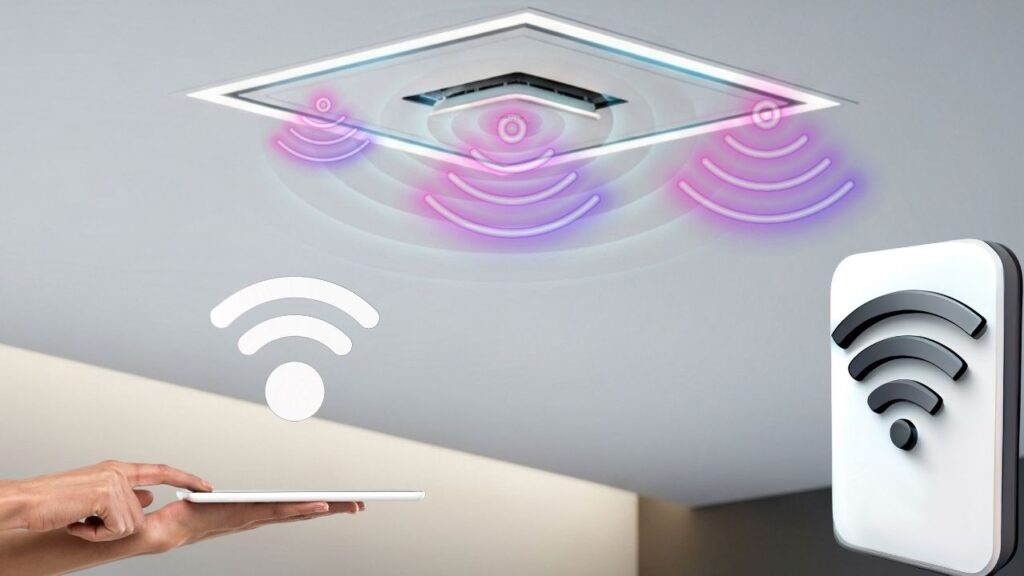
Wi-Fi Through the Ceiling Enhances Indoor Connectivity: In the age of remote work, smart homes, and ultra-connected offices, Wi-Fi through the ceiling has emerged as a powerful solution to improve indoor wireless connectivity. Traditionally, Wi-Fi routers have been placed on desks, bookshelves, or walls, but these setups often lead to poor signal distribution, dead zones, and security concerns. By moving access points to the ceiling, users can now experience wider coverage, faster speeds, and cleaner aesthetics, with the added benefit of being ready for next-gen technologies like Li-Fi and WiGig.

Whether you’re a homeowner upgrading your Wi-Fi or a facility manager rolling out enterprise-grade infrastructure, understanding the benefits and implementation of ceiling-mounted wireless solutions is essential. Let’s explore why the ceiling is becoming the new frontier in wireless networking.
Wi-Fi Through the Ceiling Enhances Indoor Connectivity
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Focus | Using ceiling-mounted Wi-Fi, Li-Fi, and mmWave tech to boost indoor wireless coverage |
| Key Technologies | Wi-Fi 6/6E, WiGig (802.11ad/ay), Li-Fi, Infrared Optical Wireless Communication |
| Major Benefits | Wider signal coverage, less interference, cleaner installations, enhanced security |
| Best Use Cases | Smart homes, large offices, hospitals, labs, industrial IoT, education |
| Wi-Fi 6 Max Speed | Up to 9.6 Gbps according to |
| Wi-Fi 6E Band Advantage | Adds 6 GHz spectrum for reduced congestion |
| PoE Compatibility | Supports Power over Ethernet to reduce wiring complexity |
| Official Standards | IEEE 802.11ax/ay |
| Security | Physical tamper resistance, WPA3 encryption support |
| Smart Tech | Beamforming, AI-driven beam steering (e.g., Georgia Tech’s WiMove) |
Wi-Fi through the ceiling isn’t just an aesthetic choice—it’s a strategic move toward smarter, faster, and more secure indoor wireless infrastructure. Whether you’re future-proofing your home or deploying enterprise-grade networks, ceiling-mounted access points powered by Wi-Fi 6/6E, mmWave, or Li-Fi deliver unmatched performance.
With the convergence of beamforming, PoE, and optical wireless tech, the ceiling has become the new networking hub—solving Wi-Fi headaches and enabling the next generation of smart connectivity.
The Connectivity Challenge: Why Traditional Wi-Fi Setups Fail Indoors
Even the best Wi-Fi routers can struggle in real-world environments due to:
- Physical obstructions: Furniture, walls, and people block signals.
- Signal degradation: Wi-Fi waves weaken over distance and materials.
- Interference: Overlapping signals from neighboring routers, microwaves, or Bluetooth.
This is especially problematic in multi-floor homes, schools, hospitals, and corporate buildings. Signal interference not only causes slow speeds and buffering but also impacts mission-critical IoT systems and smart devices.
According to a Statista report, the global smart home market is projected to exceed $231 billion by 2028, meaning more devices, more bandwidth demand, and more complexity.
Why Mounting Wi-Fi on the Ceiling Works
Ceiling-mounted access points solve many of the above problems by:
Improving Line-of-Sight
Wi-Fi signals spread out in a dome-shaped pattern. Placing APs on ceilings helps project that signal downward evenly, minimizing interference from furniture or walls.
Centralizing Coverage
Rooms and halls receive uniform signal distribution when APs are placed overhead, reducing blind spots—especially in open-plan layouts or auditoriums.
Boosting Security
It’s much harder for unauthorized users to tamper with or unplug a ceiling-mounted AP, enhancing physical security in sensitive environments like banks, hospitals, or classrooms.
Enabling Scalability
With ceiling integration, adding new access points or upgrading tech becomes modular. Many enterprise solutions support remote configuration via centralized dashboards.
The Technologies Making Ceiling Wi-Fi Possible
Let’s break down the core technologies transforming ceiling-based indoor connectivity:
1. Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E (802.11ax)

