Researchers Demonstrate Advanced Cooling in Data Centers: In today’s digital world, data centers are the backbone of everything from your favorite apps to global financial systems. But as our reliance on digital services grows, so does the environmental impact of these massive facilities.

That’s why the recent breakthrough—advanced cooling in data centers to cut emissions by 15–21%—is such a game changer. This innovation brings hope for a greener tech future and offers practical solutions for businesses, IT professionals, and communities worldwide.
Researchers Demonstrate Advanced Cooling in Data Centers
| Feature/Stat | Details/Impact |
|---|---|
| Emissions Reduction | 15–21% lower greenhouse gas emissions with advanced cooling |
| Water Savings | 30–50% less water used across the data center’s life span |
| Energy Demand Reduction | 15–20% less energy needed for cooling |
| Cooling Technology | Cold plates, immersion cooling, closed-loop zero-water systems |
| Industry Adoption | Microsoft, WSP Global, and top cloud providers |
| Official Resource | Microsoft Sustainability |
The move to advanced cooling in data centers to cut emissions 15–21% isn’t just a technical upgrade—it’s a game changer for the environment, business, and society. By embracing cold plate, immersion, and closed-loop zero-water cooling, the tech industry is setting a new standard for sustainability, resilience, and innovation.
Whether you’re a business leader, IT professional, policymaker, or just a curious digital citizen, now is the time to learn, adapt, and champion these changes. The future of the internet—and the planet—depends on it.
Understanding the Context: Why Data Center Cooling Matters

Data centers are like the brains and heart of the internet. They house thousands of powerful computers (servers) that generate a lot of heat as they process information. Cooling is essential to keep these machines running safely and efficiently, preventing overheating that can cause costly downtime or even permanent damage.
Traditionally, data centers have relied on air cooling or water evaporation systems. While these methods work, they use huge amounts of electricity and water, which increases greenhouse gas emissions and puts stress on local water supplies—especially in places already facing water shortages.
The Environmental Challenge
- Data centers consume 1–2% of global electricity—and this number is rising as digital services expand.
- Cooling can account for up to 40% of a data center’s total energy use.
- Water usage is a major concern, with some facilities using millions of liters annually just for cooling.
The Breakthrough: Advanced Cooling Technologies
What’s New?
Researchers and industry leaders have developed advanced cooling methods that dramatically reduce the environmental footprint of data centers. The most promising solutions include:
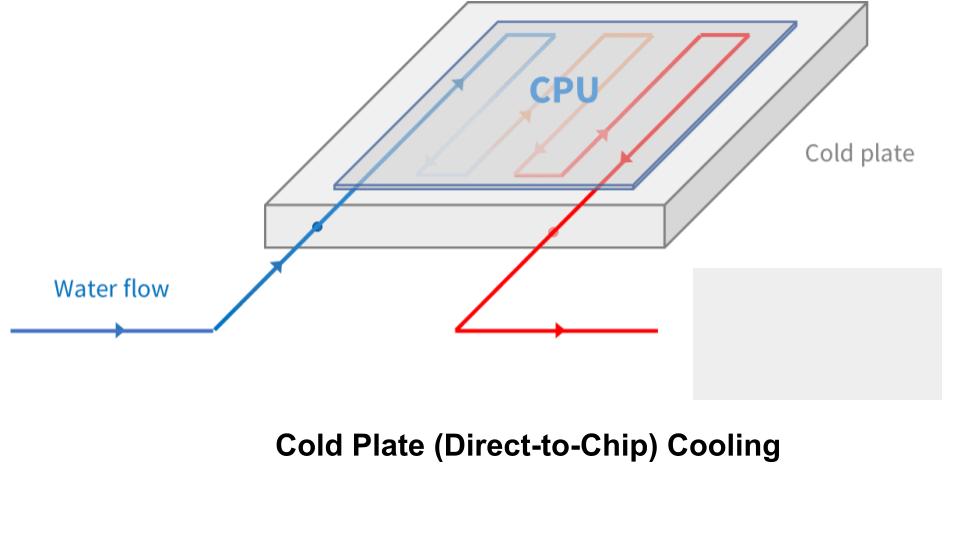
- Cold Plate (Direct-to-Chip) Cooling: Liquid coolant flows through plates directly attached to the hottest parts of the server, pulling heat away efficiently.
- Immersion Cooling: Servers are submerged in special non-conductive liquids, which absorb and carry away heat much more effectively than air.
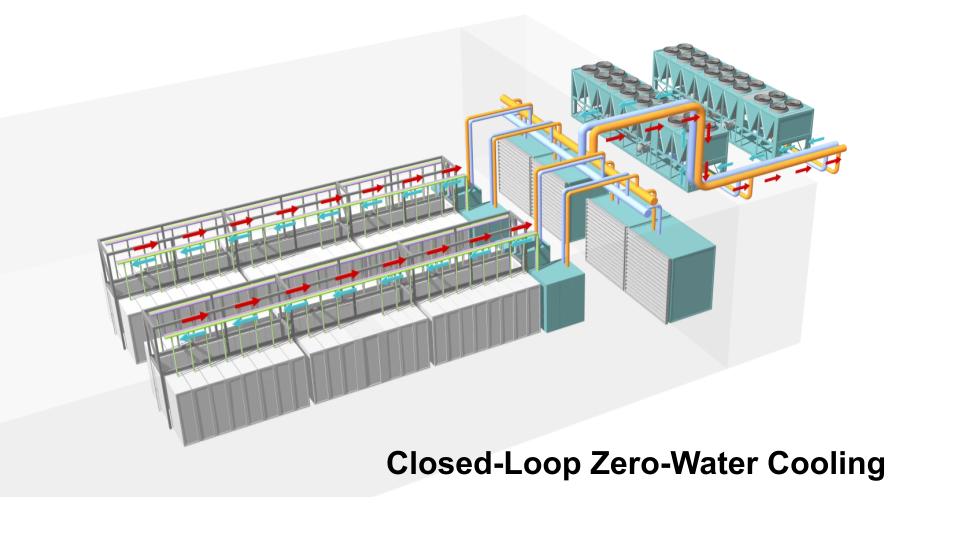
- Closed-Loop Zero-Water Cooling: Systems recycle the same water or coolant, eliminating the need for constant water replenishment and evaporation.
How Much Better Are These Solutions?
- Greenhouse gas emissions drop by 15–21% over the entire life cycle of a data center.
- Energy demand for cooling falls by 15–20%.
- Water consumption is reduced by 30–50%, with some new designs using virtually zero water for cooling.
These numbers come from rigorous life cycle assessments (LCA), which measure environmental impacts from manufacturing to daily operation and eventual decommissioning.
How Advanced Cooling Works: A Step-by-Step Guide
1. Cold Plate Cooling
How it works:
A flat, metal plate filled with coolant is attached directly to the hottest chips inside a server. As the chips heat up, the coolant absorbs the heat and carries it away to be cooled elsewhere.
Benefits:
- Highly targeted cooling
- Uses less energy and water than traditional air cooling
- Supports denser, more powerful computing setups
Example:
Microsoft has begun rolling out cold plate cooling in its latest data centers, seeing immediate reductions in emissions and water use.
2. Immersion Cooling
How it works:
Servers are placed in a tank filled with a special liquid that doesn’t conduct electricity. The liquid absorbs heat directly from every surface of the server, then circulates to a cooling unit where the heat is removed.
Benefits:
- Even more efficient than cold plates
- Allows for ultra-compact server arrangements
- Reduces noise and dust
Example:
Some cloud providers are piloting immersion cooling for high-performance AI workloads, where traditional cooling can’t keep up.
3. Closed-Loop Zero-Water Cooling
How it works:
Instead of evaporating water into the air, these systems circulate water or coolant in a sealed loop. Once filled, the system reuses the same water over and over, only needing a refill in rare cases.
Benefits:
- Saves over 125 million liters of water per year, per data center
- Reduces risk in drought-prone regions
- Supports sustainability goals
Example:
Microsoft’s new data centers in Arizona and Wisconsin will be among the first to use this technology at scale, with more sites planned globally.

