Imagine being able to take any video—whether it’s a home movie of your backyard or a professional film clip—and instantly change the lighting, materials, or even the weather, all with the precision of a Hollywood visual effects studio. That’s exactly what NVIDIA’s new DiffusionRenderer makes possible. Announced at the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2025 conference, DiffusionRenderer is a breakthrough AI tool that bridges the gap between traditional graphics and the next generation of generative artificial intelligence. It allows users to edit 3D environments and photorealistic images with unprecedented accuracy, speed, and ease—even if you’re starting with nothing more than a regular 2D video.

This technology isn’t just for movie studios or game developers. It’s designed to be accessible to filmmakers, advertisers, educators, robotics engineers, and even curious hobbyists. In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into how DiffusionRenderer works, why it’s a game-changer, and how you can start thinking about using it in your own projects—whether you’re a professional looking to streamline your workflow or a newcomer eager to experiment with the future of digital creativity.
NVIDIA’s DiffusionRenderer
| Feature | Description | Professional Impact |
|---|---|---|
| AI-Powered Lighting Control | Edit lighting in real-world or AI-generated videos (e.g., day to night, sunny to cloudy) | Faster, cheaper post-production for film, ads, games |
| Material & Geometry Editing | Change object textures, colors, and even insert new objects with realistic lighting | Rapid prototyping and asset creation for 3D artists |
| No 3D Data Required | Works directly from 2D video, estimating geometry and materials using AI | Lowers barriers for small studios and indie creators |
| Synthetic Data Generation | Automatically creates diverse, photorealistic training data for robotics and AVs | More robust AI training, safer autonomous systems |
| Open-Source Release | Now available as open-source, powered by NVIDIA Cosmos | Accelerates research and custom tool development |
| Conference Presentation | One of over 60 NVIDIA papers at CVPR 2025, a top computer vision event | Positions NVIDIA as a leader in AI graphics innovation |
NVIDIA’s DiffusionRenderer is a leap forward for both creative professionals and AI researchers. By combining the precision of traditional graphics with the flexibility of generative AI, it makes advanced scene editing accessible to everyone—from Hollywood studios to hobbyists in their bedrooms. Whether you want to experiment with new looks, speed up your workflow, or train better AI, DiffusionRenderer is a tool worth exploring.
For the latest updates and to explore DiffusionRenderer yourself, visit the official NVIDIA blog.
What Is DiffusionRenderer and Why Does It Matter?
DiffusionRenderer is a new kind of neural rendering tool. In simple terms, it uses artificial intelligence to understand and manipulate the way light interacts with objects in a scene—all from a regular 2D video. Traditional rendering, the process used in movies and video games, relies on building detailed 3D models and then using complex math to simulate how light bounces around. This is called physically based rendering (PBR), and while it produces stunning results, it’s also slow, expensive, and requires a lot of technical skill.
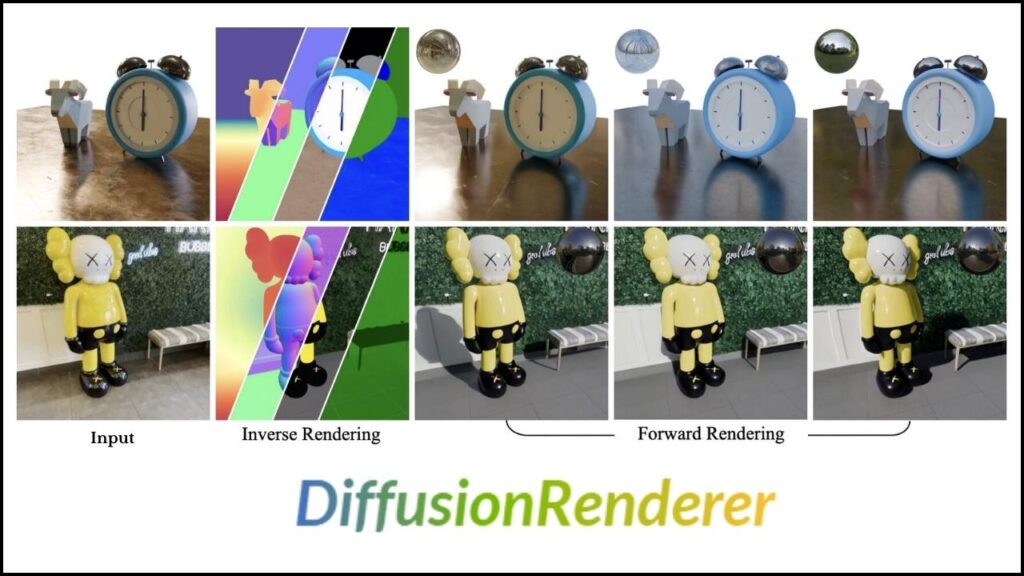
DiffusionRenderer changes all that. Instead of starting with a 3D model, it starts with a video. The AI “watches” the video and figures out where objects are, what they’re made of, and how light is hitting them—just by looking at the flat images. This process is called inverse rendering. Once the AI understands the scene, you can make changes: adjust the lighting, change the color or texture of objects, or even add new elements. The AI then generates a new, photorealistic image or video that reflects your edits—a process called forward rendering.