Wi-Fi 6 brings massive upgrades:
- Higher speeds: Up to 9.6 Gbps
- OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access): More devices can talk at once
- Target Wake Time (TWT): Extends battery life for IoT devices
- MU-MIMO (Multi-User Multiple Input, Multiple Output): Delivers data to multiple devices simultaneously
Wi-Fi 6E expands on this by using the 6 GHz band, drastically reducing congestion and improving performance in crowded buildings.
2. WiGig and 802.11ad/ay (60 GHz)
WiGig, based on IEEE 802.11ad/ay, uses the 60 GHz millimeter-wave band to offer wireless speeds rivaling Ethernet—up to 10 Gbps. The challenge? These signals can’t penetrate walls. That’s where ceiling mounting helps:

- Ceilings offer ideal reflection angles for mmWave beams
- Beamforming antennas dynamically track user devices
- Ideal for AR/VR, wireless monitors, and local 4K streaming
Georgia Tech’s WiMove project has developed AI-powered ceiling APs that rotate or reposition for optimal mmWave transmission, keeping line-of-sight even as users move around a room.
3. Li-Fi and Infrared-Based Optical Wireless Communication (OWC)

Li-Fi stands for Light Fidelity, using modulated visible or infrared light to transmit data at high speeds.
Advantages:
- No RF interference (ideal for hospitals, airplanes)
- Higher security due to light being contained in a room
- Low latency, suitable for medical or industrial automation
Li-Fi can reach speeds of 100 Gbps+ in lab conditions and is being piloted in aircraft cabins and smart cities.
How to Install Ceiling Wi-Fi at Home or in Business
Here’s a step-by-step guide to getting started:
Step 1: Analyze Your Space
- Measure square footage
- Use apps like Ekahau or NetSpot for Wi-Fi heat mapping
- Identify dead zones and high-traffic areas
Step 2: Select the Right Access Points
| Use Case | Recommended Setup |
|---|---|
| Home | Wi-Fi 6/6E Mesh System (e.g., ASUS, TP-Link Deco) |
| Office | Ceiling-mount PoE APs (e.g., Ubiquiti UniFi, Aruba Instant On) |
| Hospital | Li-Fi & Infrared OWC (e.g., Signify Trulifi) |
| Industry | WiGig with beam steering and ceiling mounts |
Step 3: Use PoE for Simplified Wiring
- Power over Ethernet (PoE) provides power and data through one cable
- Reduces need for electrical sockets
- Ideal for false ceilings or industrial ceilings
Step 4: Optimize Your Network
- Enable band steering to push devices to faster channels
- Set up VLANs for security
- Schedule firmware updates
- Run regular speed tests to monitor performance
Real-World Applications
Healthcare Facilities
Hospitals use Li-Fi to avoid RF interference with sensitive medical devices. Ceiling-mounted infrared systems offer secure, fast, and EMI-free data transmission in operating rooms and ICUs.
Smart Offices
Modern workplaces deploy ceiling-based digital ceilings integrating Wi-Fi, lighting, HVAC sensors, and even environmental monitoring, controlled via a single PoE infrastructure.
Multi-Floor Homes
Families benefit from mesh Wi-Fi with ceiling-mounted nodes to cover basements, upper floors, and patios—ensuring uninterrupted Zoom calls, streaming, and smart device management.
Wipro Predicts Scalable Quantum Computing Solutions by Year-End
Caltech Achieves Quantum Hyper-Entanglement Using Laser Tweezers: A Landmark in Quantum Science
FAQs About Wi-Fi Through the Ceiling Enhances Indoor Connectivity
Can ceiling-mounted Wi-Fi improve performance in large rooms?
Absolutely. It allows for better line-of-sight and signal spread, minimizing dead zones and improving connection quality.
Is ceiling installation only for commercial buildings?
No. With affordable mesh systems and PoE injectors, homeowners can also benefit from ceiling APs.
Does Li-Fi require special lights?
Yes. Li-Fi uses LED fixtures that modulate light signals for data transfer. Devices need compatible receivers.
Are there any health concerns with ceiling Wi-Fi or Li-Fi?
No known health risks exist. In fact, Li-Fi avoids electromagnetic radiation entirely, making it safer for sensitive environments.
Can I use my existing router with a ceiling mount?
Not usually. Most home routers aren’t designed for ceiling use. Instead, opt for dedicated ceiling APs that support PoE and controller-based management.