Bitcoin’s future is facing an unprecedented challenge: quantum computing. As this groundbreaking technology evolves, it could undermine the cryptographic security that protects Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. In this article, we’ll explore what quantum computing is, why it’s a risk to Bitcoin, who could be affected, and how both everyday users and professionals can prepare. Whether you’re a curious student, a crypto investor, or a tech expert, you’ll find practical advice, clear examples, and the latest data to help you understand and navigate this complex topic.

Table of Contents
Quantum Computing Threatens Blockchain Security
| Key Point | Details | Stats & Data | Professional Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quantum Threat | Quantum computers could break Bitcoin’s cryptography, risking theft of coins. | 4 million BTC (25% of supply) at risk; $40+ billion potentially exposed. | Urgent need for post-quantum cryptography skills and blockchain security expertise. |
| Timeline for Risk | Experts estimate practical quantum attacks are at least a decade away, but rapid progress is ongoing. | Current quantum computers: 100–1,000 qubits; millions needed to break Bitcoin. | Security professionals must monitor advances and prepare for rapid protocol upgrades. |
| Vulnerable Addresses | Old/reused Bitcoin addresses most at risk; new ones less so. | 25% of all Bitcoin (4–6 million BTC) vulnerable if public key has been exposed. | Crypto custodians, exchanges, and high-net-worth holders should audit and migrate assets. |
| Industry Response | Developers and institutions are monitoring the threat and exploring upgrades to quantum-resistant cryptography. | Community preparing for protocol upgrades and new standards. | Developers and investors must coordinate for smooth transitions and risk mitigation. |
| Practical Advice | Use new addresses for each transaction; watch for post-quantum upgrade announcements. | “Harvest Now, Decrypt Later” attacks are a real concern for sensitive data. | Security teams should educate clients and monitor regulatory and technical updates. |
Quantum computing is no longer just science fiction—it’s a real and growing threat to the future of Bitcoin and blockchain security. While the technology isn’t ready to break Bitcoin today, experts warn that the window for action is closing fast. With billions of dollars and the trust of millions at stake, the crypto community must act swiftly to upgrade to quantum-resistant solutions. For now, the best defense is awareness, good security practices, and staying informed about the latest developments.
What Is Quantum Computing?
Quantum computers are a new kind of computer that use qubits instead of regular bits. While traditional computers process information as 0s and 1s, qubits can be both at the same time, thanks to a property called superposition. This allows quantum computers to solve certain problems much faster than any normal computer.
Why does this matter for Bitcoin? Bitcoin’s security relies on math problems that are extremely hard for regular computers, but much easier for quantum computers. For example, finding a Bitcoin private key from a public key would take a regular computer billions of years, but a quantum computer could do it in minutes with enough qubits and the right algorithms.
Why Quantum Computing Puts Bitcoin at Risk
How Does Bitcoin Security Work?
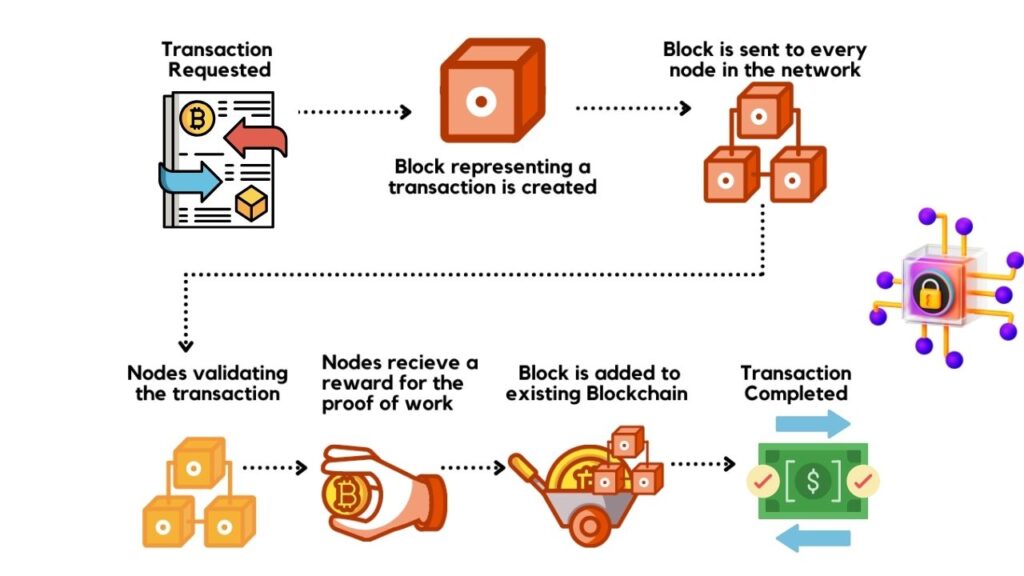
- Bitcoin uses cryptography to keep coins safe. Each wallet has a private key (secret) and a public key (shared).