Why is this important? For creative professionals, it means you can make changes that used to take hours or days in just minutes. For AI researchers, it’s a way to generate huge amounts of realistic training data automatically. And for educators and hobbyists, it’s a chance to experiment with advanced graphics without needing a Hollywood budget.
How DiffusionRenderer Works: A Step-by-Step Guide
Let’s break down how DiffusionRenderer turns ordinary videos into editable, photorealistic scenes. This process might sound complex, but we’ll explain it in simple, easy-to-follow steps.
Step 1: Scene Analysis (Inverse Rendering)
When you feed a video into DiffusionRenderer, the first thing it does is analyze the scene. The AI looks at each frame and tries to “reverse engineer” what’s happening. It estimates where objects are, what they’re made of (like metal, plastic, or fabric), and how light is hitting them—all from the 2D images. This is called inverse rendering.
Think of it like this: if you see a photo of a shiny red apple on a wooden table, your brain can guess that the apple is round, the table is flat, and the light is coming from above. DiffusionRenderer does something similar, but with much more detail and accuracy, using advanced AI.
Step 2: Scene Representation (G-Buffers)
Next, the AI creates special images called G-buffers. These aren’t the final pictures you’ll see; they’re more like secret maps that describe the scene’s geometry, materials, and lighting in a way computers can understand. Each G-buffer might show where objects are, what color they are, how shiny or rough they are, or where shadows fall.
These G-buffers are the “ingredients” of your scene, separate from the final “recipe” (the rendered image). By separating these elements, DiffusionRenderer makes it easy to edit just one part of the scene—like changing the lighting without affecting the objects, or changing an object’s color without altering the lighting.
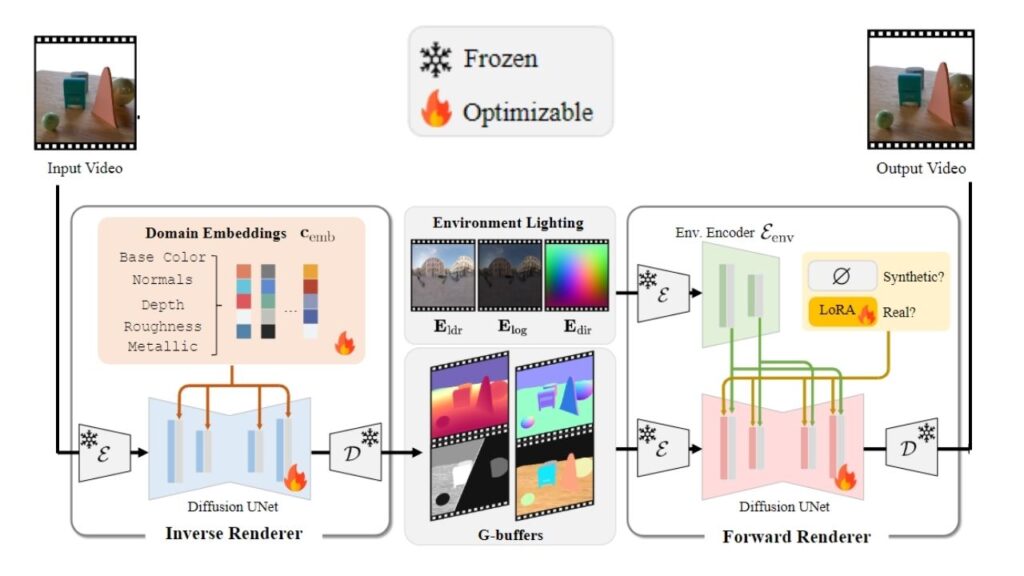
Step 3: Editing and Generation (Forward Rendering)
Now comes the fun part: editing. With DiffusionRenderer, you can tweak these ingredients. Want to change the time of day? Adjust the lighting. Want to make a wall look like brick instead of plaster? Edit the material. You can even add new objects, like placing a lamp on a table or changing the color of a car.
Once you’re happy with your edits, DiffusionRenderer uses forward rendering to combine everything and generate a new, photorealistic image or video. This process is powered by diffusion models, a type of AI that’s really good at creating realistic images by refining random noise into coherent pictures. Diffusion models are the same technology behind popular tools like DALL-E and Stable Diffusion, but here they’re used to edit existing scenes, not just generate new ones from text.
