Quantum Dots Power Next-Gen Displays: In the ever-evolving world of display technology, quantum dots are emerging as a game-changer. Whether you’re watching your favorite show on a smart TV, scrolling through photos on your smartphone, or exploring immersive content in augmented reality (AR), quantum dot displays promise to transform the way we experience visuals. Their ability to produce vibrant, true-to-life colors and reduce energy consumption makes them the gold standard for modern displays.

In this article, we’ll explore what quantum dots are, how they work, and why they matter so much for the future of screens. From stunning color accuracy to energy-efficient displays, we break down the science, the innovation, and the real-world impact of this exciting technology. Whether you’re a casual viewer or a tech professional, this guide has something for everyone.
Table of Contents
Quantum Dots Power Next-Gen Displays
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Keyword Focus | Quantum Dots Power Next-Gen Displays |
| Color Performance | Enables up to 90% of Rec. 2020 color space |
| Energy Efficiency | Consumes up to 20-30% less power than traditional LCDs |
| Display Types | QD-LCD, QD-OLED, QD-MicroLED |
| Key Applications | TVs, smartphones, laptops, AR/VR headsets |
| Toxicity Concern | Cadmium-based QDs being replaced by Indium Phosphide (InP) alternatives |
| Major Companies | Samsung, Sony, TCL, Nanosys |
| Official Resource | Samsung Quantum Dot Displays |
Quantum dots power next-gen displays by delivering brighter, more energy-efficient, and color-accurate visuals than ever before. As this technology becomes mainstream — from TVs and laptops to medical devices and AR glasses — expect a major leap in how we view digital content. It’s not just about pretty screens; it’s about a smarter, greener, and more immersive future for all kinds of visual experiences. The innovations happening today will shape the displays of tomorrow, touching every aspect of our digital lives.
What Are Quantum Dots?
Quantum dots (QDs) are tiny semiconductor particles, only a few nanometers wide — that’s about 10,000 times smaller than the width of a human hair! When exposed to light, they emit vibrant, pure colors. The exact color depends on the size of the quantum dot: smaller dots emit blue light, larger ones emit red.
Think of them like tiny color machines. When you shine light on them (like from a backlight in a TV), they glow in bright, precise colors that are far more accurate than what traditional LCD screens can produce. This makes them perfect for applications where clarity, vibrancy, and precision are crucial.
Their ability to convert light into specific wavelengths with remarkable efficiency also makes them suitable for use in solar panels, biological imaging, and other advanced technologies beyond just displays.
Moreover, quantum dots are being studied in fields like quantum computing and photonics, thanks to their unique optical properties. Their capacity to absorb and emit light with such high control makes them versatile tools for both consumer electronics and next-generation scientific instruments.
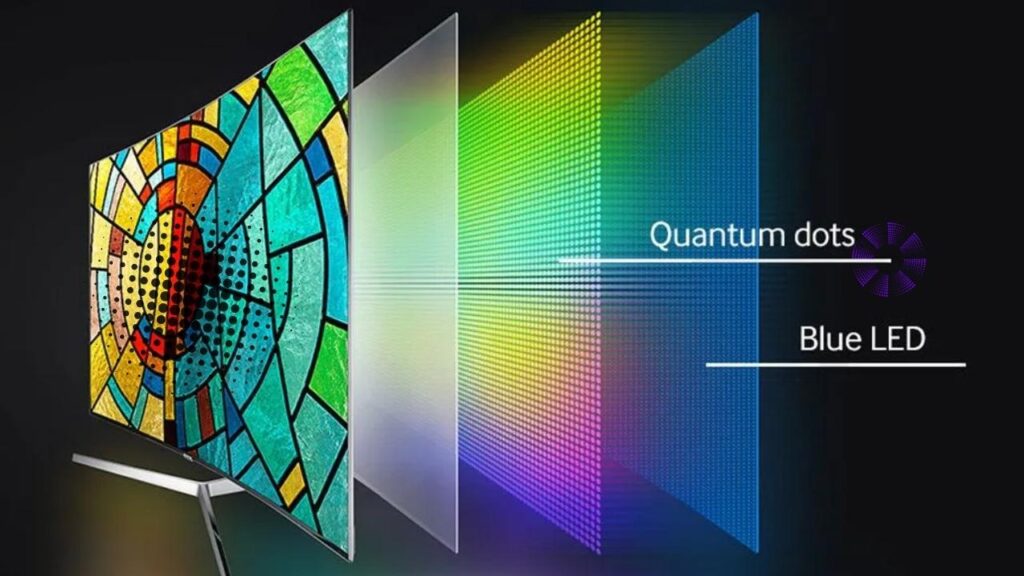
How Do Quantum Dot Displays Work?
Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Backlight: A blue LED light source provides the base illumination.
- Quantum Dot Film: Light passes through a layer of quantum dots that convert the blue light into pure red and green.
- Display Layer: These colors combine with the remaining blue light to form full-color pixels on your screen.
Because the colors are so precise, quantum dot displays can show a much wider range of colors, also known as a wide color gamut. This leads to more lifelike images — perfect for professional photo editing, gaming, or binge-watching your favorite series.
Additionally, these displays maintain color accuracy at wide viewing angles and perform well in both dark and brightly lit environments. This flexibility is driving their adoption in professional displays used in creative studios and medical imaging.
In emerging applications, engineers are exploring direct-emissive quantum dot displays, which do away with the need for a backlight altogether. These next-gen versions promise even thinner devices with better efficiency and enhanced brightness control.
Why Are Quantum Dots a Big Deal?
Let’s break it down into some real benefits:
Vivid and Accurate Colors
Traditional LCDs struggle to produce truly vibrant reds and greens. Quantum dots fix this by emitting highly saturated colors, helping displays achieve up to 90% of the BT.2020 color standard, which is far better than most OLEDs and regular LCDs.
This enhanced color fidelity is especially important in industries like film production, graphic design, and e-commerce where accurate color representation can make or break a product.
Energy Efficiency
Because quantum dots convert light more efficiently, they use less power. This means:
- Longer battery life for laptops and smartphones
- Lower electricity bills for home TVs
- Cooler operation and less heat output
In large-scale deployments like digital signage and smart displays in public areas, the energy savings from quantum dots can translate into substantial cost reductions and environmental benefits over time.
Longevity and Durability
Unlike OLEDs, which can suffer from burn-in and color degradation over time, quantum dot displays have excellent stability. They last longer without losing their brightness or color performance.
Their inorganic structure means fewer chemical reactions and reduced degradation, making them a solid choice for long-term investments like high-end home theater setups or professional-grade monitors.
Even in demanding environments such as outdoor kiosks, airport terminals, and medical facilities, quantum dots maintain consistent performance over years of continuous use.
Types of Quantum Dot Displays
Not all quantum dot displays are created equal. Let’s look at the three main types used today:
QD-LCD (Quantum Dot LCD)
This is the most common type and the easiest to manufacture. It adds a layer of quantum dots to a regular LCD screen to enhance color and brightness.
Used in: TVs, monitors, some laptops
Brands: Samsung QLED, TCL, Hisense
This format is ideal for consumers looking to upgrade from standard LCDs without paying a premium for OLED or MicroLED technologies.
QD-OLED (Quantum Dot OLED)
Combines OLED’s perfect blacks with quantum dots’ vivid color. You get both deep contrast and sharp color, making it ideal for cinematic viewing.
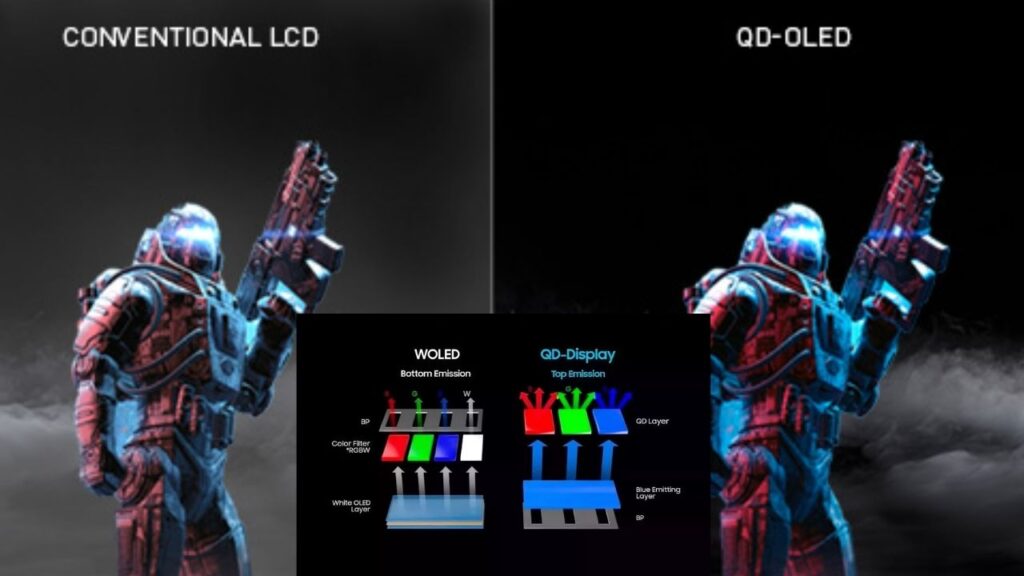
Used in: Premium TVs, gaming monitors
Brands: Sony A95K, Samsung S95B
It’s the preferred choice for gamers and cinephiles who want the best of both worlds: inky blacks and popping colors, all with fast response times.
