The rise of humanoid robots in factories is no longer a vision from science fiction. Today, two of the world’s most powerful tech players—Nvidia and Foxconn—are teaming up to introduce these advanced robots directly into real manufacturing processes. Their collaboration, focused on Foxconn’s massive new Houston plant, represents a bold leap in the transformation of how things are made and who (or what) makes them.
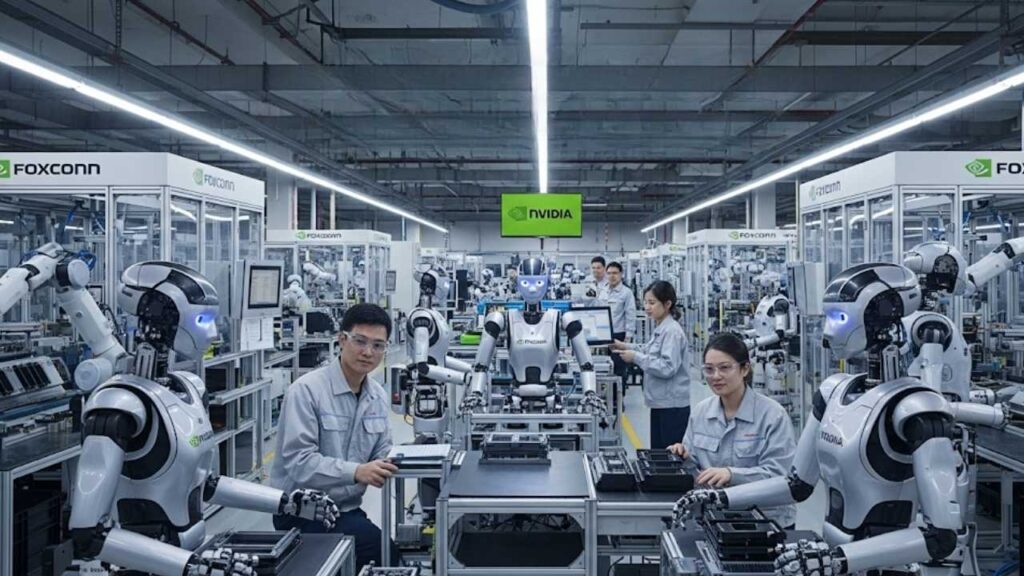

In early 2026, Foxconn’s Houston facility will begin assembling Nvidia’s next-generation GB300 AI servers with both human workers and a new breed of smart, human-shaped robots sharing the assembly line. For the first time, humanoid robots will play an integral role in building advanced computers, blending technology with traditional manufacturing in a truly groundbreaking way.
This transformation impacts more than just factory workers—it affects society as a whole, changing the skills needed for future careers and shaping global industry dynamics. Let’s break down what this means, how it works, and how you can prepare for the new world of collaborative manufacturing.
Table of Contents
Nvidia and Foxconn Want Humanoid Robots in Factories
| Feature / Topic | Details & Insights |
|---|---|
| Project Start | Early 2026: Humanoid robots to be deployed in Foxconn’s Houston factory |
| Partners | Nvidia (AI & semiconductor leader), Foxconn (largest electronics manufacturer globally) |
| Robot Tasks | Assembly, cable insertion, picking and placing parts, complex and repetitive handling |
| Robot Types | Bipedal (walking humanoid); wheeled autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) |
| Industry Firsts | Debut of humanoid robots in direct assembly roles for Nvidia servers and Foxconn high-tech production |
| Technology Used | Nvidia’s Isaac robotics platform, Omniverse digital twin, partnerships for benchmarking with UBTech |
| Factory Impact | Significant automation, changes to job roles, enhanced safety and efficiency |
| Broader Trend | Similar robotics pilots at BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and Tesla. China is prioritizing humanoid robot development at scale |
| Authoritative Source | Nvidia Newsroom – Foxconn AI Factory Collaboration |
Nvidia and Foxconn’s plan to integrate humanoid robots in factories marks a defining moment for the entire manufacturing industry. These smart machines offer safer workspaces, faster assembly, and more consistent quality—all while opening new opportunities for workers willing to learn new skills. Boston Consulting Group and McKinsey both estimate that advanced automation could boost global productivity by tens of trillions of dollars over the next decade.