Why This Matters: Real-World Impact
For the Environment
- Lower emissions mean less contribution to climate change.
- Water conservation protects local ecosystems and communities, especially in areas facing water shortages.
- Energy efficiency helps reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
For Businesses
- Lower operating costs: Using less energy and water saves money in the long run.
- Regulatory compliance: Stricter environmental laws are coming, and early adopters will be ahead of the curve.
- Reputation boost: Customers and investors increasingly favor companies with strong sustainability records.
For IT Professionals
- Future-proof skills: Understanding and managing advanced cooling systems will be a must-have skill.
- Career opportunities: Demand for sustainability experts in IT is growing rapidly.
Practical Advice: How to Prepare for the Shift
For Data Center Operators
- Assess your current cooling systems: Use life cycle assessment tools to understand your environmental impact.
- Explore upgrades: Consider pilot projects with cold plate or immersion cooling.
- Monitor water and energy use: Set targets to reduce both, and track your progress.
For IT Teams
- Stay informed: Follow industry leaders like Microsoft and WSP Global for the latest best practices.
- Get trained: Seek certifications in sustainable IT and data center management.
- Advocate for change: Make the case for greener technology in your organization.
For Policymakers and Community Leaders
- Support incentives: Encourage tax breaks and grants for sustainable data center investments.
- Promote transparency: Require public reporting of data center energy and water use.
- Foster partnerships: Bring together tech companies, utilities, and local governments to share solutions.
Quantum‑Si to Participate in GenomeWeb Webinar on Proteomics Data Standardization
James Webb Telescope Data Suggest Universe Might Be Inside a Huge Black Hole
Tsinghua’s Theater-Based Immersive Neuroaesthetics Study Sparks Public Interest
FAQs About Researchers Demonstrate Advanced Cooling in Data Centers
What is the biggest source of emissions in a data center?
The largest source is usually the electricity needed to power and cool thousands of servers, especially if the local grid relies on fossil fuels.
How does advanced cooling reduce emissions?
By using more efficient methods to remove heat, less energy and water are needed, which directly lowers greenhouse gas emissions and conserves resources.
Is zero-water cooling really possible?
Yes! New closed-loop systems use the same water or coolant over and over, only needing a refill in rare cases. Microsoft’s latest data centers are already piloting this technology.
Will these new cooling methods increase costs?
Initial setup can be more expensive, but the savings on energy and water bills—and the benefits of regulatory compliance—often outweigh the upfront costs over time.
How can I learn more or get involved?
Visit Microsoft’s Sustainability page or the Open Compute Project for resources, case studies, and open research repositories.