Step 4: Output and Integration
The final output can be a still image, a video, or even a 3D scene ready for use in games, movies, or training AI. Because DiffusionRenderer is designed to work with existing graphics tools, it fits smoothly into professional workflows. This means filmmakers, game developers, and other professionals can use it alongside the software they already know, making it easier to adopt and integrate into real-world projects.
Who Can Use DiffusionRenderer—And How?
DiffusionRenderer isn’t just for big studios or tech companies. Its open-source release means anyone—from students to startups—can experiment with the technology. Here’s how different groups might use it:
- Filmmakers & Ad Agencies: Quickly test different lighting setups, change locations, or fix mistakes in post-production without costly reshoots.
- Game Developers: Prototype levels, tweak materials, and generate assets faster than ever before.
- Robotics & Autonomous Vehicle Researchers: Create endless variations of training data with different lighting and weather conditions, helping AI learn to handle the real world.
- Educators & Hobbyists: Learn about computer graphics and AI in a hands-on way, with tools that were previously out of reach.
Practical Example: Imagine you’re making a short film set in a café. You shoot your scene on a sunny afternoon, but decide it should feel like a cozy evening. With DiffusionRenderer, you can change the lighting, add warm lamps, and even alter the color of the coffee cups—all without reshooting or building a 3D model from scratch.
Why Is This Better Than Old-School Rendering?
Traditional physically based rendering (PBR) requires exact 3D models and painstakingly accurate lighting setups. It’s powerful, but slow and expensive. DiffusionRenderer skips the 3D modeling step, working directly from video, and uses AI to fill in the gaps. This makes it:
- Faster: Edits that took hours now take minutes.
- Cheaper: No need for expensive 3D scans or specialist artists.
- More Flexible: Try out ideas quickly, and undo changes with a click.
- More Accessible: Anyone with a camera and a computer can get started.
The Technology Behind the Magic
DiffusionRenderer is built on diffusion models, the same AI behind tools like DALL-E and Stable Diffusion. But instead of generating images from text, it edits existing videos by understanding and manipulating their underlying structure. The system was trained on a high-quality synthetic dataset with accurate lighting and materials, so it “knows” what different surfaces and lights should look like. Integration with NVIDIA Cosmos, a powerful AI world model, makes the results even sharper and more consistent.
Real-World Applications and Impact
DiffusionRenderer isn’t just a cool demo—it’s already being used to solve real problems:
- Content Creation: Speed up post-production, experiment with looks, and fix mistakes in footage.
- Synthetic Data: Generate realistic training data for AI in robotics and self-driving cars, which need to recognize objects in all kinds of lighting and weather.
- Education: Teach computer graphics and AI with interactive, visual tools.
- Research: Push the boundaries of what’s possible in neural rendering and generative AI.
Getting Started with DiffusionRenderer
Ready to try it yourself? Here’s how you can get started:
- Visit the Official Page: Check out the NVIDIA blog for the latest news and demos.
- Download the Open-Source Code: The tool is now available on GitHub as part of the NVIDIA Cosmos project. Even if you’re not a coder, you can explore sample projects and see how it works.
- Experiment with Your Own Videos: Try editing lighting or materials in your own footage. Start simple—change the time of day or the color of an object.
- Join the Community: Share your results, ask questions, and learn from others experimenting with DiffusionRenderer.
GPUHammer Exploit Targets NVIDIA GPUs, Threatens AI Model Integrity With Memory Flaw
Nvidia-Backed CoreWeave Just Made a $9 Billion Move to Dominate Cloud Data Wars
NVIDIA Powers Europe’s Fastest Supercomputer With Game-Changing Grace Hopper Platform
FAQs About NVIDIA’s DiffusionRenderer
Q: Do I need to be a programmer to use DiffusionRenderer?
A: The open-source release is aimed at developers and researchers, but user-friendly applications built on top of DiffusionRenderer are likely to appear soon. For now, some technical skill is helpful, but tutorials and sample projects make it easier to get started.
Q: Can DiffusionRenderer edit any video?
A: It works best with clear, well-lit footage. The AI needs to “see” the scene well to estimate geometry and materials accurately. Very blurry or dark videos may not give good results.
Q: Is DiffusionRenderer free to use?
A: The core technology is open-source, so it’s free to download and experiment with. Commercial applications may require licensing, depending on how you use it.
Q: How does this compare to other AI image editors?
A: Most AI image editors change the whole picture at once. DiffusionRenderer lets you edit specific parts—like just the lighting or just one object—while keeping the rest of the scene realistic.
Q: Can I use DiffusionRenderer for 3D printing or VR?
A: While it creates 3D-like scene representations, the main output is images and videos. For true 3D printing or VR, you’d still need a dedicated 3D model, but DiffusionRenderer could help you prototype or visualize ideas faster.