Vaping has become a popular alternative to traditional smoking, especially with products like nicotine and CBD vape oils. However, recent scientific studies reveal alarming evidence about the potentially harmful chemicals produced during vaping. One particularly dangerous chemical formed is cannabidiol hydroxyquinone (CBD-Q), which actively destroys human tissue, specifically lung cells. This groundbreaking discovery raises important health concerns and urges caution for current and potential vape users.
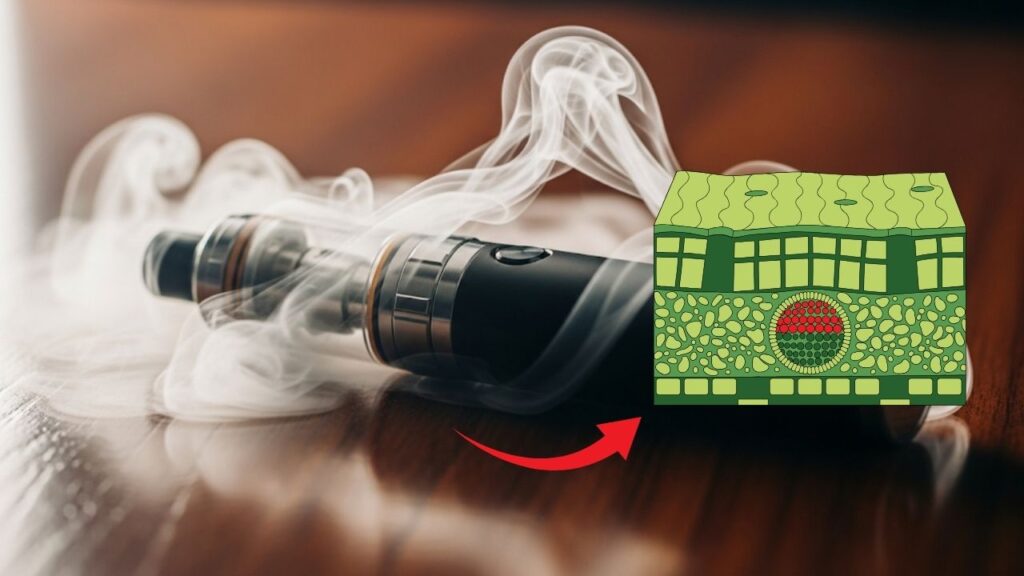

Table of Contents
Scientists Find Chemical That Actively Destroys Human Tissue
| Topic | Details |
|---|---|
| Harmful Chemical | Cannabidiol hydroxyquinone (CBD-Q) forms when CBD is oxidized by vaping heat |
| Effect on Human Tissue | CBD-Q kills lung cells on contact, destroying tissue |
| Other Harmful Substances | Metals (lead, nickel, antimony), aldehydes (formaldehyde), acrolein |
| Health Risks | Lung inflammation, DNA damage, acute lung injury, possible increased cancer risk |
| Vaping Trends | Disposable vapes release higher metals than older refillables or cigarettes |
| FDA Position | No e-cigarette recognized as safe or effective quitting aid |
| Official Vaping Info Site | CDC – Health Effects of Vaping |
Recent scientific evidence reveals that vaping is far from benign. The formation of cannabidiol hydroxyquinone (CBD-Q) during CBD vaping, alongside inhalation of heavy metals and toxic aldehydes, poses serious risks to lung tissue and overall respiratory health. Vaping products—especially disposables and flavored CBD oils—can actively damage lung cells and increase risks of chronic diseases, including lung cancer. Consumers should be fully aware of these risks and use safer, approved methods for smoking cessation. Staying informed and cautious can protect your lungs and long-term health.
Understanding Vaping and Its Hidden Dangers
Vaping involves inhaling vapor produced by heating liquids containing substances such as nicotine, CBD (cannabidiol), flavorings, and other chemicals. Marketed as a safer alternative to smoking and a quitting aid, vaping has gained massive popularity worldwide, including among youth. However, new scientific research uncovers that vaping is not risk-free and may actively harm lung tissue.