Whether you’re a student, professional, or business leader, now is the time to build the digital and critical-thinking skills that will keep you vital in an AI-powered workplace. Humanoid robots are no longer the future—they’re part of a present that’s rapidly changing the way the world works.
The New Era: Why Humanoid Robots in Manufacturing Matter
A Pioneering Collaboration
Foxconn, well-known as the world’s largest electronics contract manufacturer (handling assembly for brands like Apple, Sony, Dell, and more), has a reputation for introducing groundbreaking production systems. Nvidia leads the global market in artificial intelligence (AI) hardware, powering everything from gaming PCs to self-driving cars and giant data centers.
Their team-up means expertise from both sides: Foxconn’s vast manufacturing know-how and Nvidia’s cutting-edge AI and robotics. This fusion is set to redefine the assembly line.
Why Is This So Revolutionary?
- First-of-its-kind deployment: Never before have humanoid robots and humans shared such complex, high-stakes tasks on a live electronics production line.
- Flexible, human-like operation: Humanoid robots, unlike traditional robotic arms or conveyors, can adapt to many tasks—the way humans switch jobs during a shift.
- Built for innovation: The Houston facility was planned with open layouts, advanced sensors, and safety systems tailored for mixed human-robot teams.
The Big Picture: From Conventional Robots to Humanoids
In the past, factories used single-purpose robots—arm-like machines locked in place to weld car parts or screw on bottle caps. Those remain critical, but they’re designed for one job, in one spot.
Humanoid robots are different. With two arms, vision systems, and (for bipeds) legs, they’re engineered to work like humans: walking, lifting, assembling, and interacting with tools and machines. This makes them ideal for jobs that need flexibility, delicacy, and real-world problem-solving—without constant reprogramming or hardware swaps.
Practical Example
Instead of buying a special robot for every new product, Foxconn could program its humanoid robots to handle new assemblies with just software updates—making the Houston plant far more agile and competitive.
The Technology Behind Humanoid Robots in the Factory
What Makes These Robots Smart and Useful?
1. Advanced Sensors and Vision
Modern humanoid robots use high-resolution cameras, depth sensors, and force-feedback “tactile” sensors. These eyes and fingers let them:
- Spot and identify tiny electronic parts
- Pick up fragile components without damage
- Position cables and connectors with pinpoint accuracy
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
Nvidia’s AI platforms—like Isaac and Omniverse—train robots using massive data sets and sophisticated simulation, allowing machines to learn tasks the way a person might. For example, a robot can:
- Watch thousands of simulated assembly steps in an Omniverse digital twin (a complete 3D software replica of the real factory)
- Experiment with ways to grip and move a part, improving until its error rate is lower than a human’s
3. Digital Twins and Simulation
Every major change in the factory is tested in virtual reality first. Engineers use Nvidia Omniverse to build a 1:1 scale copy of the Houston line—then run millions of robot “practice rounds” to refine the workflow, avoid mistakes, and guarantee safety.
4. Multiple Robot Types for Optimal Roles
Foxconn’s system uses both:
- Bipedal humanoids: Can walk to different stations and fit in spaces designed for humans
- Wheeled AMRs: Simpler, faster in open areas, more affordable for non-human-specific tasks
Manufacturers pick and mix these robot types based on job complexity, cost, and speed requirements.
Why Now? What’s Driving the Adoption of Factory Robots
1. Explosive Demand for AI and Data Center Hardware
AI powerhouses like ChatGPT, DALL-E, and Google Bard all need enormous server farms to learn and serve users. Nvidia’s new GB300 AI server is built to supply this demand (“AI Gold Rush”). Production must scale rapidly—and efficiently.
2. Labor Market Pressures
Industrial labor shortages, especially in advanced economies, mean fewer human operators are willing or able to fill tough, repetitive roles. Human wages, benefits, and turnover are rising. Robots can help factories run near 24/7, year-round.
3. Efficiency and Quality
Automated robots never get tired, distracted, or sick. They can work through holidays and nights, track error rates precisely, and help reduce product defects if programmed and managed correctly.