- When you send Bitcoin, you use your private key to sign the transaction. The network checks your public key to make sure it’s really you.
- With current technology, it’s impossible to guess someone’s private key from their public key.
What Changes with Quantum Computers?
- Quantum computers can run special algorithms (like Shor’s algorithm) that can quickly solve the math problems behind Bitcoin’s security.
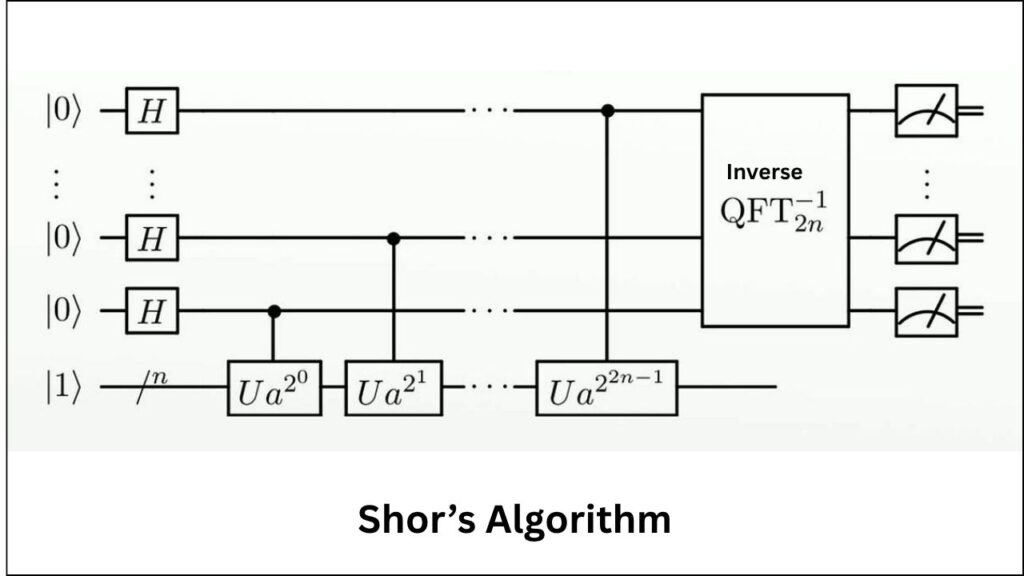
- If a quantum computer can find a private key from a public key, it can steal coins from any address where the public key is exposed.
- Addresses that have never been used to send Bitcoin are safer because their public keys are not public yet. But once you make a transaction, your public key is out there, and your coins could be at risk.
How Big Is the Risk?
- About 25% of all Bitcoin—around 4 to 6 million BTC—are at risk because they are stored in addresses with exposed or reused public keys. This represents over $40 billion at today’s prices.
- The risk is especially high for old wallets, early adopters, and anyone who has reused addresses.
- The vulnerability is not just theoretical: researchers have mapped out which types of addresses are most exposed, showing that coins in early address formats and reused addresses are the most likely targets.
How Soon Could Quantum Computers Break Bitcoin?
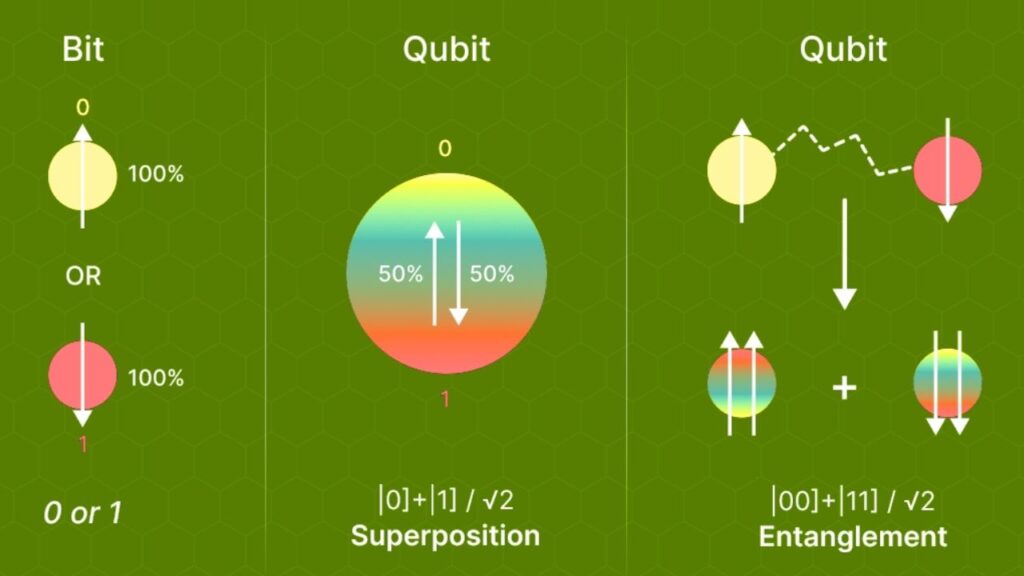
There’s ongoing debate about when quantum computers will be strong enough to threaten Bitcoin:
- Most experts say a practical threat is at least a decade away. Current quantum computers have between 100 and 1,000 qubits, but breaking Bitcoin’s cryptography would require millions of stable, error-corrected qubits.
