Edge AI helps first responders by analyzing video, audio, and sensor data on-site, sending only critical alerts—improving response times and protecting privacy.
These are just a few examples. In reality, Edge AI is being adopted in nearly every industry that needs instant, safe, efficient, and private intelligence.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Edge AI for Everyone
For those who want to understand, use, or even build Edge AI solutions—here’s a clear, practical guide, whether you’re a beginner, an educator, a maker, or a professional.
1. What You Need to Get Started
- A Device: Almost any modern gadget—smartphone, camera, sensor, robot, even a Raspberry Pi—can be an edge device if it has the right hardware.
- An AI Model: Choose a model that fits your device’s power and memory. For cameras, try MobileNet. For language tasks on small devices, try TinyBERT.
- A Framework: Use lightweight tools like TensorFlow Lite or PyTorch Mobile to deploy your AI model onto your edge device.
- Data: Your device gathers data—images, sounds, temperature, etc.—and uses the AI to make sense of it locally.
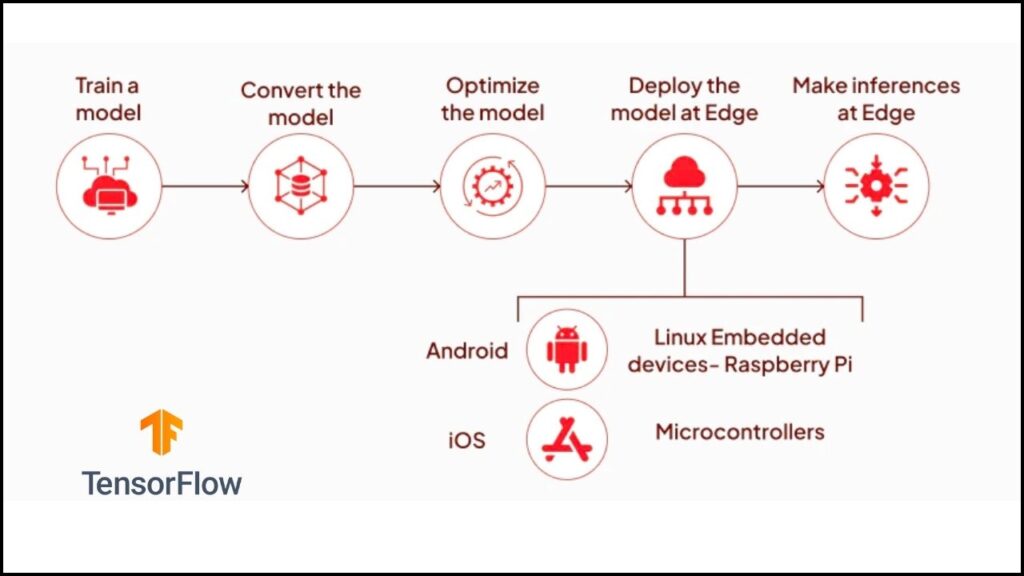
2. How to Deploy Edge AI
- Train Your Model: Start by training a simple AI model on a powerful computer using lots of data. If you’re a beginner, use pre-trained models and focus on deployment.
- Optimize It: Make your model smaller and faster with quantization, pruning, or by choosing a compact architecture.
- Put It on the Edge: Use your chosen framework to install the optimized model on your device.
- Test and Improve: See how well your AI works in real life. Use techniques like federated learning to let devices learn together without sharing raw data.
3. Tips for Success
- Start Small: Begin with a simple project, like a smart doorbell that recognizes family members, or a plant sensor that texts you when it’s thirsty.
- Focus on Privacy: Design your system so personal data never leaves the device. This builds trust and complies with privacy laws.
- Think About Power: Choose hardware and models that don’t drain the battery—critical for mobile and IoT devices.
- Stay Updated: Edge AI moves fast. Follow industry news, join online communities, and keep experimenting as the tech evolves.
IBM Overhauls Quantum Codebase With New ‘IQL’ Language—The Future of Quantum Starts Now
Massive Doudna Supercomputer Will Use IBM Tech to Drive AI-Powered Science
IBM Expands Quantum Computing Footprint With Major Launch of Quantum Computer in Japan
FAQs About New AI Strategy Brings High-Powered Intelligence to Low-Energy Edge Devices
Q: What’s the difference between Edge AI and cloud AI?
A: Cloud AI processes data in huge remote data centers, while Edge AI does the thinking right on your device—instant, private, and energy-efficient.
Q: Can any device be an edge device?
A: Not all. Devices need enough memory and the right kind of processor. But many modern phones, cameras, and IoT gadgets now have these features.
Q: How does Edge AI save energy?
A: By processing data locally, it avoids heavy internet use, which uses lots of power. Also, new AI chips are designed to sip battery, not guzzle it.
Q: Is Edge AI secure?
A: In many ways, yes—your data stays local. But devices still need protection from hacking, so regular security updates are important.
Q: What jobs are there in Edge AI?
A: Lots! Design energy-saving chips, optimize models, build smart devices, work on privacy/ethics, or help companies roll out Edge AI at scale. It’s a growing, innovation-rich field.
Q: What are the biggest challenges for Edge AI?
A: Not all devices are equally powerful, so performance varies. There’s always a trade-off between smartness and efficiency. Managing and updating thousands of edge devices is complex. And as AI becomes more powerful, fairness, transparency, and environmental impact become more important.
Challenges and the Road Ahead for Edge AI
Edge AI isn’t perfect—here’s what experts are working on next:
- Hardware Diversity: Not all edge devices are created equal—some have powerful AI chips, others don’t. This makes it tougher to ensure a consistent experience everywhere.
- Model Limits: There’s a natural trade-off between how smart an AI is and how much power it uses. Some advanced tasks may still need cloud help, at least for now.
- Deployment Complexity: Managing, updating, and maintaining AI models across thousands or millions of devices—each in a different location—is a huge operational challenge.
- Ethics and Explainability: As AI makes more decisions, it’s vital those decisions are fair, explainable, and accountable. Explaining why an AI on a tiny device made a certain choice is an active research area.
- Sustainability: While Edge AI can cut energy use in some ways, making and recycling all these smart devices has its own environmental impact—something researchers and companies are starting to address.
Despite these hurdles, the future is bright. As chips get faster and greener, models get smarter and smaller, and developers learn more, Edge AI will become even more powerful, widespread, and integrated into our lives—changing not just technology, but society itself.