4. Regulatory and Safety Enhancements
Modern safety rules encourage “collaborative robots” (cobots) that work around humans. Digital twins and real-time AI monitoring help spot hazards long before anyone’s at risk, making mixed teams safer than ever.
Step-by-Step: Bringing Robots to Life at Foxconn and Nvidia
1. Prototyping and Pilot Testing
Robotics engineers at Foxconn and partners develop prototype humanoids, using benchmarking data from companies like UBTech for comparison. The prototypes are tasked with everything from precise cable insertion to bulk part movement.
2. Virtual Integration
Before assembly-line robots arrive in Houston, they train and “work” in digital spaces. This means months of practice in a virtual copy of the real production line—testing for tasks, timing, and safety.
3. Upgrading Factory Designs
Houston’s floorplan features wide aisles, low obstructions, and multiple safety sensors. Real-time data lets both machines and supervisors monitor every step and intervene if problems arise.
4. Incremental Rollout
Humanoid robots are first trialed on narrow sets of tasks—such as picking and assembling specific server components—alongside human technicians. Metrics like uptime, accuracy, incident rates, and cycle times are monitored closely.
5. Scale and Evolution
Success leads to expansion: more robots, broader tasks, and full integration into the assembly process. Human workers move toward quality assurance, robot maintenance, safety management, and process optimization.
Jobs, Careers & Future Skills
How Will Humans Fit in Once Robots Arrive?
Robots don’t “take over”—they transform roles:
- Humans supervise, program, and diagnose robots
- Quality assurance specialists ensure robots meet strict production targets
- Safety experts develop strategies to prevent collisions or mishaps
- IT support and robot maintenance roles multiply
New Opportunities
Workers with experience on the floor are valuable for helping robots adapt to unexpected problems or rare issues not coded into AI routines.
What Skills Are Most Valuable?
For Students & Young Learners:
- Coding basics: Python or visual block programming
- Mechanical reasoning: Understanding how things move/work
- Robotics club participation: Hands-on experience solves real problems
- Critical thinking: Robots handle routines—humans tackle surprises!
For Professionals:
- Industrial automation programming (PLC, robotics languages)
- Digital twin and AI simulation training
- Human-robot collaboration safety certifications
- Continuous learning in AI, data analysis, and troubleshooting
For Factory Workers:
- Transition programs are encouraged—employers may offer retraining for:
- Robot supervision and support
- Preventive maintenance
- QA roles checking system outputs and performance
NVIDIA’s DiffusionRenderer: The Future of AI-Powered 3D Scene and Image Editing
GPUHammer Exploit Targets NVIDIA GPUs, Threatens AI Model Integrity With Memory Flaw
Nvidia-Backed CoreWeave Just Made a $9 Billion Move to Dominate Cloud Data Wars
FAQs About Nvidia and Foxconn Want Humanoid Robots in Factories
Q1: When will humanoid robots start working in Foxconn’s Houston factory?
A: The first robots are scheduled for live production use in early 2026 after months of digital and physical pilot testing.
Q2: What kinds of assembly jobs will robots handle?
A: Tasks include picking and placing server parts, cable insertion, component fitting, and repetitive or hazardous jobs best suited to automation.
Q3: Will robots replace all human workers in the factory?
A: No. Robots handle repetitive/manual tasks. Humans remain vital for troubleshooting, quality control, robot programming, and overall system supervision.
Q4: How is safety ensured with robots and humans working side by side?
A: Factories use digital simulations, physical barrier systems, and real-time sensors to maintain “safe zones” and stop robots if a hazard is detected.
Q5: Are other companies using humanoid robots in factories?
A: Yes. BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and Tesla have begun piloting humanoid robots for tasks that are physically demanding or ergonomically risky for people. China has also prioritized humanoid robotics at a national policy level.
The Bigger Picture: Global Industry Impact
Governments and multinational companies are racing to modernize factories. In China, for example, the government’s “robotics-plus” initiative calls for tens of thousands of factories to adopt robots—including humanoids—by the end of the decade. The European Union is investing in robotics innovation for manufacturing competitiveness. The United States continues to see major investments in automation, particularly in hi-tech and semiconductor manufacturing.
The outcome? Countries leading in robotics and AI will set the pace for global production and innovation—offering better jobs for those ready to upskill and adapt.