QD-MicroLED
This is the holy grail of displays — microscopic LEDs paired with quantum dots to produce self-emissive, ultra-bright pixels with zero backlight needed. It’s still in early stages but holds massive promise.
Used in: AR/VR headsets, future smart glasses, high-end signage
Brands: Experimental devices by Samsung and others

QD-MicroLEDs are being eyed for mission-critical environments like medical diagnostics, aerospace cockpits, and industrial design where every pixel matters.
Researchers expect these displays to redefine immersive media by delivering micro-scale screens that feel holographic in quality.
Real-World Applications of Quantum Dot Displays
Quantum dots aren’t just for fancy TVs. They’re already making their way into everyday tech:
- Smartphones: Brighter screens that remain clear even under sunlight
- Laptops: Better battery life and color accuracy for content creators
- AR/VR Headsets: High-resolution, lifelike visuals that reduce eye strain
- Medical Displays: Enhanced detail and contrast for accurate diagnoses
- Industrial Monitoring: Real-time dashboards with crystal-clear visuals for operators
Expect to see more consumer electronics adopting this tech as it becomes more affordable and scalable.
Additionally, quantum dots are entering wearables, automotive displays, and education tools like smart whiteboards, where clarity and durability are key.
Are There Any Drawbacks?
Yes — but they’re being solved.
Toxic Materials
Early quantum dots used cadmium, a heavy metal that poses environmental and health risks. However, the industry is rapidly shifting to cadmium-free QDs, often using indium phosphide (InP). These alternatives offer similar performance with a greener footprint.
Governments and regulatory bodies are also introducing strict compliance measures like RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) to ensure safety and environmental responsibility.
Cost
Quantum dot displays are more expensive than basic LCDs — but costs are dropping quickly. As production scales, expect to see more affordable models in the next few years.
Tech giants and startups alike are investing in improving yield rates, automation, and sustainable materials to drive prices down and broaden market accessibility.
The Future of Quantum Dot Technology
The roadmap for quantum dots is exciting. Here’s what’s coming next:
Printable Quantum Dots
Researchers are developing inkjet-printable QDs, which could lead to cheaper, large-area displays — even rollable or flexible ones.
This would open up opportunities for smart walls, foldable devices, and customizable interfaces in homes and vehicles.
Transparent and Flexible Displays
Quantum dots can be embedded in transparent or bendable substrates, opening the door to see-through screens, futuristic smart windows, or foldable devices.
These innovations could redefine the way we interact with digital content in smart cities, wearable tech, and even automobile windshields.
Sustainable Manufacturing
As quantum dot manufacturing becomes greener and more efficient, it aligns well with sustainability goals in tech, reducing both energy use and hazardous waste.
Companies are exploring plant-based materials, recycling-friendly processes, and low-temperature synthesis methods to further minimize environmental impact.
The push for a circular economy is driving innovation toward biodegradable display components, reducing long-term e-waste and preserving natural resources.
Recycling Electronics with Light: A Look at Laser-Assisted Material Recovery
New Organic Batteries Could Be the Key to Cleaner, Cheaper Energy Storage
Top 5 University Labs Leading the Future of Smart Materials in 2025
FAQs About Quantum Dots Power Next-Gen Displays
What is the main advantage of quantum dot displays?
The main advantage is superior color accuracy and brightness. Quantum dots create more vivid, lifelike images compared to traditional LCDs or even OLEDs in some cases.
Are quantum dots safe?
Yes. Modern quantum dots are mostly cadmium-free and use safer materials like indium phosphide. Look for “RoHS-compliant” or “eco-certified” labels on devices.
Which brands offer quantum dot TVs?
Major brands include Samsung (QLED), Sony (QD-OLED), TCL, and Hisense. Check product specs to confirm if quantum dot technology is used.
Will quantum dots replace OLED?
Not entirely. Both technologies will coexist. QD-OLED is already blending the best of both worlds, and QD-MicroLED may become the next gold standard in display tech.
Where can I see a quantum dot display in action?
Visit an electronics store and look for Samsung QLED or Sony QD-OLED TVs. You’ll notice the difference in color richness and brightness immediately.