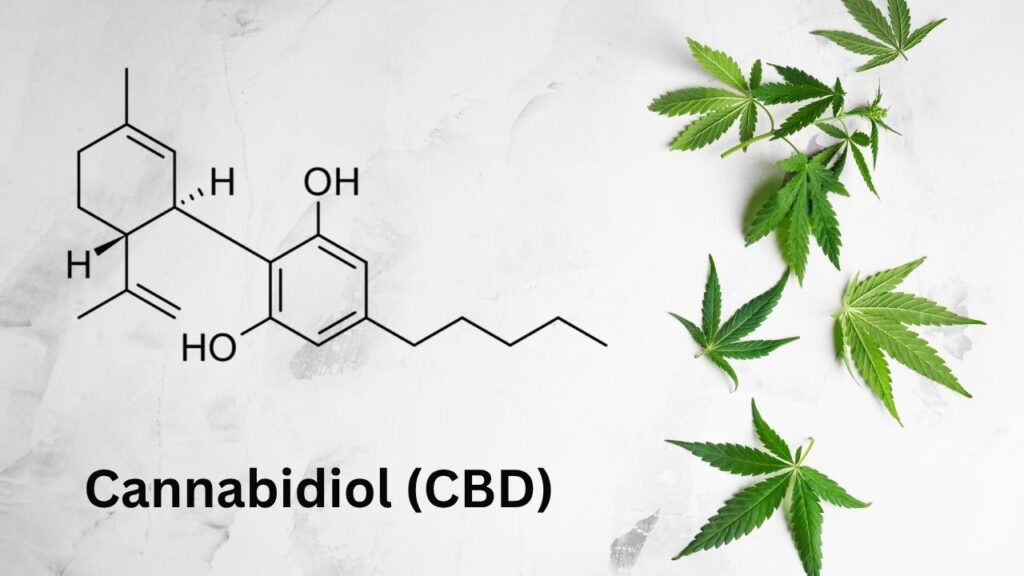
One of the most concerning discoveries is that under vaping conditions, CBD can be chemically transformed into CBD-Q, a toxic molecule. This substance is so potent that it kills lung cells upon contact, effectively destroying the tissue it touches. While CBD in its natural form is often marketed for therapeutic benefits, its oxidation product in vape form presents serious hazards.
Beyond CBD-Q, studies have also identified a slew of other dangerous chemicals generated or inhaled during vaping:
- Heavy metals such as lead, nickel, and antimony, especially prevalent in disposable vapes, exceed concentrations found in traditional cigarettes or older e-cigarettes. These metals pose risks of nerve damage, respiratory issues, and cancer.
- Aldehydes like formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, and acrolein are created during the heating process. These chemicals contribute to cellular DNA damage, inflammation, and increased risks for lung diseases including COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) and lung cancer.
- Flavoring agents linked to lung disease, such as diacetyl, are inhaled in aerosol form, causing inflammation and damage to airway tissues.
Why Does This Matter? The Science Behind Lung Damage from Vaping
How Does CBD Turn Into a Tissue-Destroying Chemical?
When CBD oils are vaporized by heating coils inside vape pens, they undergo a chemical reaction known as oxidation. This process turns CBD into cannabidiol hydroxyquinone (CBD-Q). According to research from the University of California Merced, this chemical is highly toxic to lung cells, killing healthy tissue at the point of contact. Strikingly, CBD-Q shares properties with compounds used in cancer therapies to selectively destroy tumor cells, highlighting its destructive potential when inhaled unintentionally.
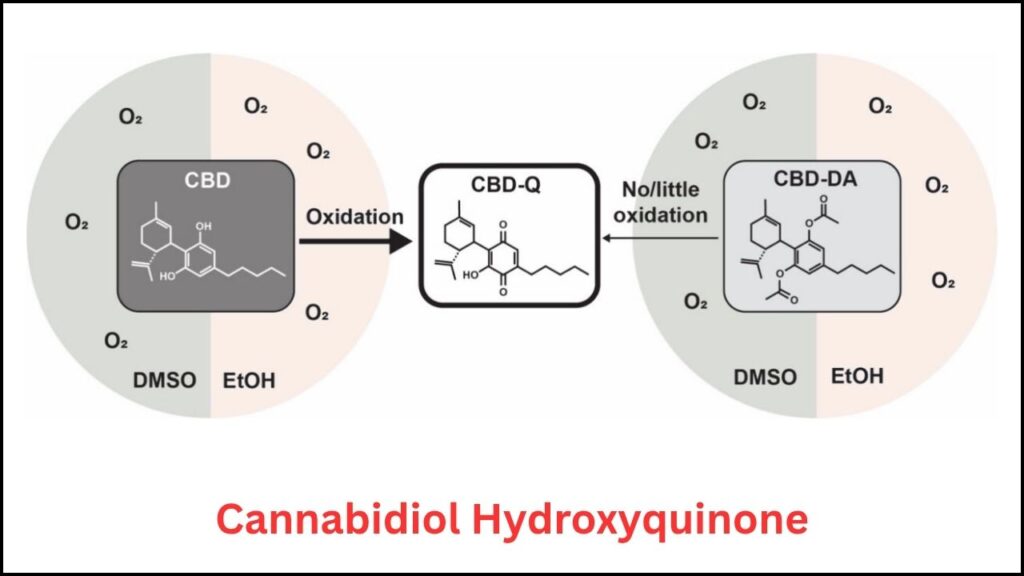
The Broader Chemical Cocktail from Vaping
Besides CBD-Q, the vapor contains a toxic mix of substances produced by the heating of vape liquids:
- Formaldehyde and acrolein, created when propylene glycol and vegetable glycerin (common vape solvents) are heated, irritate and inflame lung tissue.