- Some recent breakthroughs, such as improvements in quantum algorithms and reductions in qubit requirements, have made the timeline less predictable.
- Even though the threat isn’t immediate, the rapid pace of quantum research means the crypto community must stay vigilant and proactive.
Who Is Most at Risk?
1. Old and Reused Bitcoin Addresses
- Early Bitcoin addresses (especially those created before 2010) and addresses that have had their public keys exposed multiple times are the most vulnerable.
- Many of these addresses are believed to hold coins that have not moved in years—possibly lost, but also potentially at risk if quantum computers become powerful enough.
2. Large Holders and Institutions
- Crypto exchanges, custodians, and institutional investors who manage large pools of Bitcoin must audit their holdings and migrate funds to safer address formats.
3. Everyday Users
- Anyone who has ever reused a Bitcoin address or failed to update their wallet software could be exposed if quantum computers become a reality sooner than expected.
What Would Happen If Quantum Computers Break Bitcoin?
- Hackers could steal millions of Bitcoins from vulnerable addresses, causing huge losses for investors and institutions.
- The price of Bitcoin could crash, and trust in cryptocurrencies could be severely damaged.
- Other cryptocurrencies and even banks could face similar risks, as many use the same types of cryptography.
- There could be a rush to upgrade to new, quantum-resistant security systems, but this might cause network slowdowns or even temporary shutdowns.
Can Bitcoin Survive the Quantum Threat?
The Good News
- The threat is not immediate. Experts say it will take at least a decade before quantum computers can realistically break Bitcoin’s encryption.
- The crypto community is already discussing solutions, including new cryptographic algorithms that are resistant to quantum attacks.
- Best practices, such as using new addresses for each transaction and avoiding address reuse, greatly reduce the risk for most users.
The Challenges
- Upgrading Bitcoin’s security is not simple. It would require a coordinated effort from developers, miners, exchanges, and users worldwide.
- Migrating millions of coins to new, quantum-resistant addresses could take months and would need careful planning to avoid chaos.
- There is a risk of “harvest now, decrypt later” attacks, where attackers collect public keys now and wait until quantum computers are ready to crack them.
What Can You Do to Protect Your Bitcoin?
1. Use New Addresses for Each Transaction
- Always use a fresh Bitcoin address when receiving funds. This keeps your public key hidden until you spend the coins, making it much harder for quantum attackers to target you.
2. Avoid Reusing Addresses
- Never reuse old addresses for new transactions. Reusing addresses exposes your public key multiple times, increasing your risk.
3. Stay Updated on Quantum Computing Developments
- Follow official resources like Bitcoin.org and reputable news outlets for updates on quantum computing and blockchain security.
4. Prepare for Post-Quantum Upgrades
- The Bitcoin community is working on quantum-resistant cryptography. Watch for announcements about protocol upgrades or forks, and be ready to migrate your coins when needed.
5. Consult Security Professionals
- If you hold significant amounts of Bitcoin, consider seeking advice from cybersecurity experts who specialize in blockchain and quantum risks.
What Is the Industry Doing About This?
- Developing quantum-resistant algorithms: Researchers and developers are working on new encryption methods that quantum computers can’t easily break. Some, like CRYSTALS-Dilithium and SPHINCS+, have already been standardized by NIST.
- Community debates and proposals: Experts are calling for emergency solutions, including hard forks and new address formats.
- Regulatory awareness: Major institutions and regulators are now treating quantum risk as a serious issue, and some are including it in risk disclosures and compliance planning.
Oxford’s 1-in-6.7 Million Qubit Leap Could Redefine the Future of Quantum Computing
Randomness Unlocked as the Secret Fuel Behind Quantum Computing Power
Quantum Networking May Be the Missing Link to Unlocking Scalable Quantum Computing
FAQs About Quantum Computing Threatens Blockchain Security
What is “Q-Day”?
Q-Day is the term for the day when quantum computers become powerful enough to break current cryptographic systems, putting Bitcoin and other digital assets at immediate risk.
Are all Bitcoin addresses at risk?
No. Only addresses where the public key has been revealed (usually after making a transaction) are immediately vulnerable. New, unused addresses are much safer.
Can quantum computers break Bitcoin today?
Not yet. Today’s quantum computers are not powerful enough, but experts warn that the technology is advancing quickly and could pose a real threat within the next decade—or even sooner if breakthroughs occur.
What is post-quantum cryptography?
It’s a new kind of cryptography designed to be secure even against quantum computers. The Bitcoin community and other blockchain projects are researching ways to upgrade to these new standards.
How can I keep my Bitcoin safe?
Use new addresses for every transaction, avoid reusing addresses, and stay informed about quantum developments and upcoming protocol upgrades.