- Heavy metals released from coils and device parts accumulate in vapors, posing carcinogenic and neurotoxic threats.
- DNA-damaging agents in the vapor can trigger mutations and potentially lead to cancer development, according to biomarker studies.
Health Implications Documented by Science
- Acute and chronic lung injury, including chemical pneumonitis and worsening of asthma or COPD symptoms
- DNA damage in lung and oral cells, increasing the likelihood of lung and other cancers
- Inflammation and cell death in lung epithelial tissue, compromising respiratory function
- Accelerated lung aging, even in non-smokers who vape
- Potential for cardiovascular harm related to inhaled toxicants
Practical Advice: What Should Consumers Know and Do?
- Understand the Risks: Vaping—even with CBD or flavored liquids—is not harmless. The inhalation of toxic chemicals can cause serious lung damage, inflammation, and may increase cancer risk.
- Avoid Disposable Vapes: Studies show disposable devices may release more heavy metals than refillable ones or cigarettes, representing an added danger.
- Use FDA-Approved Quitting Methods: If you’re seeking to quit smoking, vaping is not FDA-approved as a safe cessation tool. Instead, consult healthcare professionals about proven options like nicotine replacement therapy or prescription medications.
- Stay Informed and Skeptical: The vape industry is relatively new and evolving. Regulatory oversight is still catching up, so always scrutinize product claims and seek information from trusted health authorities.
- Report Problems and Seek Help: If you experience breathing difficulty, persistent cough, or chest pain after vaping, seek medical attention immediately.
Breaking Down the Science: A Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: What Happens Inside a Vape Device?
- The liquid inside a vape pen contains carrier solvents (propylene glycol, vegetable glycerin), nicotine or CBD, flavoring agents, and sometimes other chemicals.
- When the device is activated, a heating coil vaporizes the liquid, producing inhalable aerosol.
Step 2: Chemical Changes Due to Heat
- Heat causes CBD to oxidize into CBD-Q.
- Heating solvents produces harmful aldehydes.
- Metal parts release harmful heavy metals into the vapor.
Step 3: Inhalation and Lung Impact
- Users inhale chemical-laden vapor deep into the lungs.
- Toxic compounds damage lung cells, cause inflammation, and can kill tissue.
- DNA damage from reactive chemicals could initiate cancerous changes.
Step 4: Health Outcomes
- Immediate effects: coughing, airway inflammation, worsening asthma.
- Long term: higher risk of lung disease, chronic injury, potentially lung cancer.
New Genetic Discovery Could Unlock Powerful Breakthroughs in Disease Treatment
FAQs About Scientists Find Chemical That Actively Destroys Human Tissue
Q1: Is vaping safer than smoking cigarettes?
A1: While vaping may reduce exposure to some harmful substances found in cigarette smoke, it still introduces toxic chemicals, including heavy metals and tissue-destroying compounds like CBD-Q, posing significant health risks.
Q2: Can vaping cause lung cancer?
A2: Emerging evidence shows vaping causes DNA damage and promotes oxidative stress, which are linked to cancer risk. However, long-term human studies are ongoing and conclusive evidence is still being gathered.
Q3: Is CBD safe to vape?
A3: Although CBD itself may have therapeutic properties, when vaporized it forms CBD-Q, a highly toxic chemical that destroys lung tissue. Vaping CBD is therefore risky.
Q4: Are flavored vape products more harmful?
A4: Many flavor chemicals increase toxicity, causing more lung inflammation and injury than unflavored products.
Q5: What should someone do if they want to quit smoking?
A5: It is best to use FDA-approved cessation methods and consult healthcare providers rather than rely on vaping.